* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multiple Choice: Choose the one best answer to each question
Survey
Document related concepts
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
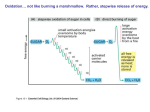
Name:____________Practice Test______________ Cell Biology Unit Test #3: 50 points Multiple Choice (1 pt each): Choose the one best answer for each question on the scantron (double check for smears) and put “written” answers on the back of the scantron. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Which of the following is a voltage gated channel that you would expect to find at a pre-synaptic end of an axon (nerve ending) that is specifically responsible for causing exocytosis of vesicles contianing acetylcholine (neurotransmitter). a) K+ b) Na+ c) Ca++ d) Cl2) What second messenger activates protein kinase A to phosphorylate specific serines and theronines? a) Diacylglycerol b) Calmodulin c) Inositol triphosphate d) Cyclic AMP e) Cyclic GMP 3) During the light reactions of photosynthesis the absolute required first step is to excite electrons at what location? a) P700 b) P680 c) d) NADPH d) Beta-carotene 4) a)True/b) False: Carbon fixation occurs when the five carbon Ribose-1,5-bisphosphate accepts carbon dioxide to become two 3-phosphoglycerates. Simplified GHK Equation Vm=2.303RT/F log Pk(K)o+Pna(Na)o Pk(K)i+Pna(Na)i 5) If potassium permeability is increased, the cell becomes more: a) Depolarized b) Hyperpolarized 6) If sodium permeability is increased, the cell becomes more? a) Depolarized b) Hyperpolarized 7) a)True/b)False: The ATP synthase generates ATP using a proton gradient in mitochondria and thylakoids. 8) a)True/b)False: Glycolysis produces pyruvate in the mitochondrial matrix. 9) a)True/b)False: Six carbon dioxide molecules are united at the same time to make a single glucose in the dark reactions of photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle). 8) A _________channel opens when its threshold membrane potential has been reached. a) Ligand-gated b) Voltage-gated c) Mechanosensitive 9) Which enzyme breaks down the second messenger cyclic GMP (cGMP)? (viagra blocks this process). a) Phosphodiesterase b) Calmodulin c) Guanylyl cyclase d) Stimulatory α-GTP 10) Pyruvate dehydrogenase oxidizes pyruvate into acetyl-CoA and ______B__. A B C D 11) For eukaryotic cells glycolysis occurs in the ______and the tricarboxylic acid cycle occurs in the ______. a) Mitochondria, Chloroplast b) Cytosol, Golgi apparatus c) Cytosol, Smooth endoplasmic reticulum d) Cytosol, Mitochondria 12) Which of the following are directly produced by photosynthesis (P-680 and P-700)? a) FADH2 ATP! b) NADH c) Glucose d) Pyruvate e) None are directly produced-NADPH and 13) The insect poison malathion blocks acetylcholinesterase from degrading the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. If malathion was present…. a) the post synaptic cell would be less likely to depolarize when acetylcholine is released b) the post synaptic cell would be more likely to depolarize when acetylcholine is released 14) a)True/b)False: Saltatory conduction of an action potentials is fastest because it uses gaps in the myelin to expose sodium and potassium voltage-gated channels at Nodes of Ranvier. 15) a)True/b)False: After an action potential has depolarized an excitable membrane by opening sodium channels, the potassium permeability temporarily increases causing sustained depolarization. 16) a)True/b)False: Voltage gated channels have a gate that closes a few milliseconds after the gates open during depolarization, this limits the duration of membrane potential depolarization. 17) a)True/b)False: During a typical action potential the sodium and potassium voltage-gated channels open at the exact same time and close at the exact same time. 18) a)True/b)False: Gap junctions create passages that allow sodium entering a cardiac cell to directly pass into the cytosol of a second cell causing it to depolarize. 19) ________hormones are produced locally and only act on cells in a close proximity to the origin. a) Autocrine b) Paracrine c) Endocrine d) Neuroendocrine 20) Which subunit of a G-protein dissociates and stimulates adenylyl cyclase when GDP is displaced? a) Alpha-GTP b) Beta-GTP c) Gamma-GTP d) Calmodulin 21) Which second messenger stimulates protein kinase C to phosphorylate target protein serines and threonines? a) Acetylcholinesterase(ACH) b) Diacylglycerol(DAG) c) Phosphodiesterase (PDE) d) Na+/K+ATPase 22) Which of the following can increase calcium permeability to cause contraction or exocytosis? a) Inositol triphosphate b) Voltage-gated channels c) Calcium d) All of above 23) Hormones like testosterone have a _________charge and must have a carrier to bring them from the plasma membrane through the watery cytosol to the DNA in the nucleus. a) polar b) non-polar 24) Which amino acid residue would be the worst choice for phosphorylation by protein kinases? a) Tyrosine b) Serine c) Threonine d) Lysine d) All of above have hydroxyls and are good targets IF the kinase is specific for that protein and residue 25) a) True/b) False: All living cells have a membrane potential (mV) but only excitable cells can create and send action potentials down their length. 26) a) Trueb) Fa/lse: All cells have silimar receptors for the same hormones on the intracellular side of their plasma membranes 27) a) True/b)False: Insulin binds its plasma membrane receptor which is a tyrosine kinase that used a Gprotein to autophosphorylate itself, then it phosphorylates amino groups on target proteins in the cytosol. 28) a)True/b)False: Typically extracellular sodium is 145 mM, intracellular sodium is 10 mM, extracellular K+ is 5 mM, and intracellular K+ is 125 mM. Name:________________Written Questions to Test #3 29) How many of the items indicted below would be produced if palmitate (a 16 carbon long fatty acid) underwent beta-oxidation (BUT NOT TCA) in the mitochondrial matrix? 4 pts Acetyl-CoA= 8 NADH= 7 FADH2= 7 GTP= 0 . 16 carbons cut 7 times (7 NADH and 7 FADH2) to create 8 acetyl-CoA……GTP would only come from TCA 30) How many of the items below are produced when a TWO acetyl-CoAs enter the citric acid cycle and are oxidized? 6 pts NADH= _6_ FADH2= _2_ GTP= 2 CO2= _4 (2X2=4 CO2)_ Oxaloacetate= 2 Pyruvate= 0 31) 5 points: How do mitochondria produce ATP from ADP, Pi and the NADH and FADH2 generated in the question above? You will need to indicate/name all enzymes, proton gradients, and enzyme complexes. A sketch of the mitochondria will also probably be needed to answer this question. See notes 32) 2 points: Why is intracellular amplification needed for hormones to change cellular functions? See notes 33) 5 points: Describe how epinephrine could cause calcium to enter a smooth muscle cell leading to its contraction via an alpha-1 receptor and phospholipase-C? Name enzymes, proteins, and second messengers making this possible. See notes Extra Credit: 2 points-On The Back Describe how epinephrine could cause a calcium to enter a heart muscle cell leading to its contraction via an Beta-1 receptor and cyclicAMP? Name enzymes, proteins, and second messengers making this possible. See notes