* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular forces
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
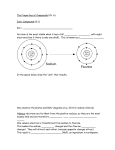
Unit 7 Notes: Compounds All atoms will try to gain or lose __________ until they have _________ valence electrons. Metals will __________ electrons and nonmetals will __________ electrons. Example: After an atom has gained or lost electrons, it has a ___________ and is called an _________. A positive ion is called a ___________ and a negative ion is called an ___________. These charges are called ___________ ___________. Using the periodic table for oxidation numbers: What are the oxidation numbers for the following elements? Fr _____ Au _____ Kr _____ C _____ Ba _____ Na ______ S ______ O _____ ___________ ____________ occurs when metals make compounds with nonmetals. ___________ ____________ occurs when only nonmetals are making compounds with each other. Electrons are ___________. Example: Carbon Dioxide Water Label the following compounds ionic or covalent: NaCl _________ H2O _________ CO _________ CaF2 _________ AgBr _________ NO _________ ___________ ____________ occurs when metals are sharing electrons with each other. IONIC COVALENT METALLIC Ionic compounds that just have 2 elements are called ___________ ionic compounds. When naming binary ionic compounds, write the name of the __________ and change the ending of the nonmetal to _________. NaCl ________________________________ BaO ________________________________ K2S _________________________________ AlP _________________________________ LiBr _________________________________ ZnI2 ________________________________ Sr3N2 _______________________________ When an ionic compound has more than 2 elements, it contains a _______________ _______________. These are groups of atoms that act like one ion when bonding with other elements. Use your polyatomic ion sheet to help name these compounds. CuSO4 __________________________________________ KMnO4 __________________________________________ Ca3 (PO4)2 __________________________________________ Fe(OH) 2 __________________________________________ NaNO3 __________________________________________ NaNO2 __________________________________________ NaHCO3 __________________________________________ CaCO3 __________________________________________ NH4Cl __________________________________________ (NH4) 3PO4 __________________________________________ Writing Formulas (ionic): When atoms combine to make compounds, the overall charge is _____. Atoms will gain, lose, and share e- so that each atom can have _____ valence e- while still maintaining an overall ____________ charge. 1. Write ___________ for each element or polyatomic ion. (Metal is always written first!) 2. Write the __________ ___________ above each symbol. (Positive element always written first!) 3. Swap-n-drop charges to make them ____________. 4. ____________ if necessary: Ca2O2 = __________. Write the correct chemical formulas for the following compounds: sodium chloride sodium oxide sodium nitride aluminum sulfide potassium iodide aluminum phosphide magnesium bromide lithium phosphide francium oxide Sometimes transition metals have more than one possible charge. The name will include a ____________ ____________ so that you will know which charge to use. Iron (II) oxide silver (I) sulfide tin (IV) chloride Use your polyatomic ion sheet to look up charges when a compound is not binary. Use parentheses when necessary! Magnesium phosphate copper (II) sulfate sodium hydroxide Beryllium nitrate aluminum hydroxide tin (IV) phosphate Naming covalent compounds: Covalent compounds occur when nonmetals ___________ e-. 1. Use ____________ to represent the number of atoms present. mono: hexa: di: hepta: tri: octa: tetra: nona: penta: 2. Still change the ending of the 2nd element to ____________. CO2 N2Cl4 CS2 CO P2S5 N2O4 Carbon monosulfide tetrasulfur tetranitride Disulfur hexabromide iodine heptafluoride Boron trihydride dinitrogen tetraoxide