* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EVEN/ODD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
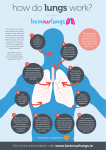
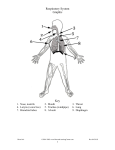
Name ____________________________________ PD _______ EVEN/ODD Body Systems – Part 2 Vocabulary – Lesson 5 1. plasma – 2. hemoglobin – 3. carbon dioxide – 4. antibodies – 5. platelets – 6. atrium – 7. ventricle – 8. lymph – Notes – Lesson 5 – Circulatory System 1. What is your blood? a. 1 gallon (_____liters) of blood in your body b. It circulates through your body over and over and never stops moving c. Body cells take from your blood what they need and send their wastes to be taken away d. Most of the red blood seen with a cut is made up of a clear, lightyellow liquid called _________ i. Cells in the plasma give your blood the red color ii. Blood also contains 1. __________________________________ a. _______________________ – makes the cells red and picks up oxygen in lungs, carries it to the body cells b. When cells pick up oxygen the release carbon dioxide (CO2) to the hemoglobin – CO2 is a waste made by the cells c. Blood has more red blood cells than any other kind – 60,000 would fit in the dot of an “i” d. RBC looks like a doughnut with the hole filled in 2. __________________________________ a. largest cell b. actually have no color c. help fight disease by destroying germs (_________________) d. different kinds of WBC that defend the body in different ways i. some destroy disease causing microbes ii. some make antibodies that attack and destroy microbes so that they cannot make you ill again iii. made in lymph 3. __________________________________ a. platelets help your blood become ____________ by sticking to the walls of injured blood vessels b. other cells are trapped making a clot that closes the torn vessel c. scabs are dried clots 4. Plasma – light yellow liquid 2. Heart a. Hollow, muscular and about the size of your ________________ b. A wall divides the right side from the left and each side has an upper and lower half (________ chambers) c. Upper chamber – _________________ d. Lower chamber – _________________ e. Right ventricle pumps blood to lungs to get __________________ and give off ________________________________ f. Left ventricle pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of your body where the cells take the oxygen from the blood and give carbon dioxide g. Blood flows back to the atrium on the __________________ side of your heart 3. Blood Vessels a. _____________________ – carry blood __________ from your heart i. thick, flexible muscle walls to stand pressure of blood being pumped out of the heart b. ____________________ – carry blood ________________ your heart i. thinner walls than arteries because the pressure of blood is lower in veins ii. they have small flaps in veins keep blood flowing in 1 direction c. ____________________ – thin blood vessels that connect arteries to veins i. very thin walls ii. every tissue has these next to it iii. nutrients, oxygen, and wastes pass in and out through capillary walls iv. plasma also passes through walls d. _____________________ – excess plasma, plus tissue fluid that surrounds body cells, colorless (blister) i. carries cell wastes and other materials ii. lymph tissue also produces a kind of white blood cell Review – Lesson 5 1. What are two main kinds of cells in blood? 2. How do white blood cells help fight disease? 3. What are the chambers of the heart called? Vocabulary – Lesson 6 – Respiratory System 1. trachea – 2. bronchial tubes – 3. alveoli – 4. inhalation – 5. exhalation – 6. breathing – 7. diaphragm – Notes – Lesson 6 1. Organs that help you breath make up the respiratory system – draws air into your lungs, takes _____________ from the air for your body to use, helps remove ________________________________ 2. How does air travel to your lungs a. Air comes into your body through your nose and mouth b. It then enters your throat (pharynx) to your voice box (larynx) c. From this point it moves through a pipe called the trachea, or ______________________ d. The trachea is divided at the end into 2 branches called bronchial tubes or bronchi e. Air moves into your lungs through these tubes, which branch into smaller tubes (_______________________), which lead to tiny air sacs called _______________________ f. In the lungs (sponge like) i. Air you breathe in fills up the alveoli ii. Oxygen passes from the ________________ into the ____________________ iii. RBC in the capillaries pick up the oxygen iv. Your blood takes the oxygen to the rest of your cells g. Deoxygenated blood i. Blood delivers _________________ and picks up ___________________________ given off by your cells ii. Carbon dioxide moves through the body to the capillaries in the alveoli and into the lungs iii. It then leaves the body when you breathe out 3. The breathing process a. ________________________ – moving air in and out of the lungs b. Breathing involves both ________________ and ________________ c. _________________ – is the process in which the air enters the lungs d. _________________ – is the process in which the air leaves the lungs e. Inhalation occurs when the diaphragm contracts and the rib cage expands f. _________________– is a muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen, helps to also force air out of the lungs 4. How does your body clean the air you breathe? a. Hairs in your nose being the cleaning by screening out some particles b. Sticky ____________________ traps more i. this lines your nasal passages and the walls of your trachea and bronchial tubes ii. it may trap germs and other harmful matter c. Trachea and bronchial tubes have tiny hairs called _______________ i. Cilia wave quickly back and forth and push mucus that has trapped dirt and dust up toward your __________________ d. When you swallow, much of the mucus passes into the _____________________________________ Review – Lesson 6 1. What does your respiratory system do? 2. What is the job of the alveoli? 3. How is the air you breathe cleaned by the respiratory system? Vocabulary – Lesson 7 – Nervous system 1. neurons – 2. cerebrum – 3. cerebellum – 4. hemispheres – 5. brain – 6. spinal cord – 7. nerve – 8. reflex – Notes – Lesson 7 1. The nervous system _________________all the ___________ in your body 2. What do your nerve cells and nerves do? a. Cells of your nervous system are called nerve cells, or ____________ i. Neurons have long branches that come out both ends ii. They are long and thin iii. Bundles of neurons make up nerves b. nerves receive and send messages c. some carry messages to the brain to let it know what is happening in and around your body – ____________________ d. others carry messages from the brain to muscles, telling muscles what to do – __________________________ 3. How does your brain work a. The brain is the “___________________________” of the body b. Always receiving messages and sorts them out looking for meaning, then tells the body what to do c. 3 main parts i. ___________________ – largest part, where most thinking takes place, solves problems, forms emotions (feelings), makes decisions, and controls how you learn, receives and answers messages from senses 1. divided into 2 halves called ____________________, each side responsible for different tasks 2. 2 halves connected by the _________________________ 3. right side deals with imagination and the arts 4. left side deals with words and facts, math 5. both are always working ____________________ ii. _________________ – the part of the brain that makes muscles work together, helps move and keep balance, cerebellum directs most movement without you thinking about it iii. __________________ – lowest part of the brain, messages moving between brain and the rest of the body pass through he brain stem 1. ________________________ takes care of critical life functions – breathing, heartbeat, swallowing, blood vessels, controls inner organs 4. What is the job of your spinal cord? a. Starts at the __________________ of the brain, main path for messages entering and leaving the brain b. Surround and protects spinal cord connecting nerves to brain c. Sudden actions that are done without thinking are ______________ Review – Lesson 7 1. What does your nervous system do? 2. How are sensory and motor nerves different? 3. What are the jobs of the cerebrum? 4. How are the hemispheres of your brain able to exchange nerve messages?