* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Review Sheet Answers
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
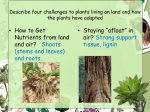
Mrs. Terhune Biology Review Sheet Chapter 19 and 20 MAJOR TOPICS - Plant Evolution - Challenges of Life on Land - Plant Diversity (Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms) - Reproductive Structures of Angiosperm - Nonreproductive Structures of Angiosperm - Seed Development/Seed Dispersal and Germination - Plant Tissues (Dermal, Ground, Vascular) - Plant Growth (Primary and Secondary) CHAPTER 19 1. What is the specific name of the organism that land plants evolved from? Charophytes (green algae) 2. What are the 4 challenges for life on land? Staying upright (lignin/vascular tissue) Maintaining moisture (stomata, cuticle) Reproducing on land (embryo develops within female) Obtaining nutrients (vascular tissue) 3. What is the function of a vascular system? Which groups of plants have a vascular system (Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms) Vascular system transports water, minerals, and nutrients such as glucose throughout the plant. The pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms have vascular tissue 4. What is the name of the chemical that helps plants to stay upright? lignin 5. What is the function of the stomata? Why do they close at night? What regulates the stomata? Stomata is where gas exchange occurs (Carbon dioxide in, oxygen out). They are regulated by guard cells and close at night to prevent water loss through the tiny openings. 6. Name the 4 groups of plants and give 2 major characteristics for each group. Bryophytes: Mosses (no lignin/vascular tissue, grow close to ground for water) Pteridophytes: Ferns (lignin and vascular tissue, no seeds, but spores) Gymnosperms: Pine trees (has seeds produced in cones) Angiosperms: Flowering plants (have flowers and seeds within ovary) CHAPTER 20: Life of a Flowering Plant Review Sheet 1. Be able to label the structures of a flower, including all reproductive structures: Petal, Sepals, Stamens: Anther and Filament, Carpel: Stigma, Style, Ovary, Ovules. Look at your HW diagrams 2. What are the male gametophytes? The female gametophytes? -Male: Pollen and Female: Ovule 3. What is the male reproductive structure? What is the female reproductive structure? Male: Stamen, Female: Carpel 4. Where are the pollen grains produced? Anther 5. Why is the stigma of the carpel sticky? To attract pollen 6. What is the embryo sac made up of? The embryo (fertilized egg) and the endosperm 7. What is the function of the endosperm? Endosperm nourishes the developing embryo 8. What is extended by the pollen grains so it can reach the ovary? Pollen Tube 9. Explain “double fertilization.” One sperm within pollen grain fertilizes the egg in ovary and becomes the embryo, the other sperm within the pollen grain fertilizes the large central cell within the ovary becoming the endosperm 10. What is the function of the cotyledon? What is the function of the fruit and where is it made? The cotyledon is the first leaf to appear during germination and it nourishes the developing plant. The fruit protects the seed and is made from the ovary 11. Explain germination. When roots and shoots develop from seed 12. Asexual reproduction in plants is known as __________vegetative__________ reproduction. 13. A plant that completes its life cycle in one year is known as a(n) annual__. 14. A plant that completes its life cycle in 2 years is known as a(n) __biennial _____________. 15. What is the difference between the terminal bud and the auxiliary bud? Terminal bud at tips of shoots, auxiliary bud is on the lateral branches 16. Photosynthesis occurs in the _____blade___________. 17. What is the difference between a fibrous root and a taproot? Fibrous root has many lateral roots off main root and taproot is one long deep root in ground 18. What is the function of root hairs? Root hairs increase surface area for absorption of water 19. What 2 types of tissues are located within the veins and are responsible water and food movement? Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves Phloem transports carbohydrates (food/glucose) from leaves to where it is stored (fruits, roots) 20. Name the 3 types of tissues that plants are made up of. Ground, Vascular, Dermal 21. The tissue that secretes the cuticle and makes up the outermost layer is the _____epidermal_________. 22. The vascular tissue that transports water is ____xylem_______________ 23. The vascular tissue that transports food and minerals is the ___phloem____________. 24. Tissue that differentiates into new tissue is called __meristematic_______________ tissue. 25. When plants grow in length this is called _primary______________ growth. 26. When plants grow in width this is called _secondary_____________ growth. 27. Be able to label the tissues of a plant cell (Labeling we did in class) Plant Tissues Lab: - What are the differences between a monocot and dicot plant? Be able to identify vascular tissue (xylem/phloem), ground tissue, epidermis, stomata if a leaf There could be a question or two from your lab.