* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systems of Equations and Inequalities
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
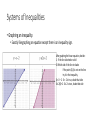
Systems of Equations and Inequalities Graphing Systems of Equations Solving Systems by Substitutions Solving Systems by Eliminations Solving Systems by Elimination using multiplication Applying Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Inequalities Graphing Systems of Equations • The goal is to find a value for x and y that make two equations true. Example • y = 3x - 1 • x+y=7 • step 1 Graph each equation • step 2 Notice the point of intersection • step 3 Find the coordinates of the point of intersection. • What do these coordinates mean? Solve Systems by Substitution • Think about parallel lines. If your two equations are parallel lines you will either have infinitely many solutions or no solutions. • Example: The sum of the measures of angles X and Y is 180 (They are supplementary). The measure of angle X is 24 greater than angle Y. • Equation one. “The sum of X & Y is 180”: x + y = 180 • Equation two. “Angle X is 24 greater than y”: x = 24 + y • Since we have x equal to something, we can substitute what x is equal to in the first equation. • (24 + y) + y = 180: notice how x is now 24 + y • 24 + 2y = 180. Solve for y: 156 = 2y; y = 78. • Now we can substitute 88 for y in either x = 24 + y or x + y = 180 • Either we get x = 24 + 78; x=102 Or we get x + 78 = 180. x = 102 Elimination using Addition and Subtraction • You can add or subtract equations with each other. • x+y=4 • x–y=8 • 2x = 12: x = 6 When we substitute 6 for y what does y equal? • Subtract • x + 4y = -4 • - x + 10y = -16 • -6y = 12: y = -2 Notice 4 – 10 = -6 and - 4 – (-16) = 12 Elimination using Multiplication • Prior to adding equations together, you can multiply an entire equation by a constant. • x + y = 2 We will take this equation and multiply by 3 • -3x + 4y = 15 • 3x +3y = 6 • 7y = 21 • There are instances where you may need to multiply 2 equations by a constant. • 8x + 3y = -7 • 7x + 2y = -3 Applying Systems of Linear Equations • Manuela has a total of 40 DVDs of movies and television shows. The number of movies is 4 less than 3 times the number of television shows. Write and solve a system of equations to find the numbers of movies and television shows that she has on DVD. Another word problem • An online music club offers individual songs for one price or entire albums for another. Kendrick pays $14.90 to download 5 songs and 1 album. Geoffrey pays $21.75 to download 3 songs and 2 albums. • How much does each song cost and each album? Systems of Inequalities • Graphing an inequality. • Exactly like graphing an equation except there is an inequality sign. After graphing the linear equation, decide: 1: If the line is dotted or solid 2: Which side of the line to shade If the point (0,0) is not on the line try it in the inequality. 0 > 0 – 2: 0 > -2 is true, shade that side 0 ≤ 2(0)+2: 0 ≤ 2 is true, shade that side Solution sets of systems of inequalities • Graph each inequality with the proper shading. • Look to see where there is an intersection of regions. • That intersection is the solution region. Try these systems • Y > -x • Y < 2x + 5 5x – y ≥ 3 2x – 4y < 1