* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download practical tech`s
Survey
Document related concepts
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
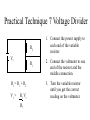
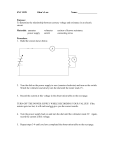
Practical Technique 1 Speed Instantaneous speed – the speed at one point in the journey. Measure the length of the mask, d. Measure the time for mask to go through the light gate, t. Calculate the average time. Calculate the speed, v = d ÷ t. Remember if distance is in metres speed will be in m/s, if distance is in centimetres speed is in cm/s Practical Technique 2 Focal Length A distant object will appear as an upside down image on the card. Measure the distance between the card an the lens when the image is in focus. This is the focal length of the lens. The power of the lens is 1÷ focal length and is measured in dioptres(D) Practical Technique 3 Refraction Refracted ray normal Incident ray Normal – a line at right angles to the boundary Incident angle – between the normal and the incident ray. Refracted angle – between the normal and the refracted ray. Practical Technique 4 Circuit Faults Space for testing Continuity tester – only tests for open circuits Using an ohmmeter to test for open and short circuits. Power source must be disconnected, Open circuit will give a very high resistance. Short circuit will give a lower than expected resistance. Practical Technique 5 V and I Ammeter needs one extra wire and is put into the circuit Voltmeter needs two extra wires and is put across the component. Practical Technique 6 Peak Voltage The peak voltage is the amplitude of the wave. Peak voltage = no. of boxes from middle to peak x volts per division Practical Technique 7 Voltage Divider R2 Vt R1 Rt = R1 + R2 V1 = R1 Vt Rt 1. Connect the power supply to each end of the variable resistor. 2. Connect the voltmeter to one end of the resistor and the middle connection. 3. Turn the variable resistor until you get the correct reading on the voltmeter. Practical Technique 8 Circuit switch resistor wire V A voltmeter ammeter