* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
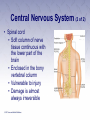
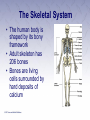
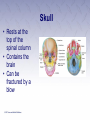
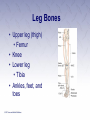
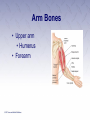
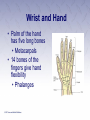
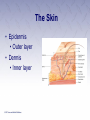
Chapter 3 The Human Body The Human Body • First aider must be familiar with the basic structure and functions of the human body. • By using proper terms, you will be able to better communicate with medical care providers. The Respiratory System (1 of 2) • Death will result in about 4 to 6 minutes unless the oxygen intake is restored. • Oxygen is made available to the blood through the respiratory system. The Respiratory System (2 of 2) • Nose • Pharynx and trachea • Lungs Mechanics of Breathing • Respiration • Passage of air into and out of the lungs • Inhalation • Breathing in • Exhalation • Breathing out Infants and Children • Infants and children differ from adults. • Respiratory structures are smaller and more easily obstructed. • Tongues take up more space in the mouth. • Trachea is more flexible. The Circulatory System • Blood • Heart • Blood vessels Heart • Pumps blood through blood vessels • Powerful, hollow, muscular organ as big as a fist Blood Vessels (1 of 3) • Arteries • Elastic, muscular tubes that carry blood away from the heart • Begin at the heart as two large tubes • Pulmonary artery • Aorta • Divides into capillaries Blood Vessels (2 of 3) • Pulse • Surge of blood that occurs each time the heart contracts • Can be felt at any point where an artery lies close to the surface of the body • Major locations include: carotid, femoral, radial, brachial, posterior tibial, dorsalis pedis arteries Blood Vessels (3 of 3) • Blood pressure • Measures of the pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the flexible arteries • Might be high or low according to the resistance offered by the walls to the passage of blood Blood • Plasma • Liquid part of the blood • Carries food materials and waste materials • Platelets • Essential for the formation of blood clots The Nervous System • A complex collection of nerve cells that coordinate the work of all parts of the human body • Keeps the individual in touch with the outside world • Neurons receive stimuli from the environment and transmit impulses to nerve centers in the brain and spinal cord. Central Nervous System (1 of 2) • Brain • Headquarters of the human nervous system • Divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem Central Nervous System (2 of 2) • Spinal cord • Soft column of nerve tissue continuous with the lower part of the brain • Enclosed in the bony vertebral column • Vulnerable to injury • Damage is almost always irreversible Peripheral Nervous System • Consists of the sensory and motor nerves • Carry sensations such as smell, touch, heat, and sound from the body to the brain and the spinal cord Autonomic Nervous System • Consists of a group of nerves that control heart rate, digestion, sweating, and other automatic body processes • Processes are not controlled by the conscious mind The Skeletal System • The human body is shaped by its bony framework • Adult skeleton has 206 bones • Bones are living cells surrounded by hard deposits of calcium Skull • Rests at the top of the spinal column • Contains the brain • Can be fractured by a blow Spinal Column • Made up of vertebrae • Bound together by ligaments • Intervertebral disks between every two vertebrae Thorax • Also known as the rib cage • Made up of ribs and the sternum • Lowest portion of the sternum is the xiphoid process Pelvis • Two hipbones and the sacrum form the pelvis • Muscles help attach the pelvic bones, the trunk, the thighs, and the legs • Forms the floor of the abdominal cavity Leg Bones • Upper leg (thigh) • Femur • Knee • Lower leg • Tibia • Ankles, feet, and toes Shoulder • Formed by the collar bone (clavicle) and the shoulder blade (scapula) • Fractures are common Arm Bones • Upper arm • Humerus • Forearm Wrist and Hand • Palm of the hand has five long bones • Metacarpals • 14 bones of the fingers give hand flexibility • Phalanges Joint • Where two or more bones meet or join • Layer of cartilage acts as a buffer • Bones of the joint are held in place by ligaments The Muscular System • Skeletal Muscles • Smooth Muscles • Cardiac Muscles The Skin • Epidermis • Outer layer • Dermis • Inner layer