* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra I Key Understandings
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
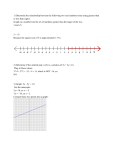
Name _____________ Mr. Schlansky Date _________________ Algebra I Algebra I Key Understandings Can I put this into the calculator?! Pre-Algebra Adding/Subtracting: -If same sign, add the numbers and keep the sign -If different sign, subtract the numbers and take the sign of the bigger number Multiplying/Dividing: -If same sign, the answer is positive -If different signs, the answer is negative Absolute value is the distance from 0, distance is always positive. Rational numbers are organized, irrational numbers are crazy! Order of Operations: PEMDAS Scientific Notation: -Decimal must go after the first non 0 digit that you see looking from left to the right -Count how many places the decimal has moved -A very LARGE number as a positive exponent, a very TINY number has a negative exponent Operations with Scientific Notation: Type into calculator (2nd EE) Number Properties: 2(4 + 3) = 2 4 + 2 3 Distributive Property 4 6 = 6 4 Commutative Property of Multiplication 2+7=7+2 Commutative Property of Addition 5 + (2 + 3) = (5 + 2) + 3 Associative Property of Addition 5 (4 3) = (5 4) 3 Associative Property of Multiplication 4+0=4 Additive Identity 7 1 = 7 Multiplicative Identity 5 + -5 = 0 Additive Inverse 1 4 = 1 Multiplicative Inverse 4 3 0 = 0 Multiplication Property of Zero *ASSociative property has two sets of parenthesis *Commutative property has numbers commute (move) *Identity is where you start and end with the same thing *Inverse is when you end up with the identity element (Addition 0, Multiplication 1) Additive Inverse: Negate every term Multiplicative Inverse: Find the reciprocal (flip) Equation Solving 1) Get rid of fractions (Cross multiply or multiply by the LCD) 2) Get rid of parenthesis (Distribute) 3) Combine like terms on each side 4) Bring all variables to one side 5) Isolate variable by proceeding in the reverse order of operations (add/subtract first) Writing Equations/Inequalities -less than and subtracted from: switch the order in which you see the terms -is less than and is more than are inequalities -quantity means parenthesis In terms of x: -When given something is less than, more than, twice, etc. of something else, call something x and express everything else in terms of x. -Consecutive integers are one apart (x, x + 1) -Consecutive even and odd integers are two apart (x, x + 2) Solving Inequalities: < less than open circle shade left closed circle shade left less than or equal to > greater than open circle shade right closed circle shade right greater than or equal to Multiple Choice: The answer must be in the solution set *When multiplying or dividing by a negative in an inequality, switch the inequality! Polynomials Adding: Combine like terms Subtracting: Distribute the negative and then combine like terms (Keep Change Change) *Subtracting from: from comes first! Multiplying: Distribute/FOIL Dividing: Divide every term in the numerator by the denominator Exponents Multiplying: Add exponents x 2 x3 x 2 3 x5 x8 x 8 5 x 3 5 x When raising a power to a ppwer, multiply exponents: ( x 2 ) 3 x 23 x 6 x0 1 Anything to the zero power is equal to 1 1 x 2 2 Negative exponents are fractions! x Drop what is being raised to the negative power Dividing: Subtract exponents: 3 If exponent is outside parenthesis, everything gets it x3 y3 xy z3 z Rates Express rates as fractions and divide! When given a rate in a word problem, set up a proportion! When you see direct variation, set up a proportion! To compare rates, find each rate, the higher/faster rate is the higher number Percents/Error part percent whole 100 amount of change percent Percent of change: original 100 | actual measured | Relative Error: , calculate the actual and measured if necessary! actual When given a percent: Geometric Measurements Area: Rectangle: A=l w 1 Triangle: A = l w 2 2 Circle: A r 1 Trapezoid: A h(b1 b2 ) (On Reference Sheet) 2 Perimeter: Add all sides Circle: C d Basketball Court Problems (Irregular Shapes): 1 1 circle is r 2 ) 2 2 1 1 Perimeter: Add up all outside pieces of the shape ( circle is d ) 2 2 Area: Add area of each individual shape together ( Radicals Write out your list of perfect squares To reduce radicals: 1) Separate into perfect squares and non-perfect squares radicals 2) Take square root of perfect squares 3) Multiply outside numbers if necessary Adding/Subtracting: Reduce each until they have the same radical, then add/subtract coefficients Multiplying/Dividing: Multiply/Divide first! Then reduce! Multiple Choice: Type original problem into calculator, type each answer in, and see which matches up. Right Triangles If only sides are involved, use Pythagorean theorem! ( a 2 b 2 c 2 ) If an angle is involved, use SOHCAHTOA 1) Label each side with O, A, and H 2) Determine whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent 3) Substitute into equation *If finding a side, cross multiply and solve *If finding an angle, use sin 1 , cos 1 , or tan 1 Sets and Functions -Intersection is elements in every (both) sets -Union is all together (elements in either set) -Complement is everything else (every element not in the subset) Set Notation: (a,b] = a x b (All numbers between a and b) -A function is when each x value “talks” to only one y value (x does not repeat) -A graph is a function if it passes the vertical line test (no line can touch twice) Absolute Value Graphs: y =|x| + A move up A units y =|x| - A move down A units y =|x + A| move left A units y =|x - A| move right A units y = -|x| Flip the graph (upside down) y =a|x| Stretch or squeeze the graph (a is the slope) Types of Functions Exponential: Absolute Value y y x x Linear: Quadratic y y x x Coordinate Geometry: -Standard form of a line is y = mx + b, m = slope, b = y intercept -To graph a line, find slope and y intercept by ISOLATING y OR type into y = -To graph a parabola, type into y = and look for a mirror image in your table -Yanci Has X-Ray Vision (YHXV), y = # is horizontal line, x = # is vertical line rise y -Slope = , count boxes on graph, positive slope is uphill, negative slope is down hill run x -Parallel lines have the same slope, x = # is parallel to y-axis, y = # is parallel to x-axis -To write the equation of a line through a point: rise a) find slope (use if necessary) run b) substitute values into y = mx + b to find y intercept -To solve a system of equations graphically, find the point of intersection. -To solve a system of inequalities: < : shade below dashed line : shade below solid line >: shade above dashed line : shade above solid line The solution set is the region that both graphs are shaded. Mark with an S. -To solve a system of equations algebraically: 1) Choose a variable to cancel and multiply each equation by the other’s coefficient *multiply by negative if they are the same sign 2) Add equations together 3) Solve equation for one variable 4) Substitute answer in to either equation to find the second variable Parabolas: -The vertex is the turning point of a parabola and the middle point in your table of values - The roots are where the graph crosses the x-axis and where y is equal to zero -The roots are the answer to the quadratic equation b -Axis of symmetry = 2a Factoring/Rational Expressions -Is there a Greatest Common Factor? Divide by GCF and put GCF outside parenthesis –Is there Difference of Two Squares? Two parenthesis, opposite signs, take square root of each – -Is there a Trinomial? 1) First sign comes down 2) Second sign determines the second sign (+ is same sign, - is different signs) 3) Look for two numbers that multiply to the last number and add/subtract to middle number -Can it be factored further? -Undefined: Set the denominator equal to zero -Reducing/Multiplying: FACTOR MARRIED TERMS, Reduce single terms, write out exponents -Dividing: Keep/Change/Flip and then follow the rules of multiplication -Adding and Subtracting: Find a common denominator -To find a common denominator: Put all of your factors together Probability: Probability of an event = # of possible successes # of possible outcomes Probability of multiple events: multiply probabilities of each If choosing a certain # out of a certain #: n C r or n Pr (PERMUTATIONS POSITIONS, COMBINATION COMMITTEES) Word Permutations: If same # of letters: (number of letters)!, If different # of letters: n Pr Statistics: Scatter Plots: Positive slope is a positive correlation, negative slope is negative correlation, 0 slope is a 0 correlation, and if there is no line of best fit, there is no correlation. To find measures of central tendency: Type into Stat: Edit, Stat: Calc:1 – Var Stats L 1 , L 2 Range = max – min, Mode is the number with the highest frequency Box and Whisker Plot: Need min, Q1, Med, Q3, and max, box connects the quartiles Histograms: Cumulative frequency means add up the frequencies, make each bar the same width, use a lightning bolt if the first interval is not 0 and label! Causal relation is when one variable causes the other to happen Univariate data has one variable involved while bivariate data has two variables involved An unbiased sample is completely random and should have no influence on the topic Qualitative has to do with quality(opinions and evidence of knowledge), quantitative has to do with quantity(facts). Miscellaneous: --Solving for x/finding the roots: Follow the mr. x 2 story: Everybody comes to mr. x 2 ’s house to party, once everyone comes over, they party with bubbles. (Bring everything to one side and factor). Don’t forget to set each factor equal to zero! Interest/Depreciation Problems: A P(1 r ) t , where A is the current amount, P is the initial amount, r is the rate as a decimal, and t is time.