* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the plant kingdom - 1st ESO Bilingual Science
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
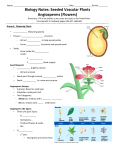
DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA T TH HE EP PL LA AN NT TK KIIN NG GD DO OM M U UN NIIT T 1100 The plant kingdom is made up of organisms with many cells. Cells are organised according to tissues Plants get the nutrients, but they don’t eat other organisms. They have these common characteristics: Plants are multicellular organisms. They are made up of many cells which form tissues. Plants have got eukaryotic cells. The cell has got a nucleus and organelles surrounded by membranes. It is surrounded by a cell-wall made up of cellulose. It has got chloroplasts filled with chlorophyll. This green pigment is responsible for photosynthesis Plants have autotrophic nutrition. They get organic matter through photosynthesis. This process requires light, which is captured by chlorophyll, a green substance found in the plant’s leaves All of plants have got roots, stems and leaves. These vary according to the species Plants cannot move. They live anchored to the ground by roots. But they can make some movements ( for example, they can open and close their flowers and leaves ). (Vocabulary: tissue: tejido / nutrients: nutrientes / to surround: rodear / cellulose: celulosa / made up of: hecho de / according to: segun / to vary: variar / ground: suelo / chemical reactions: reacciones químicas / specie: especie / anchored: ancladas, agarradas ) Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 2 3 4 5 6 Multicellular Autotrophus Eukaryotic cells Photosynthesis Chlorophyll Chloroplasts A B C D E F Living beings that get organic matter through photosynthesis. Chemical reactions by which green plants make their food Green pigment responsible for photosynthesis Organelles in plant cell which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll Cells that have got nucleus Living beings that are made up of many cells Answers: 1 .............. 2 ............ 3 ............. 4 ............. 5 ............. 6 ............. Fill the gaps with the following words from the list Many multicellular autotrophic eukaryotic nucleus nutrients organic chlorophyll movements ground tissues photosynthesis The plant kingdom is made up of organisms with ............................ cells, so they are .............................. organisms. Cells are organised according to ................................... Plants get the ...................................., but they don’t eat other organisms. Plants have got ................................. cells. The cell has got a .................................... and cell-wall. It has got chloroplasts filled with ........................................ This green pigment is responsible for ....................................... Plants have ......................................... nutrition. They get ........................................ matter through photosynthesis. Plants cannot move because they live anchored to the ..................................................., but they can make some ........................................... (for example, they can open and close their flowers and leaves ). Answer the following questions 1. What kind of cells have plants got?........................................................................................................................ 2. Are plants unicellular or multicellular living beings?................................................................................................ 1 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA 3. Why are plants autotrophus?................................................................................................................................... 4. What is the difference between animal cell and plant cell?..................................................................................... 5. How do plants get their food?.................................................................................................................................. 6. What is the name of the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis?............................................................... 7. Why can’t plants move?.......................................................................................................................................... 8. What kind of movements can plants make?............................................................................................................ P Pllaanntt ccllaassssiiffiiccaattiioonn We can classify plants depending if they produce flowers or not. N Noonn fflloow weerriinngg ppllaannttss.. ((P Pllaannttss w wiitthh nnoo fflloow weerrss)) They are simple plants with no flowers or seeds. M Moosssseess aanndd LLiivveerr w woorrssttss They are the smallest and simplest plants. They are non-vascular plants (with no conductor vessels which transport water) so they depend on the water to survive, and have not got any vegetative organs (no roots, no stem, and no leaves). They live in damp places; on the ground, on the surface of rocks, and on tree trunks. FFeerrnnss They are medium-sized vascular plants (with conductor vessels which transport water and nutrients). They have got vegetative organs (root, stem, and leaves) but they have not got flowers or fruits. They have large leaves, called fronds, which are separated into small leaflets. They also live in damp places. F Flloow weerriinngg ppllaannttss.. ((P Pllaannttss w wiitthh fflloow weerrss)) They are more complex plants and they are vascular plants with flowers and seeds. G Gyym mnnoossppeerrm mss These plants are vascular. They have got flowers but not fruits. Their seeds are inside a false fruit, like a pinecone. A Annggiioossppeerrm mss These plants are vascular. They have got flowers and fruits. Their seeds are inside a real fruit. (Vocabulary: seeds: semillas / mosses: musgos / liver worsts: hepáticas / conductor vessels: vasos conductores / to survive: sobrevivir / damp: húmedo / ferns: helechos / medium-sized: de tamaño medio / leaf: hoja / leaves: hojas / leaflets:hojitas / gymnosperms: gimnospermas / pinecone: piña / angiosperms: angiospermas) Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 2 3 4 5 6 Mosses Non-vascular plants Ferns Gymnosperms Angiosperms Vascular plants A B C D E F These plants have got their seeds inside a fruit These plants have not got their seeds inside a fruit Plants with conductor vessels which transport water They are medium-sized vascular plants with large leaves They are non-vascular plants and live in damp places Plants with no conductor vessels which transport water Answers: 1 .............. 2 ............ 3 ............. 4 ............. 5 ............. 6 ............. 2 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA Fill the gaps with the following words from the list Complex vascular medium-sized Liver worsts fruits seeds damp inside leaves simplest flowers survive Mosses and .................................... are the smallest and .................................. plants. They are non-vascular plants (with no conductor vessels which transport water), so they depend on the water to .................................... and for this reason they live in ....................... places. Ferns are ..................................... vascular plants (with conductor vessels which transport water). They have no ...................... or fruits. They have large .................................................. which are divided. They also live in damp places. Plants with flowers are more ............................................... plants and all of them are vascular plants. Gymnosperms are vascular plants and they have got flowers and not ............................. Their ......................... are inside a false fruit. Angiosperms are ....................... plants. They have got flowers and fruits. Their seeds are ........................ a real fruit. Answer the following questions 1. What are the smallest and simplest plants?............................................................................................................... 2. What does “non-vascular plant” mean?..................................................................................................................... 3. What is the difference between ferns and mosses?.................................................................................................. 4. What kind of plants live in damp places?................................................................................................................... 5. What is the name of plants which have got their seeds inside the fruit?.................................................................... 6. What is the difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms?............................................................................ G Gyym mnnoossppeerrm mss The pine tree, the cypress or the sequoia belong to this group. They are mainly big trees and form big forests. Gymnosperms are mainly evergreen-leaves trees. The leaves are hard and strong and usually have needle-shape, like the pine tree, or scales like the cypress. Gymnosperms have got small, insignificant flowers. The flowers group together into inflorescences or cones. These cones are male and female. Their seeds are not protected by a fruit. It has got two types of flowers, males and females located in different places of the plant. 3 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA A Annggiioossppeerrm mss The olive tree, the oak tree, and the wheat belong to this group.They have got very different sizes; herbs, shrubs and trees. They live in all kind of climates. Many angiosperms are deciduous. They lose all their leaves in winter so they can live in the cold weather. The leaves have got very different sizes and shapes. Angiosperms have got fruits which contain the seeds, so the seeds are protected and they can spread easily. Angiosperms have got brightly coloured flowers. The flowers attract animals and so they help pollination. The flowers are hermaphrodite mainly. (Vocabulary: pine tree: pino / cypress: ciprés / sequoia: secuoia / forests: bosques / evergreen-leaves: hojas perennes / needle-shape: con forma de aguja / scales: escamas / insignificant: poco llamativo / inflorescences: inflorescencias, grupo de flores / cones: conos / olive tree: olivo / oak tree: roble / wheat: trigo / herb: hierba / shrub: matorral / climates: climas / deciduous: caduca / to lose: perder / to spread: dispersar / brightly: brillantemente / pollination: polinización) Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 2 3 4 Deciduous trees Angiosperms Evergreen trees Gymnosperms A B C D E F Their leaves are hard and strong Each tree has got two types of flowers, males and females They lose all their leaves in winter They have got brightly coloured flowers They have got fruits which contain the seeds They have got small,insignificant flowers in groups Answers: 1 .............. 2 ............ 3 ............. 4 ............. 4 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA Fill the gaps with the following words from the list cypress seeds spread flowers strong females climates deciduous evergreen leaves groups sizes pollination cold shapes. needle-shape places fruits hermaphrodite scales Gymnosperms are mainly ........................................ leaves trees, as the .......................... The leaves are hard and ........................................ and usually have ................................, like the pine tree, or ....................... like the cypress. Gymnosperms’ .......................................... are not protected by the fruit. Gymnosperms have got small, insignificant flowers in ............................................. Each tree has got two types of flowers, males and .......................................... located in different .............................................. of the plant. Angiosperms have got very different ................................................ and they live in all kind of .................................. Many angiosperms are ......................................... They lose all their ...................................... in winter so they can live in ....................................... weather. The leaves have got very different sizes and .............................................. Angiosperms have got ............................................... which contain the seeds, so the seeds are protected and can ....................................... easily. Angiosperms have got brightly coloured .......................................................... This attracts animals and so they help ................................................... The flowers are .......................................... mainly. Answer the following questions 1. Can you give three names of gymnosperms?.......................................................................................................... 2. Are gymnosperms lonely trees or do they form big forests?..................................................................................... 3. What does “evergreen leaves” mean?...................................................................................................................... 4. Are the seeds of gymnosperms protected by the fruit?............................................................................................. 5. Have gymnosperms got big flowers or small ones?.................................................................................................. 6. How many types of flowers have gymnosperms got?............................................................................................... 7. What is the difference between evergreen and deciduous leaves?.......................................................................... 8. What is the function of fruits in angiosperms?.......................................................................................................... 9. Why have angiosperms got brightly coloured flowers?............................................................................................. 5 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA TThhee lleeaavveess,, tthhee sstteem m,, aanndd tthhee rroooott The plants cells group together into tissues, and tissues group together into organs. All plants have got three parts or organs: leaves, stems , and roots. LLeeaavveess Leaves are mainly green and have got different shapes. In leaves take place the photosynthesis and the change of gases with the environment. Leaves have got two parts: TThhee llaam miinnaa oorr bbllaaddee It is the biggest part of the leaf and has two different surfaces, the front part or topside, and the back part or underside. Inside the underside part of the lamina there are a lot of tiny pores called stomata. Gases and water vapour enter the leaf and are expelled through the stomata. TThhee ppeettiioollee It is the stalk that joins the leaf to the plant’s stem TThhee sstteem m Plant stems are usually above ground but some stems grow bellow ground level. The stem has four main functions which are: It keeps the plant upright and supports the leaves, flowers and fruits. The stem keeps the leaves in the light. It transports fluids between the roots and the leaves. The stem stores food and water. For example, the potato acumulates reserves of water and food. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes. Leaves and branches are joined to the stem at the nodes. The internode is the area of a stem between two nodes. Stems grow upwards from the apical bud. Lateral branches grow out of auxilliary buds along the stem TThhee rroooott The root is the part of a plant that is underground and grows downwards into the ground. The two functions of the root root are: A Abbssoorrppttiioonn of water and inorganic nutrients or mineral salts. A Anncchhoorriinngg of the plant body to the ground. Roots often contain food, such as the carrot or the sugar beet. The root surface is covered with many tiny hairs which absorb the water and mineral salts. The root has got a branch structure. It has a main root with secondary roots. Each root ends in a root cap. 6 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA (Vocabulary: to group together: agruparse en / leaf: hoja / leaves: hojas / stem: tallo / root: raiz / environment: medio ambiente / lamina: limbo / topside: haz / underside: envés / stomata: estoma/ to expell: expulsar / petiole: peciolo / stalk: tallo pequeño / upright: derecho, erguido / bellow: bajo / level: nivel / to support: sostener / to store: almacenar / nodes: nudos / internodes: internudos / underground: subterráneo / downwards: hacia abajo / absorption: absorción / anchoring: fijación / carrot: zanahoria / sugar beet: remolacha azucarera / branch: rama / main: principal / root cap: cofia) Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 2 3 4 5 6 Root Lamina Stem Petiole Leaf Node A B C D E F It transports fluids between the roots and the leaves Photosynthesis takes place in it It is the area of the stem where leaves can grow It is the part of a plant that is underground It is the biggest part of the leaf It is the stalk that connects the leaf to the plant’s stem Answers: 1 .............. 2 ............ 3 ............. 4 ............. 5 ............. 6 ............. Fill the gaps with the following words from the list pores green hairs water carrot surface petiole divided underground lamina leaves nodes absorption photosynthesis internode roots nutrients stomata fruits shapes gases two back part anchoring Leaves are mainly .......................... and have got different ....................... In leaves take place ........................ and the change of ..................................... with the environment. The ............................... is the biggest part of the leaf and has ....................... different surfaces, the front part, and the back part. Inside the .................................. of the lamina there are a lot of tiny ................... called ....................... The ............................... is the stalk that connects the leaf to the plant’s stem The stem supports the ......................., flowers and .............................. The stem transports fluids between the .................................... and the leaves, and stores ......................... and water. The stem is ............................... normally into ....................... and internodes. Leaves can grow through the nodes. The ............................................ is the area of a stem between two nodes. The root is the part of a plant that is .................................... It has two functions: ............................. of the ................................. and the mineral salts and ............................... the plant body into the ground. The root contains food, such as the ................................ or the sugar beet. The root .................................. is covered with many tiny ................................ which absorb the water and minerals Answer the following questions 1. Where does photosynthesis take place?.................................................................................................................. 2. What is the biggest part of the leaf?.......................................................................................................................... 3. What is the name of the tiny pores inside the back part of the leaf?......................................................................... 4. What is the name of the stalk that connects the leaf to the plant’s stem?................................................................ 5. What is the structure of the plant which supports the leaves, flowers and fruits?..................................................... 6. The stem transports fluids between which parts of the plant?.................................................................................. 7. What kind of materials does the stem store?............................................................................................................ 8. Where can leaves grow ?.......................................................................................................................................... 7 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA 9. What kind of materials does the root absorb?........................................................................................................... 10. How can the plant be anchored into the ground?.................................................................................................... 11. Give the name of two types of food that the roots often contain.............................................................................. 12. What is the name of the end part of the root? ......................................................................................................... Fill the boxes with the corresponding part of the plant (ROOT, LEAF, FRUIT, SEED, STEM, FLOWER) that you eat . Use the table of food below to get information CAULIFLOWER GREEN BEAN TOMATO LETTUCE ALMOND BEAN CARROT ARTICHOKE ORANGE NUT PEPPER POTATO AUBERGINE COURGETTE APPLE BROCCOLI GARLIC STRAWBERRY RED BEET ASPARAGUS ONION CHERRY PEAR CELERY ACORN LENTILS RADISH PARSLEY CHICKPEA PLUM PRICKLE PEAR AVOCADO LEMON CHARD PEA ARTICHOKE COURGETTE (UK) ZUCHINI (USA) AUBERGINE (UK) EGGPLANT (USA) ACORN CARROT LENTILS NUT LETTUCE GREEN BEAN APPLE 8 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA BEAN TOMATO CAULIFLOWER ORANGE PEPPER POTATO ALMOND CELERY RADISH PARSLEY ONION PEAR GARLIC RED BEET CHICKPEA GARBANZO BEAN BROCCOLI PLUM ASPARAGUS CHERRY STRAWBERRY CHARD PEA AVOCADO LEMON PRICKLE PEAR 9 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA P PLLA AN NTT R RE EP PR RO OD DU UC CTTIIO ON N TThhee fflloow weerr Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms The parts of a flower are as follows: PPeedduunnccllee.. It is the part that joins the flower to the stem. C Caallyyxx. It is made of little green leaves called sepals. They are in the base and protect the flower before it opens when it is still a bud. When the flower opens you can see the sepals behind the petals. Sepals are usually green or brown, although in some plants they are the same colour as the petals. C Coorroollllaa. It is made of little brightly coloured leaves called petals. They are coloured to attract insects, such as bees or butterflies, into the flower. The insects pick up pollen from the flower, and carry it to the next flower they visit. This is how most flowers are pollinated. Not all flowers have got brightly coloured petals. Some plants have got small flowers with no colour. This is because they are not pollinated by insects or other animals, but the wind. The wind blows their pollen grains to other plants. SSttaam meennss. They are the male reproductive organs. Each stamen has got a thin stalk or filament with an anther at the end. Each anther is made up of pollen sacs, which contain grains of pollen. Pollen contains the male gametes. PPiissttiill.. It is the female reproductive organ where the seeds are made. It has three parts: the stigma, the style, and the ovary. The ssttiiggm maa is the receptor of pollen. It is covered in a sticky substance. Its job is to catch the grains of pollen (which usually come from another flower) The ssttyyllee is the stalk that holds up the stigma and is the way for pollen tubes. The oovvaarryy contains one or more tiny bodies called ovules or “eggs”. Each ovule contains a female gamete or sex cell. When the flower is pollinated, the pollen sticks to the stigma. It then travels down the style to the ovary. In the ovary, the male gametes of the pollen joins with the ovules, and the ovules become seeds. This is called fertilisation. After fertilisation, the ovary turns into the fruit. 10 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA (Vocabulary: peduncle: pedicelo / corolla: corola / calyx: cáliz / to join: unir / bud: capullo de flor / male: masculino / stamen: estambre / anther: antera / pollen sacs: sacos polínicos / gamete: gameto / pistil: pistilo / ovary: ovario / stigma: estigma / style: estilo / sticky: pegajoso / to hold up: sostener / stalk: tallo pequeño / to pick up: recoger / to stick: pegarse / to travel: viajar) Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Stamens 2 Pistil 3 Corolla 4 Calyx 5 Petal 6 Sepal 7 Peduncle 8 Stigma 9 Style 10 Ovary A B C D E F G H I J It contains one or more tiny bodies called ovules It is the receptor of pollen. It is the stalk that holds up the stigma and is the way for pollen tubes It is the female reproductive organ of the plant They are the male reproductive organs It is made of little green leaves called sepals It is made of little coloured leaves called petals It is a little coloured leaf It is the part that joins the flower to the stem It is a little green or brown leaf locate in the base of the flower Answers: 1 .......... 2 ........ 3 ......... 4 ......... 5 ......... 6 ......... 7 ......... 8 .......... 9 ......... 10 ......... Fill the gaps with the following words from the list stigma peduncle female ovary holds up pollen insects anther wind stamens tubes sacs pollinated sticky stalk sepals seeds bees carry bud corolla ovule small The ............................. is the part that joins the flower to the stem. The calyx is made of little green leaves called ............................. They are in the base and protect the flower before it opens when it is still a ................................ The .............................. is made of little coloured leaves called petals. They are coloured to attract ......................, such as .............................. or butterflies, into the flower. The insects pick up .............................. from the flower, and ............................... it to the next flower they visit. This is how most flowers are ..................................... Some plants have got ....................... flowers with no colour. This is because they are not pollinated by insects or other animals, but use the ................................ to blow their pollen grains to other plants. 11 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA The .................................... are the male reproductive organs. Each has got a thin .................... or filament with an ................................. at the end. Each anther is made up of pollen ......................, which contain grains of pollen. The pistil is the ........................................ reproductive organ where the .......................... are made. It has got three parts The ............................. is the receptor of pollen, and is covered in a ....................... substance. The style is the stalk that ..................................... the stigma and is the way for pollen ........................ The ................................ contains one or more tiny bodies called ............................ or “eggs”, each of which contains a female gamete. Answer the following questions 1. What is the name of the part that joins the flower to the stem?............................................................................... 2. What is the calyx made of ?..................................................................................................................................... 3. What is the name of the little coloured leaves that make the corolla?..................................................................... 4. Why is the corolla brightly coloured?....................................................................................................................... 5. How is the pollination of a flower with a non-coloured corolla?............................................................................... 6. What is a stamen?.................................................................................................................................................. 7. What does an anther contain?................................................................................................................................. 8. How many parts has the pistil got?.......................................................................................................................... 9. Why is the stigma covered with a sticky substance?............................................................................................... 10. What is the name of the tiny bodies that an ovary contains?................................................................................... 11. What does the pollen join the ovary with?................................................................................................................ 12. What does the ovule become when the male gametes joins it? ............................................................................. TTH HE ER RE EP PR RO OD DU UC CTTIIO ON NP PR RO OC CE ES SS S P Poolllliinnaattiioonn It is the transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of another flower. There are two kinds of pollination: Through the wind or through animals. W Wiinndd ttrraannssppoorrtt. The plant must produce a lot of pollen and the wind transports them. A Anniim maall ttrraannssppoorrtt. Insects carry pollen in their legs or bodies and take it to other flowers FFeerrttiilliissaattiioonn The grain of pollen gets the pistil of a new flower. It sticks the stigma and forms a pollen tube. The tube grows down through the style and enters an ovule. There the male and female gametes fuse together. Then the fertilised ovule becomes a seed. Afterwards the calyx and the corolla dry and fall, the ovary ripens into the fruit. The ovules are transformed into seeds inside the fruit. The fruit job is to protect the seed and help its dispersal carrying the seed or seeds. D Diissppeerrssaall oorr ddiisssseem miinnaattiioonn When fruits or seeds are mature, they split from the plant and scatter, or releases the seeds. The fruits and seeds are scattered by animals, by the wind, and by the water. This process is called dispersal. G Geerrm miinnaattiioonn When the environment conditions are right, the seeds germinate on the ground: The seeds swell and break and the embryo begins to grow into a new plant. 12 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA (Vocabulary: Afterwards: posteriormente / to enter: entrar / to fuse: fusionarse / to dry: secarse / to ripen: madurar / to scatter: esparcir / dispersal: dispersión / to split: separse / to release: liberar, soltar / environment conditions: condiciones ambientales / to swell: hincharse / to grow: crecer / to germinate: germinar / to become: convertirse) Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 2 3 4 5 6 Wind transport Pollination Germination Animal transport Dissemination Fertilisation A B C D E F It is the transfer of pollen from a flower to another . The plant must produce a lot of pollen. It takes place when fruits or seeds are mature The pollen tube grows down through the style and enters an ovule The seeds swell and break Insects carry pollen in their legs or bodies Answers: 1 .............. 2 ............ 3 ............. 4 ............. 5 ............. 6 ............. Put the names of the following numbers of the life cycle of a flowering plant 13 DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA Y GEOLOGÍA I.E.S. LLANES SEVILLA Answers: 1 .................................... 2 ...................................... 3 .................................... 4 .................................. 5 ...................................... 6 ............................................. 7 ....................................... 8................................... 9 .................................... 10 ........................................... Answer the following questions 1. What is the female organ of a flower called? a) The sepal b) The pistil c) The stamen 2. What do the stamens do? a) They attract insects c) They make pollen b) They provide food for insects 3. The movement of pollen from the stamens to the pistil has a special name. What is this? a) Pollination b) Fertilisation c) Germination 4. Which of these sentences is true? a) After pollination, the pollen grains break down into the pistil b) All flowers are pollinated by insects c) All flowers are pollinated by pollen of different flowers 5. When an ovule is fertilised, it turns into: a) A bud b) A leaf c) A seed 6. Which of these sentences are not true? a) Animals eat seeds and deposit them in other places b) The wind blows the seeds. c) Some seeds grow legs and walk. 7. What is the main job of petals? a) To attract insects. b) To provide food for insects 8. Which of these is the correct order or the life cycle of a plant? a) Pollination – germination – fertilisation - seed dispersal b) Germination – fertilisation - seed dispersal - pollination c) Germination – pollination – fertilisation - seed dispersal 9. What will happen if plants and animals don’t reproduce? a) Plants will occupy the whole world b) All life on Earth die out in the end c) All living beings will just get older and older 14 c) To make pollen