* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers to Grade 7 - 1.2 and 1.3 in Student Book
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
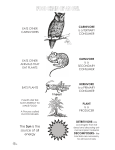
1.2 The Roles of Producers (See Student Book pages 17–23) How Producers Use the Sun’s Energy Sunlight is an important abiotic element in most ecosystems. Sunlight enables photosynthesis to take place. Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that uses sunlight to produce food for plants. • Carbon dioxide from the air combines with water from the roots to make food (a type of sugar) and oxygen. • The food is stored in the plant, and the oxygen is released back into the air. • Animals, including humans, use the oxygen that plants produce during photosynthesis. Write the labels below in the correct place on the diagram. • Carbon dioxide from the air enters the leaf. • Sunlight shines on the leaf and brings heat and light energy, causing a chemical reaction. • A sugar called glucose is produced. • Oxygen is released from the leaf. • Water and nutrients from the soil come to the leaf through the plant stem or trunk. Sunlight shines on the leaf and brings heat Note: “photo” means light and “synthesis” means to combine things together. So, “photosynthesis” means using light to combine different materials. and light energy, causing a chemical reaction. A sugar called glucose Carbon dioxide from the is produced. air enters the leaf. Oxygen is released Water and nutrients from from the leaf. the soil come to the leaf through the plant stem or trunk. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves of plants. It uses light energy from the Sun. Key Term photosynthesis: a chemical reaction that takes places in plant leaves and changes sunlight into food for the plant Producers’ Roles Plants are considered producers. Producers can make their own food. This food supplies the energy the plants need to survive. Producers have three main roles: • they provide oxygen • they provide a place to live • they supply food Note: Think about where your food comes from. For example: french fries— potatoes that grow on farms; pizza—flour crust that comes from wheat grown on farms; toppings are fruit, vegetables, and meat—all from farms (not from supermarkets!). This garden is a place where living things can feed and live. Circle the producers in the above illustration. Most living things have to eat in order to get energy. Many living things eat only plants. Others eat the living things that have eaten the plants. The producers are the beginning of all food interactions. Circle the homes you see in the illustration. Plants provide homes for many animals. A tree can die and become an abiotic part of the system. Even then, it can still provide a home for living things. In a pond, fish shelter under the plants that grow there. Interactions in Ecosystems Interactions happen throughout ecosystems. Plants take in energy from the Sun and water and nutrients from the soil. Animals eat plants Plants provide homes for animals. and other animals, find shelter, and find water. Interactions can be helpful or harmful to living things. When a bee buzzes from flower to flower, the bee gets food and the flower is able to produce new seeds. When a spider eats a fly, the fly dies, while the spider gets energy. Key Term producer: a plant or plant-like living thing that can make its own food to provide it with the energy it needs to survive Section 1.2 3 Populations and Communities Biotic parts of communities are easier to study if you know the words you can use to discuss them. The table shows the words used to describe different groups in an ecosystem. Term Relationship to Ecosystem Example Species Closely related group of living things. • Mallard duck in a pond They can produce babies and their • Willow tree at the edge of children can produce babies when the pond they become adults. Population A group of the same type of living things living in the same place. • All the ducks living near the pond • All the water lilies on the surface of the pond Community All the different populations of different species that live and interact in a habitat. • The duck, fish, all the plants, the soil, rocks, and water of a pond Think of a wooded area or a park near where you live. What makes up the community of living things that exist in that area? Name four species in that area. plants of various kinds, trees, raccoons, squirrels, birds, insects Name four populations of living things in that area. dandelions, maple trees, raccoons, squirrels, Canada geese, mosquitoes Use the above living things to write three sentences that describe the community. Be sure to include the abiotic factors as well in your description. The following kinds of descriptions are possible: Insects breathe the air, live in the bark of trees, and eat leaves. Birds breathe the air, live in nests, and eat small insects. Squirrels breathe the air, live in hollows or nests in trees, and eat nuts. Note: Have students transfer the information in the table to their notebooks using the first and third columns and using drawings for the third column instead of words. Have them add one or two examples of their own of species and population. This will help you assess their understanding of these concepts. Section 1.2 4 1.2 Check and Reflect 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct words so that the paragraph describes how plants work. carbon dioxide photosynthesis oxygen Sun producers food Plants are producers because they can use energy from the Sun to make their own food . During the process of photosynthesis they take carbon dioxide out of the air and they put oxygen back into the air. 2. Read the following statements about producers. If they are true, circle T; if they are false, circle F. (a) Producers supply oxygen. T F (b) Producers destroy food. T F (c) Producers supply minerals. T F (d) Producers supply shelter. T F 3. Which of the following is not involved with the process of photosynthesis? (a) sunlight (b) habitat (c) carbon dioxide (d) sugar 4. Plants provide a number of necessary elements in an ecosystem. Which do they not provide? (a) shade (b) heat (c) oxygen (d) shelter 5. Which living thing found around a pond is not a producer? (a) lily plant (b) willow trees (c) pond snails (d) reed sweet grass 6. Which statement about the role of producers in supporting life on Earth is true? (a) Producers provide many things, but they do not provide shelter. (b) Producers use oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere to produce carbon dioxide and sugar. (c) Producers are green because their leaves contain large amounts of oxygen. (d) Producers are the only organisms that can use the Sun’s energy to make food. 1.2 Check and Reflect 5 1.3 Producers and Consumers (See Student Book pages 24–30) Types of Consumers All animals are consumers. Consumers are living things that cannot make their own food. They must eat, or consume, other living things in order to survive. We describe consumers by what they consume. Look at the table below to find three types of consumers and the type of food each consumes. Type of Consumer Food Eaten Examples Herbivores Plants Deer, Canada goose Carnivores Meat Hawk, polar bear Omnivores Meat and plants Raccoon, pig Predators and Prey Animals that eat other animals must hunt for their food. An animal that hunts for its food is a predator. Wolves, hawks, and Great Blue Herons are predators. An animal that is hunted by a predator is the prey. Any animal eaten by another animal is the prey. A Great Blue Heron is a predator. It catches and eats fish as its prey. Draw lines from the predators to their prey. cat mosquito bird fish spider mouse bat worm sea lion fly Special Consumers All living things die. After they die, they are taken care of by a special group of consumers. These consumers feed on dead material and waste produced by living things. There are three main types of these special consumers: • scavengers • detritivores • decomposers Key Terms consumer: a living things that eats (feeds on) other living things predator: an animal that hunts another animal for food prey: an animal that is hunted by another animal 1.2 Check and Reflect 6 Note: “detritus” is a term for waste produced by plants and animals. It is combined with a Latin word, vorare, which means to devour. A detritivore is a consumer that devours waste left by plants and animals. Vultures and crows are scavengers. Scavengers feed off animals that are already dead. Without scavengers there would be dead bodies lying all over the ground in every ecosystem. Why would you call a crow a scavenger? A crow serves a useful purpose in ecosystems. It feeds off dead animals. An earthworm is a detritivore. Detritivores feed off waste products from other living things and dead insects. Waste products allow the earthworm to get the nutrients it needs. It then produces waste that is returned to the soil, improving the quality of the soil for plants. A mushroom is a decomposer. Decomposers are living things that break down waste products and dead plants and animals into smaller pieces. Bacteria are also decomposers. Without decomposers, dead leaves, trees, and other plants would never disappear. Like detritivores, decomposers return good nutrients to the soil for plants to use. Earthworms feed off the wastes of other living things. Mushrooms are one of the types of decomposer that breaks down dead plant material. Worm—waste product and dead insect; Mushroom—leaf; Crow—dead insect Some special consumers help to get rid of dead things in ecosystems. Draw arrows from each of the special consumers to the thing it consumes. Key Term decomposer: a living thing that breaks down dead plants, animals, and waste products into smaller pieces Section 1.3 7 Food Chains All animals need to eat in order to survive. Look how the wolf below gets the energy it needs. small plants (sedges) caribou wolf The wolf is a carnivore and it eats the caribou to get the energy it needs to survive. The caribou is a herbivore and eats small grasses and other plants to get the energy it needs to survive. This feeding relationship is called a food chain. A food chain is a way to show how each consumer gets energy. Food chains can be long or short, but they all begin with plants. Look at the living things below and use the blank lines under the pictures to create three food chains. All of these living things are part of food chains. plants rabbit fox grain chicken adult grass cow (milk) child Section 1.3 8 1.3 Check and Reflect 1. Beside each description, write the word that describes it. herbivore scavenger carnivore predator (a) an animal that eats meat carnivore (b) an animal that hunts other animals for food predator (c) an animal that eats dead animals but does not often kill them itself scavenger (d) an animal that eats plants herbivore 2. Read the following statements about organic matter. If they are true, circle T; if they are false, circle F. (a) A scavenger is not involved in recycling organic matter. (b) A decomposer is not involved in recycling organic matter. (c) A producer is not involved in recycling organic matter. (d) A detritivore is not involved in recycling organic matter. 3. A mushroom is an example of (a) a decomposer (b) a herbivore (c) a scavenger (d) a producer 4. A food chain always begins with the Sun and (a) a consumer (b) a decomposer (c) a herbivore (d) a producer T T T T F F F F . . 5. Your pet dog likes to eat meat, but he also enjoys nibbling on grass, garden peas, and berries. Based on what he eats, your dog is . (a) a herbivore (b) a carnivore (c) a decomposer (d) an omnivore 6. A Venus fly trap is a plant that catches and eats insects. It needs several hours of sunlight a day, like other plants. It can therefore be described as . (a) a herbivore and a carnivore (b) a producer and a scavenger (c) a carnivore and a producer (d) a decomposer and a producer Section 1.3 9