* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download file - MabryOnline.org
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
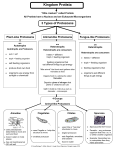
#3 Protist Protists are also called as “Odds and Ends”. Protists have different organisms that differ greatly from one another. Some protists are unicellular and some are multi-cellular. Some protists are autotrophs while some are heterotrophs. All the protests however are eukaryotes and live in moist conditions. Because of the variety of organisms found in the kingdom, protists are divided into three categories: Plant like (Algae), Animal like (Protozoan) and Fungi like (Molds). Animal like (Protozoan) Plant like(Algae) Fungi like( Algae) Heterotrophs Autotrophs Heterotrophs Can move _______________ Can move at some point of their life Mostly Unicellular Mostly Unicellular Mostly Unicellular No Cell wall Cell wall Has Cell wall Reproduce by Binary fission and Conjugation Reproduce by Spores #4 Protozoans Protozoans are divided into four different groups according to the way they move or live. Protozoan with Pseudopod Protozoan with Cilia Protozoan Other Protozoans Class: Sarcodines Class: Ciliates Class: Zooflagellates Class: Sporozoans Example :ameba Example: Paramecium Example: Giardia Example :Plasmodium Has Contractile Vacuole to expel water. Has Contractile Vacuole to expel water. Has 2 nucleus Example of mutualism: Zooflagellate inside the intestine of a Termite Parasite With Flagella Mutualism: Interaction between two organisms where both the organisms are benefited. Symbiosis: Interaction where only one organism is benefited.