* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
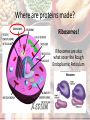
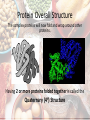
Protein Structure Proteins are made out of C, H, O and N What are the monomers/building blocks for proteins? • Amino Acids! There are 20 different types. They are connected by Peptide Bonds to form Proteins Proteins are also called Polypeptides Protein Structure What functional groups do you see in every protein? Proteins ALWAYS have an Amine Group (-NH2) on one side and a Carboxyl Group (-COOH) on the other Where are proteins made? Ribosomes! Ribosomes are also what cover the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Where are proteins made? The process of making proteins is simply called ‘Protein Synthesis’ Amino Acids RNA Protein Ribosomes use RNA as instructions to know what order to put the amino acids in to create proteins. Protein Overall Structure Proteins are formed by linking a lot of Amino Acids together. This chain/sequence of amino acids is called the Primary (1ᵒ) Structure Protein Overall Structure The chain of amino acids will then fold and form either a spiral or pleated shape This alpha helix or beta pleated sheet is called the Secondary (2ᵒ) Structure Protein Overall Structure The spiraled or pleated chains now fold and coil even more. This complex shape is called the Tertiary (3ᵒ) Structure This is when the protein becomes functional Protein Overall Structure The complex proteins will now fold and wrap around other proteins. Having 2 or more proteins folded together is called the Quaternary (4ᵒ) Structure Protein Overall Structure Primary (1ᵒ): Amino Acids in a chain/sequence Secondary (2ᵒ): Alpha helix or Beta pleated chain Tertiary (3ᵒ): Complex shape Quaternary (4ᵒ): 2 or more proteins folded on each other Functions • Speed up chemical reactions (Enzymes) • Transport things through the body (Hemoglobin) • Transport things through the cell membrane (Channel Proteins) • Defend the body against infections (Antibodies) • Growth, Maintenance, and Repair • Some Hormones (such as Insulin) Denaturing Proteins can become unfolded which is called denaturing. This is bad news and will cause the protein to no longer function. Denaturing is caused by a change in temperature or pH. Examples Proteins can be found in a lot of places! • • • • • • • • Meat Eggs Nuts Beans Hair/Nails Muscles Vegetables Milk