* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Lesson Plan
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
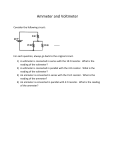
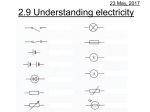
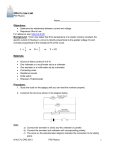
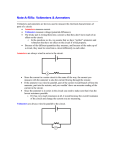
Physics Lesson Plan Teacher Howard Unit Title Length Goal(s)/PLO(s): Course Grade Level Block/Period draw and interpret circuit diagrams construct circuits from schematic diagrams demonstrate the correct placement and use of an ammeter and voltmeter define electromotive force (emf), terminal voltage, and internal resistance Phys 12 12 Date Class Size Lesson #, of 19-08 solve problems using – terminal voltage – electromotive force (emf) – internal resistance – current – electric potential difference Materials: Ammeters and Voltmeters Timeline Class Activities Introduction Body Notes 19-08 Closure Questions 20-24 , Problems 53-61odd 19-08 Ammeters and Voltmeters Ammeter • device used to measure current Voltmeter • device used to measure potential difference or voltage Analog meters • a pointer moves along a scale Digital meters • display the numerical value in numbers The analog meters have a galvanometer inside them for which the amount of current passing through the device determines how much the needle deflects. In the ammeter there is a parallel circuit so only a fraction of the current passes through the galvanometer and the rest goes through the shunt resistor (very low resistance) so it doesn’t break and there is minimal impact on the circuit. The ammeter must be connected in series to function. An analogue voltmeter is also a galvanometer and a resistor but they are connected in series and the resistance is very large so that very little current passes through the voltmeter. In order to have a minimal effect on the circuit (not stop the flow of current) the voltmeter must be placed in parallel around a resistor or battery A potentiometer can measure the voltage without having any current pass through it. Multimeters • have a variety of shunt or series resistors so the galvonometer can give a reading for a variety of currents and voltages Ohmmeters • measure resistance by measuring the current through a resistor using a built in battery of known voltage • can damage the device if it sends too much current Making a measurement on a circuit changes the circuit Example 19-15 Digital meters are more precise (not necessarily accurate, depending on what is being measured) and will have less of an effect on the circuit. Question 20-24 no problems