* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organismal Biology Review for Test #1 (on 9 February 2005)
Survey
Document related concepts
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
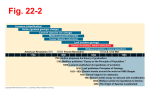
1 Organismal Biology Review for Test #1 (on 9 February 2005) Note: Chapters on test: 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27 – after putting this study sheet together, I decided to wait and put Chapter 28 (Protista) on the next test (you have plenty with the chapters up to 27) A couple questions will come from the Evolution lab – especially review similarities in vertebrate embryos Helpful study tips – READ THE CHAPTERS (but you can skip the parts I said to skip); try practice self-quizzes at the end of each chapter; if you have the CD that came with the book, it also has practice quizzes and helpful hints Don’t wait until Tuesday night to start studying – start going information now (reading, notes, etc) – write down the parts that are hard for you to remember Test will be all multiple choice – probably 50-60 questions. There will be some questions that have options like: a and b, b and c, all the above, none of the above. Chapter 22 – Descent with Modification… On the Origin of Species – written by Charles Darwin, published 1859; purpose of HMS Beagle’s trip Natural selection – what it is, examples Carolus Linnaeus – Swedish botanist – binomial nomenclature Sedimentary rocks – often hold fossils; older fossils are usually deeper “acquired traits”- WRONG – Lamarck Galapagos Islands – where they are, their biological significance, “Darwin’s Finches” Lyell – Earth is much older than people had thought before Wallace – had same ideas about natural selection as Darwin Descent with modification Page 435 – know chart – Observations and Inferences about natural selection Malthus – his writings about population increase influenced Darwin’s thinking Artificial selection Population and species – “biological” definitions Natural selection and pesticide resistance Homology (similar structures that have the same embryonic origins) Biogeography – how it tells us about related animals Endemics Difference between the word “theory” and “hypothesis” in the scientific meaning Chapter 23 – The Evolution of Populations More about populations and species Gene pool 2 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium – know what it means,recognize the equation, know what p and q are; know why this equation is used and know the assumptions it has genetic drift, bottleneck effect, founder effect – what are they and what do they have to do with gene frequency changes gene flow, gene diversity mutation polymorphism – what it is and examples cline – what it is and examples Darwinian fitness (reproductive fitness) – what it is Page 458 – know this page well – know about directional, diversifying, and stabilizing selection – under what circumstances each might occur; recognize the graphs and which one they go with advantages/disadvantages of reproducing sexually vs asexually intrasexual and intersexual selection – definitions and examples of each selection works directly on phenotype know what phenotype and genotype are Chapter 24 – The Origin of Species Patterns of speciation – anagenesis vs cladogenesis Biological species concept (breeding or potentially breeding, viable and fertile offspring) Page 467 – know Fig. 24.5 well – summary of reproductive barriers between closely related species – prezygotic and postzygotic barriers Allopatric vs sympatric speciation – what each is and how each might occur Adaptive radiation Punctuated equilibrium Horse evolution – some major phenotype changes along the way from ancestors to modern horse Chapter 25 – Phylogeny and Systematics Sedimentary rocks and fossils (again) Geological time table – page 487 – don’t have to memorize it, but should know generally what is really old and what is much newer Radiometric dating, half life of C-14 – how used to age rock and fossils Pangaea, continental drift, and how this affected speciation Mass extinctions – what were they Taxon – an example of a taxon would be Mammalia (but NOT the word Class) Systematics – definition Genus, specific epithet, species name – know the fine points Page 493 – know Fig. 25.7 – (Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, etc) Clade – know generally what it is and recognize a picture of one Analogy vs homology and convergent evolution (see page 495) 3 Chapter 26 – Early Earth and the Origin of Life Page 511 – Fig. 26.1 – know order in which different groups are found in the fossil record Oxygen on Earth – when and how did it start Spontaneous generation – experiment to discount it (Louis Pasteur) Biogenesis – life arises from the reproduction of preexisting life Page 522 – Fig. 26.15 – know 5-kingdom system Page 523 – Fig. 26.16 – know 3 systems of classification Chapter 27 – Prokaryotes… Page 527 – Fig. 27.2 – know 3 domains of life Shapes of prokaryotes– cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), helical (corkscrew-shaped) Know main characteristics of prokaryotes – Differences between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria – know structure of cell walls and why this makes one type (negative) more harmful; peptidogylcan and lipopolysaccharide Taxis – movement towards or away from a stimulus Binary fission (asexual reproduction) (but some prokaryotes can transfer genetic material between individuals) Endospore Autotroph vs heterotroph Saprobe – absorb their nutrients from dead organic mater Parasite – absorb their nutrients from the body fluids of living hosts Nitrogen fixation – what is it Obligate aerobes, facultative anaerobes, obligate anaerobes Archaea – live in extreme conditions (extremophiles) Halo – salty (saline) Thermo – usually refers to hot with respect to Archaea Page 537 – Table 27.2 – know differences for first 3 characteristics and last one Exotoxin (e.g., botulism) vs endotoxin (e.g., Salmonella) Lyme disease Symbiosis, mutualism, commensalisms, host, parasitism MSUM Home Page Stockrahm's Home Page Biology Home Page