* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s 3 Laws
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
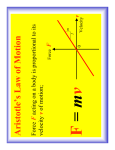
Sir Isaac Newton’s Three Laws of Motion Sir Isaac Newton was Smart! Showed that force, mass, and acceleration are related. Summarized the motion of objects in three Laws of motion. Universal Law of Gravitation explains how the planets stay in orbit around the sun. Demo—Penny on Card What forces keep the coin at rest on the note card? o Friction? o Gravity? o Both? Why didn’t the coin fly away with the card? o Did the coin’s own “stubbornness” prevent it from doing so? o Or does the card have some intrinsic property that favors its remaining in place? Demo – Table Cloth What forces keep the beaker at rest on the paper towel? o Friction, gravity, both? Why didn’t the beaker fly away with the paper towel? Have you seen this before? o Is it magic, or just demonstrating Newton’s First Law of Motion: The law of Inertia Newton’s First Law Objects at rest will stay at rest and objects in motion will stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Law of Inertia Laziness! Momentum and Newton’s Law Which object is likely to do more damage to a brick wall: a 5kg bowling ball moving at 1 m/sec or a .01kg bullet moving 1,000 m/sec? Momentum and Bad TV When a person is shot by a bullet on tv, they often fly backwards through a window. o Does this really happen? o The person would have to have a mass of less than 1kg! Momentum and Real TV This is more like what would happen—in the best case scenario where the person is on skates and almost frictionless! Momentum – The Equation p=mxv o p = momentum o m = mass o v = velocity Momentum and Newton’s Law Which object is likely to do more damage to a brick wall: (1) a 5kg bowling ball moving at 1 m/sec or (2) a .01kg bullet moving 1,000 m/sec? o p=mxv o p = 5kg x 1m/s = 5 kg m/s o p=mxv o p = .01kg x 1,000m/s = 10kg m/s Newton’s Second Law The force on an object is “proportional” to the object’s mass and acceleration. f=mxa f=force, m=mass, a=acceleration A force is a push or pull on an object. The more force applied to an object, the more it accelerates. The more massive an object is, the more force is needed to move it. Newton’s Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v3 + m2v4 Conservation of momentum. Total momentum in a “closed system” doesn’t change. Hero of Alexandria Invented the Hero engine in the 1st century B.C. Used a boiler to produce steam. The steam traveled through tubes shaped like a pinwheel. Escaping steam produced an action-reaction force, causing the sphere to spin in the opposite direction! Hero Engine