* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
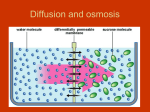
Download BIOLOGY 12 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS Diffusion – the movement
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
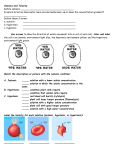
Name: ________________________ Pages: 73-75 Date: ____________________ BIOLOGY 12 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS 1) Compare the following terms: a) diffusion vs. osmosis Diffusion – the movement of molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration Osmosis – movement of water from an area of higher concentration to a lower concentration across a semi-permeable membrane Both involve movement from high to low concentration b) solute vs. solvent vs. solution solute – substance dissolved in a solvent to form a solution solvent - liquid that dissolve a solute (i.e. water) solution – solute (usually solid) + solvent (usually liquid) c) osmotic pressure vs. concentration gradient osmotic pressure – pressure created due to osmosis concentration gradient – gradual decrease in concentration over a distance 2) Explain what would happen to the concentrations of water, glucose, and copper sulphate on side A of this experiment. Water will move to side A due to osmosis. Side A [water] ↑ Copper sulphate ions will move to side A due to diffusion. Side A [ion] ↑ Glucose will not pass the membrane. Side A [glucose] ↓ The opposite will occur on side B 3) Explain the difference between the terms isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic. Isotonic – a solution that has the same solvent and concentration as the cell Hypertonic - a solution that has a greater solvent and concentration as the cell Hypotonic. - a solution that has a lower solvent and concentration as the cell 4) Amylase converts starch Æ glucose. Glucose is small enough to pass through membrane but starch is too big. Also, H2O moves in by osmosis because [H2O] is higher in the beaker than the tube. 5) Summarize what happens to ANIMAL CELLS placed in different tonicities of solution: Tonicity of Solution Cell is Put Into Isotonic Net Movement of Water No net movement Effect on Cell Remains the same Hypotonic Cell gains water Cell Swells & May Burst Cell loses water “lysis” Cell Shrinks H2O Hypertonic H2O “crenation” 6) Describe the difference between crenation and lysis. crenation – hypertonic environment causes H2O to leave the cell causing it too shrink lysis - hypotonic environment causes H2O to enter the cell Æ turgor pressure increases Æcausing the cell to swell and then burst 7) Summary of what happens to PLANT CELLS placed in different tonicities of solution: Tonicity of Solution Cell is Put Into Isotonic Net Movement of Water Effect on Cell No net movement Remains the same Hypotonic Cell gains water Greater water pressure inside cell H2O Hypertonic Cell loses water “turgor pressure” Cell Contents Shrink, but cell wall retains its shape H2O “plasmolysis” 8) Compare osmotic pressure and turgor pressure. osmotic pressure – pressure caused by the flow of water across a semipermeable membrane turgor pressure – internal pressure within a cell due to the inward flow of water due to osmosis 9) What are the similarities and differences between crenation and plasmolyis? Similar – water moves out of the cell and cytoplasm shrinks Difference – plant cells undergo plasmolysis but they do not collapse completely due to the cell wall.