* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Chapter 29
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
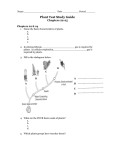
Biology Chapter 29-32 Terms Chapter 29 page 573 1. agriculture: (p 561) growing plants and animals for human use 2. botany: (561) the scientific study of plants 3. cereal: (562) grasses that contain grains 4. fertilizer: (564) a compound that provides plants with essential mineral nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus 5. fruit: (563) a mature plant ovary; a modified flower part that encloses a seed or seeds 6. gasohol: (567) an alternative fuel made from alcohol from fermented grains mixed with gasoline 7. herb: (563) a flowering, vascular seed plant that lacks a woody stem; a plant part used to add flavor to food 8. legume: (563) any plant of the family Leguminosae, such as a bean, a pea, or a lentil 9. nut: (563) have a hard outer layer, contain a dry, one-seed fruit. Includes almonds, walnuts, pecans, and halzelnuts. 10. pesticide: (564) a chemical used to control insects 11. root crop: (563) a plant grown for the nutrients it stores in its roots or modified underground stems 12. spice: (563) come from plant parts other than the leaf and are tropical, used to add taste to food 13. vegetable: (563) food derived from any part of soft plants Chapter 30 page 593 1. Alternation of generations: (p 581) a sexual life cycle in plants and algae involving two or more phases 2. angiosperm: (p 581) a flowering plant 3. cuticle: (p 579) in plants and insects, a waxy covering that prevents desiccation; in parasitic roundworms, a noncellular layer that protects the worm from the host’s digestive and immune system 4. endosperm: (p 579) a tissue in angiosperms that provides food for the developing embryo 5. gametophyte: (p 581) in plants and algae, a multicellular structure that produces gametes 6. gymnosperm: (p 581) a seed plant whose seeds are not enclosed by an ovary 7. herbaceous: (p 580) an annual plant that is nonwoody 8. nonvascular plant: (p 581) a plant that lacks vascular tissue and true roots, stems, and leaves 9. phloem: (p 580) in plants, the specialized tissue in the vascular system that transports dissolved sugars 10. seed: (p 579) a plant embryo enclosed in a protective coat 11. seed plant: (p. 581) a plant that produces seeds for reproduction 12. sporophyte: (p 581) one of the diploid generation of land plants that produce spores 13. vascular plant: (p 581) a plant that has xylem and phloem 14. vascular tissue: (p 580) a type of tissue that transports water and dissolved substances from one part of the plant to another 15. woody tissue: (p 580) in plants, formed from several layers of xylem, and is usually concentrated in the center of the stem 1 Biology Chapter 29-32 Terms 16. xylem: (p 580) the vascular tissue in plants that transfers water and minerals from the roots to the leaves. Chapter 31 page 619 1. apical merstem: (p 602) the growing region at the tips of stems and roots in plants 2. collenchyma: (p 599) plant tissue made up of elongated cells with unevenly thickened, flexible walls 3. companion cell: (p 601) a specialized plant cell that helps control the movement of sugars through sieve tubes 4. cork: (p 602) cells that are dead that provide protection and prevent water loss 5. cork cambium: (p 602) the lateral meristem of a plant; produces cork 6. cuticle: (p 600) in plants and insects, a waxy covering that prevents desiccation in parasitic roundworms a noncellular layer that protects the worm from the host’s digestive and immune systems 7. epidermis: (p 600) a layer of cells that forms a continuous sheet over the outer surface of a plant or animal 8. meristem: (p 602) the growing region in plants 9. parenchyma: (p 599) in plants, the living tissue of the ground system, consisting of cells with thin cell walls 10. pit: (p 601) thin, porous areas of the cell wall 11. sclerenchyma: (p 600) the tissue of the ground system that supports and strengthens the plant 12. sieve tube: (p 601) structure formed by stacked sieve tube members 13. tracheid: (p 601) a long, thick wall with tapering ends, forming part of the xylem tissue of plants 14. vascular cambium: (p 602) the lateral meristem in a plant that produces additional vascular tissue 15. vessel: (601) in plants, a structure formed by stacked vessel elements; in animals, a tubular conducting structure for blood or other body fluid 16. adventitious root: (604) specialized roots that grow from stems and leaves 17. cortex: (p 605) in plants, a mature ground tissue located just inside the epidermis; in animals, the outermost portion of an organ such as the kidney 18. endodermis: (p 605) in plants, a specialized layer of cells that regulates substances entering the center of the root. 19. pericycle: (p 606) in plants, the outermost cylinder of cells in the central vascular area 20. root cap: (p 604) a shield covering the apical meristem 21. root hair: (p 604) an extension of the epidermal cells 22. tap root: (603) the organ that results when the primary root grows downward and becomes the largest root 23. annual ring: (611) a yearly growth ring in a woody plant 24. bark: (611) the protective outside covering of woody plants 25. bud: (609) a structure that develops on the stem at the point of attachment of each leaf 26. cohesion-tension theory: (p 612) states that water is able to move up the stem xylem due to the strong attraction of water molecules to each other 2 Biology Chapter 29-32 Terms 27. heartwood: (p 611) the darker wood in the center of a tree 28. node: (p 609) the end of the internode where one or more leaves are attached 29. pith: (p 610) the plant tissue located in the center of the stem 30. pressure-flow hypothesis: (p 613) an explanation of the movement of sugars in the phloem of plants 31. sapwood: (p 611) lighter-colored wood near the outside of a tree trunk active in transporting sap; tissue of the secondary xylem system 32. springwood: (p 611) in woody plants, secondary xylem with cells that are wide and thing walled; the first wood of a growing season 33. summerwood: (p 611) in woody plants, secondary xylem cells that are small and thick walled and that are produced in hot, dry summers 34. translocation: (p 612) a mutation in which a broken piece of chromosome attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome; movement of organic molecules in plant tissues 35. transpiration: (p 613) the evaporation of water through stomata 36. wood: (p 610) secondary xylem 37. blade: (p 616) the broad, flat portion of a typical leaf 38. compound leaf: (p 616) a type of leaf in which the blade is divided into leaflets 39. guard cell: (p 618) one of two cells bordering a stoma, each of which has flexible cell wall that regulate gas and water exchange 40. leaflet: (p 616) one of the divisions of a blade 41. mesophyll: (p 616) in leaves, the tissue where photosynthesis occurs 42. net venation: (p 616) in plant leaves, the repeated branching of veins to form a network of smaller veins 43. palisade mesophyll: (p 616) in plants, a layer of mesophyll directly beneath the upper epidermis where most photosynthesis takes place 44. parallel venation: (p 616) in plants, the arrangement of several main veins parallel to each other 45. petiole: (p 616) in leaves, the structure that attaches blade and stem 46. simple leaf: (p 616) a leaf with only one blade 47. spongy mesophyll: (p 616) a mesophyll of irregularly shaped cells surrounded by air spaces that allow oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water to diffuse into and out of the leaf 48. tendril: (p 615) a specialized leaf found in many vines that takes on a coiled appearance 49. vein: (p 616) vascular tissue system of leaves consists of vascular bundles 50. venation: (p 616) the arrangement of veins in a leaf Chapter 32 page 641 1. antheridium: (p 625) in plants, algae, and fungi a reproductive structure that produces gametes by mitosis 2. archegonium: (p 625) in seedless plants, a reproductive structure that produces a single egg by mitosis 3. integument: (p 628) in plants, one or two outer layers of the ovule; in animals, the outer covering 4. megaspore: (p 627) a spore produced by meiosis in a megasporangium 5. micropyle: (p 628) the small opening in the integument 6. microspore: (p 627) a spore produced by meiosis in a microsporangium 3 Biology Chapter 29-32 Terms 7. ovule: (p 628) the megasporangium of a flowering plant 8. pollen grain: (p 628) the microgametophyte of seed plants 9. pollen tube: (p 628) a structure that grows from a pollen grain, down which the sperm travels to the eggs 10. anther: (p 629) the microsporangium of an angiosperm in which pollen grains are produced 11. carpel: (p 629) the innermost whorl of a flower which contains the reproductive structures 12. double fertilization: (p 633) in plants, the process in which two types of cell fusion take place in the embryo sac 13. generative cell: (p 631) in a pollen grain, the cell that forms two sperm 14. nectar: (p 632) a nourishing solution of sugars 15. ovary: (p 629) an egg-producing gonad of a female 16. petal: (p 629) one of the leaf-shaped parts of the corolla of a flower, usually brightly colored and conspicuous 17. pistil: (p 629) a plant structure formed of fused carpels 18. receptacle: (p 629) the swollen tip of a branch that is the base of a flower 19. sepal: (p 629) a modified leaf that protects a young flower 20. stamen: (p 629) the structure in the flower of plants that produces pollen 21. stigma: (p 629) an expanded apex of a pistil, supported by the style; the part of the pistil that receives pollen 22. style: (p 629) in plants, a stalklike structure of the ovary 23. clone: (p 639) an offspring produced by asexual production 24. dormancy: (p 637) a state of decreased metabolism 25. epicotyl: (p 636) the stem above the cotyledons 26. grafting: (p 640) a technique in which a portion of one plant is inserted into and grows with the root or shoot of another 27. hilum: (p 636) a scar along the edge of a plant seed marking where the seed was attached to the ovary wall 28. hypocotyl: (p 636) a stemlike area in plants between the cotyledons and radicle 29. layering: (p 640) the process of causing roots to form on a stem 30. plumule: (p 636) in plants, the structure composed of the epicotyl plus any embryonic leaves 31. radicle: (p 636) in plants, the embryonic root 32. seed coat: (p 636) the protective structure of a plant seed 33. vegetative reproduction: (p 639) reproduction with usually nonreproductive parts, such as leaves, stems or roots Chapter 33 page 659 1. 2, 4-D: (p 649) an important synthetic auxin, which is a herbicide, or weedkiller 2. abscission: (p 650) the detachment of leaves, flowers or fruits from a plant 3. Agent Orange: (p 649) a mixture of 2,4-D and another auxin, it was used to defoliate jungles in the Vietnam War 4. apical dominance: (p 649) a plant growth pattern in which branches near the shoot tip are shorter than branches farther from the shoot tip 4 Biology Chapter 29-32 Terms 5. auxin: (p 647) a plant hormone that regulates cell elongation 6. cytokinins: (p 651) plant hormones that promote cell division 7. ethephon: (p 650) a synthetic chemical that breaks down to release ethylene gas; used to ripen fruit. 8. ethylene: (p 650) a gaseous hormone produced by various parts of plants and released into the air 9. gibberellin (GA): (p 650) a plant hormone that, among other actions, stimulates bolting and cessation of dormancy 10. growth regulator: (p 647) a hormone that stimulates or inhibits plant growth 11. hormone: (p 647) a chemical secreted by an endocrine gland that specifically influences the activity of distant cells 12. chemotropism: (p 654) plant growth in response to a chemical 13. gravitropism: (p 654) a plant growth response to gravity 14. nastic movement: (p 654) a type of plant movement that is independent of the direction of the stimuli 15. phototropism: (p 652) plant growth in response to light 16. tropism: (p 652) plant movement toward or away from an environmental stimulus 17. biennial: (p 658) a plant that lives for two years, usually producing flowers and seeds during the second year 18. crtitcal night length: (p 656) each plant’s own specific requirement for darkness 19. day-neutral plant (DNP): (p 656) a plant that is not affected by day length 20. fall color: (p 658) the color of the tree leaves in fall, caused mainly by photoperiodic response buy also by a temperature response 21. long-day plant (LDP): (p 657) a plant that flowers when exposed to day lengths longer than the plant’s critical length 22. photoperiodism: (p 656) a plant response to changes in day length 23. short-day plant (SDP): (p 657) a plant that flowers when exposed to day lengths shorter than the plant’s critical day length 24. vernalization: (p 658) the requirement that some seeds or spores be exposed to cold before they can germinate 5