* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Word
Survey
Document related concepts
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
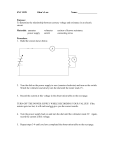
Measuring Voltages Apparatus voltmeter, batteries, low voltage power supplies, simple circuit with bare wires and resistor Action The students can either set up the circuit to measure current and voltage, or the circuit can be set up for them in advance. The students measure the potential difference across the terminals of the batteries and/or power supplies. The students measure the potential difference across the resistor (a poor conductor) and across two points a similar distance apart on the wire. They should also consider why they measure potential difference by putting the probes at different points. The Physics All points on a conductor (the wire) will be at the same potential, hence the potential difference between two points on the wire is zero. The resistor is a poor conductor (approximately an insulator) and hence there will be a potential difference across the resistor. The voltmeter is connected in parallel, because it measures the difference in potential between two points. Accompanying sheet Measuring Voltages Use the voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the terminals of the various batteries and power supplies. Voltmeters are always connected in parallel with the device you are measuring the voltage across. Why is this the case? Why do we often talk about “potential difference” rather than simply potential?