* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - RosedaleGrade10Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Gamma correction wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
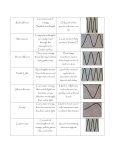
SNC2D: Physics - Optics Electromagnetic Waves in our Society (p. 466, Science Perspectives 10, Nelson) Red Violet Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum) and do not require a medium for transmission. Type of electromagnetic wave Radio Use/phenomena Wavelength Range AM/FM, tv signals, cellphones, Radar, astronomy > 1 cm long Infrared Remote controls, heat detection, physical therapy (heating) 700 nm – 0.05 cm Visible Range of human vision 400 – 700 nm Ultraviolet Causes skin to tan/burn and increases skin cancer risk, kills bacteria (sterilization) 10 – 400 nm X-rays and gamma rays Medical imaging, cancer treatment, security equipment < 10 nm In optics, we are often dealing with numbers that are very small (e.g. the wavelength of gamma rays is less than 0.01 nm = 1.0 × 1011 m) or very large (the speed of light c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum), so we often need to use scientific notation and to do unit conversions. SNC2D: Physics - Optics Electromagnetic Waves in our Society (p. 466, Science Perspectives 10, Nelson) Red Violet Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum) and do not require a medium for transmission. Type of electromagnetic wave Radio Use/phenomena Wavelength Range Infrared Visible Ultraviolet X-rays and gamma rays In optics, we are often dealing with numbers that are very small (e.g. the wavelength of gamma rays is less than 0.01 nm = 1.0 × 1011 m) or very large (the speed of light c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum), so we often need to use scientific notation and to do unit conversions. SNC2D: Physics - Optics Spectroscopes: Looking at Light White Block on the Monitor Natural Light Mercury Lamp Fluorescent Light