* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System Function
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
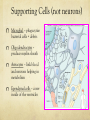
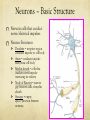
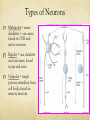
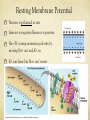
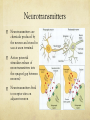
Nervous System Function Neurons and Neurotransmitters Nervous System - Pathways Sensory Receptors Somatic Nerves (muscles) Autonomic Nerves (glands/organs) Sensory Nerves Brain and Spinal Cord Motor Nerves Nervous System - Pathways Sensory Nerve Interneuron Motor Nerve Supporting Cells (not neurons) Microglial – phagocytize bacterial cells + debris Oligodendrocytes – produce myelin sheath Astrocytes – link blood and neurons helping in metabolism Ependymal cells – cover inside of the ventricles Neurons – Basic Structure Nervous cells that conduct nerve/electrical impulses Neuron Structures Dendrite = receptive region conducts impulse to cell body Axon = conducts impulse away from cell body Myelin sheath = cells that insulate nerve impulse increasing its velocity Node of Ranvier = narrow gap between cells of myelin sheath Synapse = empty space/junction between neurons Types of Neurons Multipolar = many dendrites + one axon; found in CNS and motor neurons Bipolar = one dendrite and one axon; found in eye and nose Unipolar = single process extending from cell body; found in sensory neurons Resting Membrane Potential Neuron is polarized at rest Interior is negative/Exterior is positive Na+/K+ pump maintains polarity by moving Na+ out and K+ in K+ can leave but Na+ can’t enter Action Potential Neuron depolarizes to send an electrical nerve impulse Neuron becomes positive inside and negative outside as a result of ions moving The momentary depolarization is quickly reversed and the neuron becomes re-polarized The depolarization is called an action potential Action Potential Action Potential is caused by movement of ions Depolarization = Steps 1 + 2 Action Potential = Step 3 Repolarization = Steps 4, 5, 6 Action Potential The resting membrane potential is negative and cell is polarized. Stimulus causes Na+ and then K+ gates to open, inside of cell becomes positive and is depolarized. Na+ gates close and K+ gates open, inside becomes repolarized as K+ leaves cell. Action Potential to Nerve Impulse Action potential produces a local current This causes depolarization on adjacent membrane The wave of action potentials travels down the neuron producing a nerve impulse Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and can depolarize as a result Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters are chemicals produced by the neuron and stored in sacs at axon terminal Action potential stimulates release of neurotransmitters into the synapse (gap between neurons) Neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on adjacent neuron Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters change the shape of receptors allowing movement of ions into neuron Movement of positive ions (Na+) causes depolarization and an action potential Neurotransmitters that allow this are called stimulatory Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters can change the shape of receptors preventing movement of ions into neuron Causes the interior of neuron to become more negative, preventing an action potential Neurotransmitters that do this are called inhibitory Neurotransmitters