* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Unit Test - hhs-snc1d
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
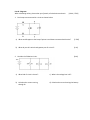
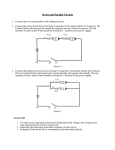
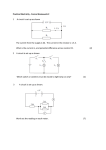
SNC1D Total marks Practice Test on Electricity /72 Knowledge and Understanding Name:___________________ /5 Thinking and Inquiry Part A: Multiple Choice Circle the best answer 1. In a conductor, the moving charges are usually: a) protons b) electrons c) neutrons d) charges cannot move in a conductor 2. A series of dry cells connected together is called a: a) resistor b) voltage c) lamp d) battery 3. a) b) c) d) 4. a) b) c) d) A good example of an insulator: salt water iron copper plastic The four basic components of a circuit are: power source, lamps, resistors, batteries wires, connectors, switches, lamps power source, connectors, loads, switches batteries, lamps, resistors, fuses 5. The invention of the voltaic cell is attributed to: a) Benjamin Franklin b) Alessandro Volta c) Guglielmo Marconi d) Andre-Marie Ampere 6. A list of materials placed according to how strongly they hold on to electrons is called: a) the electrostatic series b) the law of electrostatics c) the electronic list d) the law of electromagnetics [20 KU] 7. The three methods of charging an object are: a) contact, induction, friction b) friction, contact, deduction c) contact, induction, grounding d) induction, friction, grounding 8. One kilowatt is equal to: a) 1 Watt b) 10 Watts c) 100 Watts d) 1000 Watts 9. This is a measure of how much energy is being used per unit of time: a) current b) voltage c) power d) resistance 10. A 480W computer is left on for 8 hours during the day. The energy wasted is: a) 8 Watt hours b) 480 Watt hours c) 60 Watt hours d) 3840 Watt hours 11. The purpose of a fuse is: a) to break a circuit if too much current is passing through b) to add resistance to a circuit c) to make a battery less powerful d) to make a short circuit 12. a) b) c) d) The unit of energy is the: Joule Watt Ohm Ampere 13. a) b) c) d) The symbol for charge is: C A W Q 14. a) b) c) d) The symbol for the unit of charge is: Q C I A 15. a) b) c) d) The unit for time is the: Watt Joule metre second 18. The common term for potential difference is: a) current b) voltage c) resistance d) energy 16. A circuit consists of a dry cell and two unknown resistors in parallel. The current through one resistor is: a) equal to the current leaving the cell b) equal to the current in the other resistor c) less than the current leaving the cell d) less than the current in the other resistor Part B: Units 17. A circuit consist of a dry cell and two resistors in series. The current through one resistor is: a) equal to the current going through the other resistor b) less than the current going through the other resistor c) less than the current going through the cell d) more than the current going through the cell 19. Given the formula V = E/Q, one volt is equal to: a) one Joule-Coulomb b) one Joule per Ampere c) one Joule per Coulomb d) one Watt per Ampere 20. Given the formula E = P t, one Joule is equal to: a) one power-time b) one Ampere per second c) one Watt per Coulomb d) one Watt-second Fill in the following table: [15 KU] Measure Symbol Unit Unit Symbol Time t Second s Power Joule Ampere R Potential Difference Part C: Word Problems For each problem, show your formula and all calculations. Make sure your final answer includes units. [21 KU] 1. A 940 Watt toaster is plugged into the 120V outlet in my kitchen. a) How much current does it draw from the b) How much energy will it use up if it takes outlet? [3 KU] 40 seconds to toast bread?[3 KU] 2. A lamp has a resistance of 40Ω. Find the voltage loss in the lamp when 2.4A of current is running through it. [3 KU] 3. A current of 1.5A runs through a resistor in a circuit. A voltmeter reads a loss of 3.4V across the resistor. a) Find the resistance of the resistor. b) Find the power loss of the resistor. [3 KU] [3 KU] 4. An oven coil plugged into a 240V power source has a resistance of 30Ω. Find the power of the oven coil. [6 KU] Part D: Diagrams When calculating values, please show your formula, all calculations and units. [16 KU, 5 TIPS] 1. Four lamps are connected in a circuit as shown below: a) What would happen to the lamps if points A and B were connected with a wire? [2 TIPS] b) What do you call a wire that bypasses part of a circuit? [1 KU] 2. Consider the following circuit: [8 KU] a) What kind of circuit is shown? c) What is the voltage loss in R3? b) Calculate the current running through R2. d) Calculate the current leaving the battery. 3. Draw a diagram or diagrams illustrating charging an object negatively by induction. Write a short explanation of each step in the space on the right. [6 KU] Diagrams Explanation 4. You are making toast when you realize your toast is stuck in the toaster. You get a fork to pry out the toast from the toaster. As you pry the toast out, you get a nasty shock that damages your hand. a) Explain why you got a shock. Try to be as specific as possible. [1 KU] b) Give three ways that you could have prevented or lessened the shock and perhaps saved your hand from damage. [3 TIPS]