* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marshall Plan (1948
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Austria wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
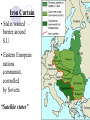
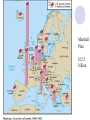
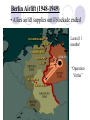
Vs. The United States The Soviet Union Post World War II Plans • Yalta Meeting (Feb. 1945): • European nations to be democratic, United Nations created Post World War II Plans • Potsdam conference (July 1945): • Germany divided into 4 zones (USA, S.U., G.B., France) Iron Curtain • Stalin wanted barrier around S.U. • Eastern European nations communist, controlled by Soviets “Satellite states” “From Stettin in the North to Trieste in the south, an iron curtain has descended over Europe.” Winston Churchill to Americans in Speech Containment Policy U.S. foreign policy that sought to prevent the spread of Soviet communism George Kennan – creator of the Containment policy Truman supported with Truman Doctrine! Truman Doctrine (1947) • Response to communist takeover attempt in Greece • Truman gives economic aid to countries fighting communism • $400 million in aid to Greece and Turkey Controversial example of containment Marshall Plan (1948-1951) • Europe needed to be rebuilt after WWII London, England Dresden, Germany Marshall Plan (1948-1951) • Sec. of State George Marshall--give friendly aid • economic recovery was necessary for world peace West German advertisement The free train of the Marshall Plan Marshall Plan $12.5 billion Marshall Plan (1948-1951) • S.U. and Eastern countries refuse aid Berlin Airlift (1948-1949) • Berlin also divided into 4 zones • Soviet zone weak, others prospered and cooperated Marshall Plan and West Berlin Berlin Airlift (1948-1949) • East Berliners could see difference and left • Stalin blockaded West Berlin to stop this Soviets closed Berlin’s railway lines, canals, roads. W. Berlin had 36 days of supplies. Berlin Airlift (1948-1949) • Allies airlift supplies until blockade ended Lasted 11 months! “Operation Vittles” Every ten minutes a plane took off with supplies for West Berlin. 327 days 277,000 flights 2.5 million tons of supplies NATO (1949) and Warsaw Pact • defensive military alliance created • called North Atlantic Treaty Organization • Warsaw Pact created in response (S.U.and E. Europe) Nuclear Arms Race • 1949--Soviet Union achieves A-bomb “Joe -1” Russian A-bomb Russian Scientist Kurchatov Nuclear Arms Race • U.S. quadruples defense spending • 1952--U.S. invents Hydrogen "super" bomb H-Bomb Test Fireball 3 miles 18 mths. later Soviets have it New Leaders 1952 Eisenhower elected 1953 Stalin dies; Nikita Kruschev takes over Nuclear deterrence begins (don’t want WWIII) Eisenhower Kruschev Metacognition Statement: I know that I know something about Cold War events. First, In addition, Finally, Now you know something that I know about Cold War events.