* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
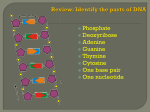
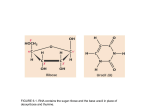
Distinguish between 5’ and 3’ ACTIVATOR CODON PROMOTER Distinguish between mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA RNA POLYMERASE Distinguish between TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION TERMINATION SIGNAL RIBOSOME TRANSFORMATION OPERON TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR ENHANCER SECRETORY PROTEIN RELEASE FACTOR Codon– A series of _____ (number) nucleotides on the mRNA. Each codon codes for a particular ________ __________. Activator– An activator binds to a ___________ which then binds to the transcription factors and RNA Polymerase to cause gene expression. 5’ – closest to carbon 5 of the sugar in a nucleic acid 3’ - closest to carbon 3 of the sugar in a nucleic acid Label the carbons in the nucleotide below: P RNA Polymerase– Enzyme that carries out the process of _________________. Breaks hydrogen bonds between nucleotides and matches the template strand with complementary bases to produce __________. mRNA– RNA that is translated into a protein tRNA– RNA that brings the appropriate amino acid to the mRNA so that translation can take place. O Promoter– Sequences at the beginning of each gene that bind to ___________________ to begin transcription. rRNA– RNA that is part of the ribosome. Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. Termination Signal– The signal that causes _______________ to end. Characterized by a string of A’s on the template DNA. Transcription Factor– Proteins that bind to the promoter sequences of ______________ to promote the binding of RNA Polymerase. Operon– Method of gene regulation in _____________. Genes coding for related proteins are grouped together. All of these genes share a single promoter. Transcription is regulated by the binding of a regulatory protein to the operator region. Transformation— process in which a foreign _________ is inserted into a host. Requires the use of __________ to neutralizes charges on cell membrane and ______________ to open up temporary holes in the membrane. Release Factor— A protein that binds to a ___________ in the mRNA to cause the mRNA, ribosome, tRNA and polypeptide to come apart from one another. This signals the end of _______________. Secretory Protein— A protein that will be _________ from the cell. The mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. Enhancer– A sequence of _______ that is far away from the gene it activates. When a molecule (ex. hormone) binds to the enhancer sequence, the sequence loops around to the ___________ of the gene it activates. This helps recruit RNA Polymerase. Transcription– The process in which _______ is copied into _________. Accomplished by the enzyme RNA Polymerase. Translation– The process in which the code in a strand of ________ is made into ____________________.