* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Webquest: Types of Forces
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Friction stir welding wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
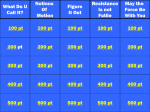
GMAS Review Web quest: Unit 1 Use the following link to answer the following questions: http://www.darvill.clara.net/enforcemot/forces.htm A. FORCES TAB: Make sure you have clicked on the forces tab for the following questions. 1. What units are forces measured in? Why are forces considered to be vectors? 2. List three things that can change a force? 3. Explain the force of gravity. (Is it weak or strong? Which direction does act on objects?) 4. What is weight? 5. What is the Earth’s gravitational strength at ground level? 6. Explain each of these: a. balanced force – b. unbalanced force- Observe the parachute picture and answer the questions below: 7. What forces are acting? What can you say about the size of the forces? 8. The resultant force is also called the net force. Explain what is meant by resultant force. B. FRICTION TAB: click on the Friction tab and answer the questions below: 1. What is friction? 2. What are the two main types of friction? 3. What does friction depend upon? Watch and read the animation about friction!! 4. What is fluid friction? 5. What does fluid friction depend upon? 6. What is drag? 7. What is meant by a viscous liquid? Give an example of a highly viscous liquid. 8. What is terminal velocity? Click on the terminal velocity graph to watch what happens to the graph when the sky diver descends. 9. List 3 ways to reduce friction. 10. List 3 ways to use friction to your advantage. C. ACCELERATION TAB: Be sure to click on the acceleration tab to answer the questions. 1. How is acceleration measured? 2. What is acceleration? 3. What happens to an object’s velocity if the forces acting on it are balanced? 4. What are three ways in which an object can accelerate? 5. What is the equation for Newton’s Second Law of Motion? D. ON YOUR OWN: For each example, tell if the forces are balanced or unbalanced. a. a see-saw goes up and down b. a heavy crate will not budge when pushed c. there is a tie in tug-o-war Draw a roller coaster with and label the area in which the greatest amount of kinetic energy occurs. Then label the area in which the least amount of kinetic energy occurs.