* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Question of Ethics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
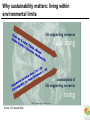
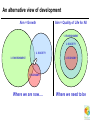
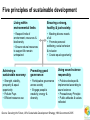
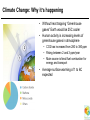
A Question of Ethics Michael Donnelly (Realeyes Sustainability) Patricia Mackey (Sustainable NI) Why sustainability matters What is Sustainable Development? “To enable all people throughout the world to satisfy their basic needs & to enjoy a better quality of life… …without compromising the quality of life of future generations” Securing the Future, UK's Sustainable Development Strategy, HM Government 2005 Why sustainability matters: living within A Global Perspective environmental limits life supporting resources declining consumption of life supporting resources rising ©2003 The Natural Step: All rights reserved Source: The Natural Step An alternative view of development Aim = Growth Aim = Quality of Life for All 1. ENVIRONMENT 2. SOCIETY 2. SOCIETY 3. ENVIRONMENT 3. ECONOMY 1. ECONOMY Where we are now…. Where we need to be Five principles of sustainable development Living within environmental limits: Ensuring a strong, healthy & just society: • Respect limits of environment, resources & biodiversity • Ensure natural resources to support life remain unimpaired • Meeting diverse needs of all • Promote personal wellbeing, social cohesion & inclusion • Create equal opportunity Achieving a sustainable economy: Promoting good governance: Using sound science responsibly: • Strength, stability, prosperity & equal opportunity • Polluter Pays • Efficient resource use • Participative governance across society • Engage people’s creativity, energy & diversity • Policies developed & implemented according to sound science • Precautionary Principle • Public attitudes & values reflected Source: Securing the Future, UK's Sustainable Development Strategy, HM Government 2005 Beyond the environment: the triple bottom line Living within environmental limits: Ensure natural resources to support life remain unimpaired Ensuring a strong, healthy & just society: Meet diverse needs of all; promote wellbeing, inclusion & equal opportunity Achieving a sustainable economy: Strong, stable, efficient & fair Global Challenges Climate Change: Why it’s happening • Without heat trapping “Greenhouse gases” Earth would be 25C cooler • Human activity is increasing levels of greenhouse gases in atmosphere • CO2 has increased from 280 to 380 ppm • Rising between 2 and 3 ppm/year • Main source is fossil fuel combustion for energy and transport • Average surface warming of 1 to 6C expected What’s at stake: projected global risks Monbiot: 90% cut by 2030 Tyndall: 90% cut by 2050 UK Gov: 60% cut by 2050 • Rice yields fall 15% • Increasing extreme weather events • Indian Ocean coral dies • 400m extra in water stress • 5m extra in hunger • 18% species loss • Greenland icecap melts o 1 C • 97% coral reefs bleach • Major city flood risk • Arctic summer sea ice melts • >50% species loss • 2.3-3bn water shortage • “Runaway” climate change • 200m more at risk from - Forest die-back malaria - Permafrost melt • Ecosystem collapse - Carbon release from soils • Human cost? o o 2 C >2 C We already have the solutions Public Transport Passive Design Energy Efficiency Renewables Emissions Trading Pollution: damaging health and the environment • “UK air pollution more dangerous than Chernobyll” • 24,000 premature deaths per year (Royal Commission on Environmental Pollution) • Over 100,000 man-made chemicals exist • Only 3,500 have been adequately tested for health and environmental impacts • Over 300 man-made chemicals can be found in the average European’s blood • With globalisation, Europe is exporting its pollution overseas Waste: our throwaway economy 10 x 10,000 kg raw materials 10 x Manufacture EXTRACT 1000 kg finished product CONVERT USE 6 months DISCARD Consumption should not be an end in itself: need to rethink value and efficiency 100 kg long-term durables Global Inequality Poverty: an ever widening gap UK average high street coffee price $2 20% of world survives on less than $2 per day Biodiversity: the sixth extinction • Up to 50% of species could be wiped out by climate change • Widespread decline in wildlife populations • • • • Habitat destruction and loss of wilderness Over-harvesting of timber, fisheries Falling fertility from pollution Invasion of alien species The goal: One planet living • Ecological footprint = equivalent area of land required to meet an individual’s needs • Food, fibre, waste, energy, space • Measured in “Global hectares per capita” (gha) “Equal sustainable share” = 1.8 gha “Global average footprint” = 2.2 gha “UK average” = 5.6 gha Group Exercise Coffee Cup Exercise • Work as groups • First map out the lifecycle of a cup of coffee: • From raw materials to disposal! • Identify impacts • Social, environmental and economic • How can this be improved?