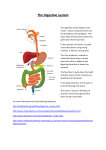
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download digestion malfunctions chart
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Name:______________________ Disease or malfunction Heartburn/ indigestion Ulcer Constipation Diarrhea Organ or part affected Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Causes Symptoms Treatment? Name:______________________ Appendicitis Gall stones Crohn’s disease Jaundice Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Name:______________________ Cirrhosis Colitis Celiac’s disease Hepatitis Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Name:______________________ Anal fissures (hemorrhoids) Dysentery E. coli Gastritis Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Name:______________________ Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Hiatal Hernia Stomach, esophagus A hiatal hernia occurs when weakened muscle tissue allows your stomach to bulge up through your diaphragm. Heartburn, Belching, Difficulty swallowing, Chest or abdominal pain, Feeling especially full after meals, Vomiting blood or passing black stools, which may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding Antacids, medications that block acid production, surgery in severe cases to repair hiatal hernia IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) Large intestine the contractions of the intestines may be stronger and last longer than normal, causing gas, bloating and diarrhea. Or the opposite may occur, with weak intestinal contractions slowing food passage and leading to hard, dry stools. Abdominal pain or cramping A bloated feeling Gas Diarrhea or constipation — sometimes alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea Mucus in the stool Eliminating high-gas foods, eliminating gluten, fiber supplements, anti-diarrheal medications, antibiotics, counseling for stress or depression Lactose intolerance occurs when your small intestine doesn't produce enough of an enzyme (lactase) to digest milk sugar (lactose). Diarrhea Nausea, and sometimes, vomiting Abdominal cramps Bloating Gas Avoiding large servings of milk and other dairy products, Including small servings of dairy products in your regular meals, Eating and drinking lactose-reduced ice cream and milk Lactose intolerance Small intestine Name:______________________ Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Pancreatitis Pancreas Pancreatitis occurs when digestive enzymes produced in your pancreas become activated while inside the pancreas, causing damage to the organ Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, losing weight without trying, oily smelly stools Fasting, pain medications, intravenous fluids Colon polyps Colon Mutations in certain genes can cause cells to continue dividing even when new cells aren't needed Often no symptoms, sometimes rectal bleeding, change in stool color, bowel habit, pain, nausea, vomiting, iron deficiency anemia Removal, if severe colon and rectum removal Menetrier’s disease stomach associated with HCMV infection in children and H. pylori infections in adults Individuals with the disease present with upper abdominal pain (epigastric), at times accompanied by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, edema, and weight loss. Anticholinergics decrease protein loss. A high-protein diet should be recommended to replace protein loss in patients with low levels of albumin in the blood (hypoalbuminemia). Any ulcers discovered during the evaluation should be treated in standard fashion. Severe disease with persistent and substantial protein loss despite cetuximab may require total removal of the stomach Wilson’s disease liver Genetic, too much copper accumulating in liver Fatigue, lack of appetite or abdominal pain, Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eye, A tendency to bruise easily, Problems with speech, swallowing or physical coordination medications called chelating agents, which prompt your organs to release copper into your bloodstream. Treatment then focuses on preventing copper from building up again. When liver damage is severe, a liver transplant may be necessary. Name:______________________ Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome stomach Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) genetic (inherited) disorder Burning pain in the abdomen, Medications to reduce stomach acid and heal the ulcers Nausea, Diarrhea, Vomiting Bleeding from the stomach, Weakness, Fatigue Alagille Syndrome Liver Genetic disorder yellowish tinge in theskin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice), itching, and deposits of cholesterol in the skin medications are used to improve bile flow, high dose of a multivitamin, certain drugs may be used to reduce itching, Corrective surgery is sometimes needed to repair heart defects Barret’s esophagus frequent and heartburn, a sour, burning sensation in the back of the throat, chronic cough,laryngitis, and nausea. Radiofrequency ablation, Photodynamic therapy, or surgery to remove the faulty esophagus tissue Diverticulosis can present with painless rectal bleeding as bright red blood per rectum. Cramps and tenderness may also occur in the affected areas. Include fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains in your diet each day. These foods are high in fiber. Drink plenty of fluids, enough so that your urine is light yellow or clear like water. Get some exercise every day esophagus longstanding heartburn, trouble swallowing, vomiting blood, pain under the sternum, weight loss because eating is painful Diverticulosis Colon increasing age, constipation, a diet that is low in dietary fiber, hereditary or genetic predisposition, and extreme weight loss Name:______________________ Diverticulitis Large intestine Hemochromatosis Liver Hirschsprung’s disease Large intestine (colon) Disease malfunctions of digestive system(**next year a section for what is it) Bacteria grow in the pouches (diverticula ), and this can lead to inflammation or infection. Hereditary hemochromatosis is caused by a mutation in a gene that controls the amount of iron your body absorbs from the food you eat. These mutations are passed from parents to children Between the 4th and the 12th weeks of pregnancy, while the fetus is growing and developing, nerve cells form in the digestive tract, beginning in the mouth and finishing in the anus. For unknown reasons, the nerve cells do not grow past a certain point in the intestine in babies with Hirschsprung's disease. Diverticulitis can cause severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea and a marked change in your bowel habits. Joint pain Abdominal pain Fatigue Weakness Not having a bowel movement in the first 48 hours of life Gradual bloating of the abdomen Vomiting green or brown fluid Mild diverticulitis can be treated with rest, changes in your diet and antibiotics. Severe or recurring diverticulitis may require surgery. Removal of iron from blood Hirschsprung's disease is treated with surgery to bypass or remove the diseased part of the colon.