* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download concentration
Survey
Document related concepts
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
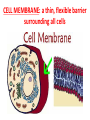
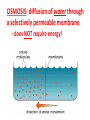
BELL WORK: Answer the following questions on your bell work page: 1. A scientist finds a unicellular organism. He can see its DNA is free-floating in the center of the cell. What kind of cell is this, and how do you know? 2. Which organelles help produce and move proteins in a cell? (hint: there are THREE) Today’s Standard (B.4B): Investigate and explain cellular processes including…transport of molecules Today’s Essential Question: How do molecules move in a cell? CELL MEMBRANE: a thin, flexible barrier surrounding all cells What is the cell membrane’s function (job)? (2 things) Two main functions: 1) regulate what enters (food, water, & oxygen) & leaves (waste) 2) provide protection & support What is the cell membrane composed (made) of? (3 types of molecules) LIPIDS: the main component of a cell membrane –Found in a double layer called the lipid bilayer –Also called the phospholipid bilayer –hydrophobic (afraid of water) DRAW THIS! PROTEINS: embedded into the lipid bilayer –Form channels or pumps (pathways) to help move large molecules CARBOHYDRATES: attached to many proteins on the outside of the bilayer – allow cells to communicate with each other carbohydrates How do molecules move in or out through the cell membrane? Why does food coloring spread out in water? • In a solution, particles are constantly moving. • They collide with one another and spread out randomly. DIFFUSION: particles move from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration CONCENTRATION: the amount of solute (stuff) dissolved into a solvent (liquid) KOOL-AID is the solute WATER is the solvent CONCENTRATION is how much Kool-Aid you put in CONCENTRATION GRADIENT: a difference between two concentrations If diffusion is going from high concentration to low concentration, what direction is it moving on the concentration gradient? High Concentration Low Concentration EQUILIBRIUM: the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system –particles continue to move –the goal of diffusion! Diffusion does NOT require energy!! The rate (speed) at which molecules pass through a membrane depends on its permeability. PERMEABLE membranes allow all substances to pass through IMPERMEABLE membranes allow no substances to pass through Biological (cell) membranes are SELECTIVELY permeable –Some substances can pass through, while others cannot OSMOSIS: diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane –does NOT require energy!