* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
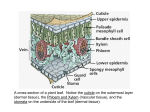
Chapter 35 List the characteristics of an angiosperm. The angiosperms are the flowering plants and are separated into two different classes, either the monocots or the dicots. Explain the differences between monocots and dicots. Monocots – one ctyledon, veins usually parallel, vascular bundles completely arranged, fibrous root system, floral parts in multiple of three Dicots – two ctyledons, veins usually netlike, vascular bundles arranged in a ring, taproot usually present, floral parts usually in multiples of four or five Describe the importance of root systems and shoot systems to plants and explain how they work together. Lacking chloroplasts and living in the dark , roots would starve without sugar and other organic nutrients imported from the photosynthetic tissues of the shoot system. Conversely, the shoot system depends on water and minerals absorbed from the soil by the roots. Describe how plant cells grow. Plants cells grow either through primary growth or through secondary growth. Distinguish between parenchyma and collenchyma cells with regards to structure and function. Parenchyma – thin alls and serve as storage, photosynthesis, and secretion Collenchyma – thick but flexible walls, serve mechanical support functions Describe the differences in structure and function of the two types of sclerenchyma cells. Fibers and sclereids. Some fibers are used commercially, such as hemp fiber for making rope. Sclerids are shorter and give fruit a gritty texture. Describe the functions of the dermal tissue system, vascular tissue system and ground tissue system. Dermal – general function is protection Vascular tissue system – in transport and support Ground tissue system – photosynthesis, storage and support Distinguish between the arrangement of vascular tissues in roots and shoots. In roots the vascular tissue is arranged in apical meristems located at the tips, lateral meristems develop in the shoots. Using a diagram, describe the basic structure of a root, a stem, and a leaf. Look at pgs. 204-206 in AP Review Book. Chapter 36 List three levels in which transport in plants occurs and describe the role of aquaporins. Cellular, Organ and whole-plant levels. Define water potential. Water potential – solute concentration and pressure are incorporated into this single measurement Explain how solute concentration and pressure affects water potential. Solute concentration and pressure affect water potential by either increasing or decreasing it Predict the direction of net water movement based upon differences in water potential between a plant cell and a hypoosmotic environment, a hyperosmotic environment or an isosmotic environment. hypoosmotic – lower concentration moves to the higher hyerosmotic – higher concentration moves to the lower isosmotic – the concentration stays the same on both sides According to the transpiration-cohesion-adhesion theory, describe how xylem sap can be pulled upward in xylem vessels. Due to negative pressure or tension the evaporation of water from plants removes water from the leaves and develops within the xylem. Explain why a water potential gradient is required for the passive flow of water through a plant, from soil. It is required for the passive flow so as to know how much concentration is needed within the plant. Describe both the disadvantages and benefits of transpiration. The benefits are that it moderates the water concentration on plants and therefore allows them to grow, but in case of drought the plants will die off quicker. List three cues that contribute to stomatal opening at dawn. light, potassium guard cells accumulate potassium Describe environmental stresses that can cause stomata to close during the daytime. Excessive potassium, flash of darkness Chapter 37 Distinguish between macronutrient and micronutrient. Macronutrient – elements required by plants in relatively large amounts micronutrient – elements required in very small amounts. List the nine macronutrients required by plants and describe their importance in normal plant structure and metabolism. Carbon - organic compound, Oxygen – organic, Hydrogen – organic, Nitrogen – nucleic acids, proteins, hormones, and coenzymes, Sulfur – component of proteins, Phosphorus – nuc acid, phospholipids, ATP, Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium. List seven micronutrients required by plants and explain why plants need only minute quantities of these elements. Chlorine – water – splitting, Iron – cytochromes, activates enzymes, Manganese – active in formation of amino acids, zinc – chlorophyll, Copper, Molybdenum, Nickel Explain how humus contributes to the texture and composition of soil. Humus us the decomposing organic material formed. It prevents clay from packing together and builds and crumbly soil. Explain why plants cannot extract all of the water in soil. The can not extract all of the water because some of it is tightly held by hydrophilic soil particles, List the three mineral elements that are most commonly deficient in farm soils. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium Describe the environmental consequence of overusing commercial fertilizers. Commercial fertilizers may lead to the pollution of lakes and streams and they are not long retained in the soil. Describe modifications for nutrition that have evolved among plants including parasitic plants, carnivorous plants, and mycorrhizae. Parasitic – uses projections called haustoria Carnivorous plants – digest insects for nutrients Mycorrhizae – they either help or invade the root Chapter 38 Outline the angiosperm life cycle. Look in notes in Biology Folder List the four floral parts in their order from outside to inside of the flower. Petal, sepal, stigma, style, anther, filament, ovary, receptacol, and the ovule From a diagram of an idealized flower, correctly label the following structures and describe their function: a. Sepals c. Stamen: filament and anther b. Petals d. Carpel: style, ovary, ovule and stigma Look in notes in Biology Folder Explain by which generation, structure, and process spores are produced. The diploid plant called a sporophyte is produces spores by meiosis. Explain by which generation, structures, and process gametes are produced. In the haploid generation, the gametophyte structure gametes are produces my mitosis. Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. Pollination is when an animal leaves behind traces of something upon a flower, fertilization is when they decompose and leave their nutrients behind for the plants Describe how pollen can be transferred between flowers. Pollen can be wind- dispersed from flower to flower. The bee can land on one plant and then may pass on that pollen to a different plant because of wind. From a diagram, identify the following structures of a seed and recall a function for each: a. Seed coat d. Radicle g. Endosperm b. Embryo e. Epicotyl h. Cotyledons c. Hypocotyl f. Plumule i. Shoot apex Look in notes in Biology notebook. Explain how a monocot and dicot seed differ. The dicot has a vascular cambium while the monocot does not. Also the monocot system has sparingly dispersed vascular cylinders within it, while the dicot has evenly spaced out and uniformly placed vascular cylinders. Describe several functions of fruit and explain how fruits form. Fruits are used for seed dispersal and protect the enclosed seed. The seed dehydrates and forms a seed coat, the fruit then begins to form.