* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cerebral Cortex
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Temporal lobe epilepsy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
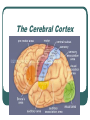
The Cerebral Cortex
What functions are served by
various cerebral cortex regions?
The main part of the brain is the cerebrum – big
piece of folded, wrinkly meat that covers the
older more primitive limbic system & brainstem.
-Gyri are the grooves in the brain & Sulci are the
humps in between the grooves.
Newer neural networks within the cerebrum form
specialized work teams that enable our
perception, thinking and speaking.
Covering our cerebral hemispheres is the thin
cap or cerebral cortex. This is your body’s
ultimate control & info-processing center.
Structure of the Cortex
20-23 billion nerve cells with 300 trillion synaptic
connections.
Neuroglia –Glial Cells: category of neural cells
that provide support network of cells surrounding
the neurons & blood vessels of the brain &
nervous system.
-Oligodendroglia & Astrocytes (CNS),
Schwann Cells (PNS)
Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes:
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe &
temporal lobe.
Functions of the Cortex
Frontal Lobe: Controls thinking & judgment {tap
your forehead as if thinking through tough
decision}
Temporal Lobe: Controls hearing {located just
beside the ears}
Occipital Lobe: Controls vision {ever gotten hit
in the back of the head & “saw stars” b/c visual
Sx is momentarily impaired}
Parietal Lobe: Controls touch & sensory
processing {Scratch top of head like you are
washing your hair...touch controlled by this part
of “head”}
Motor Functions
Motor Cortex (strip) lies within the frontal lobe
& the frontal lobe’s decision-making function
works with the motor cortex to create
purposeful movement.
Sends messages out to the body
Fingers & mouth occupy the greatest amount
of motor cortical space b/c they require precise
control (Foerster & Penfield)
2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural
prosthetics with paralyzed humans
Sensory Functions
Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the
parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s
association areas work with the sensory
cortex to process sensory signals for
accurate perception.
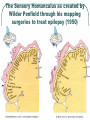
The more sensitive the body region, the
larger the sensory cortex devoted to it
(lips, fingers…)
The Sensory Homunculus as created by
Wilder Penfield through his mapping
surgeries to treat epilepsy (1950)
Association Areas
¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted
to sensory or muscular activity
Neurons in these association areas
integrate information & therefore cannot
be neatly mapped
Found in all four lobes & increase in
more intelligent animals.
Association Areas
i.e.: In frontal lobes assoc areas enable
judgment, planning & processing of new
memories. Damage to frontal lobe can
also alter personality = Phineas Gage
In parietal lobes assoc areas, they
enable math & spatial reasoning…
In temporal lobes facial recognition
{*these are just a few examples!!!!}
Phineas Gage Didactic
Broca’s Area (frontal lobe)
Controls speech muscles via the motor cortex
Damage to Broca’s area (Broca’s aphasia):
•prevents a person from producing speech
•person can understand language
•words are not properly formed
•speech is slow and slurred
Wernicke’s Area (temporal lobe)
•
•
Interprets auditory code
Damage to the Wernicke’s Area
(Wernicke’s Aphasia):
loss of the ability to understand language
person can speak clearly, but the words that are
put together make no sense. This way of
speaking has been called "word salad" because
it appears that the words are all mixed up like the
vegetables in a salad.