* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 28 - KaterinaCLHSportfolio
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
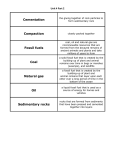
Earth History Textbook Assignment: Pgs 588-609 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Reading Checks: o Pg592: Scientists need a geologic time scale it enables them to find relationships among the geologic events, environmental conditions, and fossilized life-forms that are preserved in the rock record. o Pg598: 1. Disconformity: When a horizontal layer of sedimentary rock overlies another horizontal layer of sedimentary rock, ; eroded surface. o 2. Nonconformity: When a layer of sedimentary rock overlies a layer of igneous or metamorphic rock, i.e. granite or marble, the eroded surface is easier to identify. o Pg603: Radiometric dating is not useful for sedimentary rocks because the minerals in most sedimentary rocks were formed from pre-existing rocks. o Pg604: Tree Rings can show the past environmental conditions by consisting of a pair of early season and late season growth rings. o Pg607: Fossils with original preservation are rare because their preservation requires extraordinary circumstances, such as freezing, arid, or oxygen-free environments. o Pg608: 1. Recrystalization: When a buried hard part is subjected to changes in temperature and pressure over time. o 2.Mineral Replacement: The original mineral is replaced by a mineral from water, whereas in recrystalization the original minerals transformed into a new mineral. Questions: Pgs 613-614 Geologic Time Scale Unconformity Radioactive decay Precambrian Correlation Period: Are generally tens of millions of years in duration, though some periods of the Precambrian are longer. Epoch: Are generally hundreds of thousands to millions of years in duration. 7. Altered hard part: Fossil whose organic material has been removed and whose hard parts have been changed by recryalization or mineral replacement. Original preservation: Describes a fossil with soft and hard parts that have undergone very little change since the organisms death. 8. Absolute-age dating: Method that enables scientists to determine that actual age of certain rocks and other objects. Relative-age dating: To determine how many years ago an event occurred; gives scientists a clear understanding about geologic events in earth’s histories. 9. Fossil: The remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in a petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock. Index fossil: Remains of plants or animals that were abundant, widely distributed, and existed briefly that can be used by geologists to correlate or date rock layers. 10. Mold: Fossil that can form when a shelled organism decays in a sedimentary rock and is removed by erosion or weathering, leaving a hollowed-out impression. Cast: Fossil formed when an earlier fossil of a plant or animal leaves a cavity that becomes filled with minerals or sediment. 11. Principle of Inclusions 12. Uniformitarianism 13. Key Bed 14. Evolution 15. (1) 16. (4) 17. (1) 18. (4) 19. (3) 20. (1) 21. (2) 22. (4) 23. (4) 24. (2)