* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons - Seung Lab
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
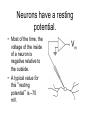
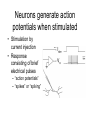
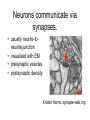
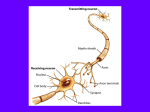
Brief introduction to neurons Sebastian Seung Neurons have branching shapes • Cell body or soma – 10-100 µm • The branches are called “neurites” – 100 µm - 1 m • Neurites are like the “wires” of the brain. Neurons have a resting potential. • Most of the time, the voltage of the inside of a neuron is negative relative to the outside. • A typical value for this “resting potential” is –70 mV. Neurons generate action potentials when stimulated • Stimulation by current injection • Response consisting of brief electrical pulses – “action potentials” – “spikes” or “spiking” There is a threshold for spiking • Sufficiently large stimuli produce action potentials. • Smaller stimuli do not. One neuron can cause a potential change in another. action potential (post)synaptic potential Neurons communicate via synapses. • usually neurite-toneurite junction • visualized with EM • presynaptic vesicles • postsynaptic density Kristen Harris, synapse-web.org Most synapses transmit chemical messages • An action potential stimulates secretion of neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors. • Binding triggers a synaptic potential. Synapses are excitatory or inhibitory • Excitatory – tends to cause spiking in the postsynaptic neuron – e.g. glutamate • Inhibitory – tends to prevent spiking in the postsynaptic neuron – e.g. GABA Neurons are excitatory or inhibitory (Dale’s Law) • Version 1: A neuron is either excitatory or inhibitory in its effects on other neurons. • Version 2: A neuron secretes a single neurotransmitter at its synapses. • There are exceptions to Dale’s Law. Synapses have strengths • Amplitude of the postsynaptic potential – typically less than 1 mV. • Duration of the postsynaptic potential – typically 1 to 1000 ms. • Estimate of strength – amplitude ⨉ duration – amplitude Dendrites and axons are types of neurites • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other neurons. The axon is the output element. • Thin and often long. • A single axon leaves the soma, but may later branch, usually at right angles. • Action potentials travel from the soma to the presynaptic terminals. Dendrites are the input elements • One or more dendrites attached to soma. • Postsynaptic densities • Hundreds of microns • Graded potentials (a simplification) • Spatial and temporal summation of synaptic inputs. Functions of the action potential • Computation – primitive form of decision-making – decision by comparison with a threshold • Communication – transmission of signals over long distances through axons