* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systems in Plants - RosedaleGrade10Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
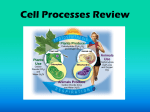
SNC2D: Biology – Cells, Tissues and Systems Tissues Working Together (pp. 136-139) A plant leaf is made up of a system of tissues, each with its own specific structure and function. The structure and location of the tissues are connected to their function. For photosynthesis, plants need to (1) absorb light, (2) obtain carbon dioxide and (3) obtain water. Absorbing Light: Leaves are green and thin – Green – colour of chlorophyll, pigment that absorbs light for photosynthesis Thin – wide and thin leaves have greater surface area for absorbing light Chlorophyll is contained in the organelles called the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are located mostly in the ground tissue system, composed of the palisade layer and spongy mesophyll. Palisade layer – closely packed, located near upper surface to capture maximum light Spongy mesophyll – loosely packed, permits gases to move around in the leaf Obtaining Carbon Dioxide: Cuticle – the layer of wax that covers the top and bottom surfaces of a leaf This keeps the leaf from drying out since gases and water can’t pass through. Stomata (singular – stomata) – tiny openings on the lower epidermis (lower leaf surface), allow gas exchange and the release of water vapour. Stomata are located on the lower surface to (1) reduce water loss, (2) provide more surface area for photosynthesis, and (3) reduce chances of viruses, bacteria or fungal spores from entering the leaf. Guard Cells - dermal cells that surround and control each stomata in a leaf SNC2D: Biology – Cells, Tissues and Systems Obtaining Water: Water loss in a leaf is reduced by the waxy cuticle, and by closing the stomata when water levels are low. Root hairs - absorb water from soil by osmosis. Xylem and Phloem – vascular tissues arranged as bundles and run through the plant from root to leaf. Water is transported by xylem from the roots, up the stem, through the leaves. Comparing Plant and Animal Systems Although plants and animals are very different organisms, there are some similarities at the cellular level, as well as at the system level: Cellular level: Both animal and plant cells use sugar and oxygen in the process of respiration, and release carbon dioxide and water. System level: Animals and plant cells both possess systems that must work together to accomplish complex tasks, in particular, the fluid circulation systems. Task Obtaining food and transporting it within the body Animal organ systems Nervous, musculoskeletal systems are involved with obtaining food Plant tissue systems Entry of carbon dioxide is controlled by cells in the dermal tissue system Digestive system processes food Ground tissue system in leaves produces the plant’s own food In the circulatory system, blood vessels transport all digested food nutrients Vascular system transports sugars and other complex compounds in phloem.