* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
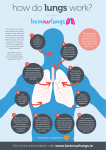
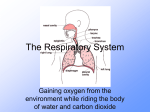
Respiratory System The function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the blood so it can be delivered to cells. Then, take the carbon dioxide out of the blood and release it from the body. Breathing is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs. The Diaphragm is the muscle that controls breathing. When we inhale the diaphragm flattens out and the rig cage moves up and out. This allows for the lungs to expand as they fill up with air. When we exhale, the diaphragm moves upward. This forces the air out of the lungs. The ribcage moves back down. Respiration Respiration is the process of creating energy in the mitochondria of the cells. Glucose and oxygen are needed for respiration to occur. The glucose is absorbed by the villi in the small intestine and put into the blood stream. Oxygen diffuses through the walls of the alveoli and capillaries and into the blood stream. Both are delivered to the body cells where they are turned into energy. The outcome of respiration is energy, carbon dioxide, and water. The cell uses the energy, and both carbon dioxide and water diffuse into the blood stream. The carbon dioxide is brought to the lungs where it can be exhaled while the extra water is removed by the kidneys. Organs of the Respiratory System Nasal Cavity- Air enters and is filtered by the nose hairs and mucus to remove any foreign particles. Pharynx- the throat. Both the nasal cavity and the mouth enter in the pharynx. The pharynx leads into the esophagus and the trachea. Epiglottis- a flap of tissue that covers the larynx to stop food from entering. When a person breathes the epiglottis opens and allows the air to enter. Larynx- located at the top of the trachea. This is where the vocal cords are located. Trachea- also known as the windpipe. The trachea is lined with cartilage rings that prevent it from closing up. It also contains mucus and cilia to prevent foreign substances from entering the lungs. Cilia are tine hairs that move the particles upward into the pharynx. Bronchi- The trachea branches into two bronchi (bronchus-singular). Each going to a lung. Bronchioles- Each bronchus branches into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles. Alveoli- Each bronchiole ends at a cluster of air sacs called alveoli(alveolus-singular). Each lung is made up of 300,000,000 alveoli. These alveoli are surround by capillaries. Oxygen will diffuse through the alveolus and capillary walls into the bloodstream. Carbon dioxide will diffuse out of the blood through the capillary into the alveolus, where it can be exhaled. Pleura- The outer protective covering of the lungs. Respiratory System Problems Chronic bronchitis- Bronchial tubes get irritated and too much mucus is produced. The more the person coughs the more the cilia can be damaged and they are unable to move mucus, dirt and other particles. This occurs from smoking. Emphysema- The aveoli lose their ability to expand and contract. Bronchi become inflamed and the cells release an enzyme the cause the aveoli stretch and lose their elasticity. As a result, the aveoli cannot push air out of the lungs. Therefore less oxygen is taken in and not as much carbon dioxide can be released. Blood becomes low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide resulting in a shortage of breath. Most cases of emphysema are caused by smoking. Lung cancer- tar and other ingredients in cigarettes can change the DNA in cells and trigger uncontrollable growth of these abnormal cells. Asthma- The muscles of the bronchiole tubes tighten causing the bronchiole to get smaller causing your lungs to take in less air. Mucus production also increases.