* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT B: Human Body Systems Review Sheet
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
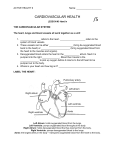
UNIT B: Human Body Systems Review Sheet 1. Know all the parts of the heart. Use the Powerpoint handout. a. Chambers b. Major vessels in and out c. Type of blood in the chambers and vessels (oxygenated or deoxygenated) d. Know there are valves, but you do not need to know their names. 2. Know how the blood flows through the heart. 3. Blood components and what each does. Plasma, Red Blood Cell, White Blood Cell & Platelets Use the Powerpoint handout. 4. Use your Notes & Study Packets (or check old homework on the website with these as attachments.) a. Facts about the heart from Bill Nye DVD. i. Pulse The number of times the heart beats in a period of time. Beats per minute. bpm ii. Heart rate resting average; 60-80 Exercising average 140 bpm b. What is the function (job) of each body system? c. Know the important organs and structures of digestion, respiration, excretion, & circulation. 5. From the experiments know a. Breakdown: Know what things represented in terms of digestion, such as vinegar represented stomach acid. The Alka Seltzer represented the food. Breaking & Crushing the tablet represented chewing (Mechanical breakdown). The reaction between the tablet & vinegar represented the stomach acid, hydrochloric acid, breaking down the food (chemical breakdown). b. Know the major conclusion for this experiment. The conclusion was: It is important to chew your food to make the chemical breakdown faster and easier. What is the relationship between the amount of Mechanical breakdown and the rate of Chemical breakdown? The more mechanical breakdown the faster the chemical breakdown. c. Gas Exchange experiment, the key concept was the use of an indicator. What is an indicator? An indicator is a compound that changes color in the presence of a particular substance. What one did we use? Bromthymol Blue BTB. What did the BTB indicate? BTB represents the presence of carbon dioxide CO2. It turns yellow or yellow green in the presence of CO2. 6. Know the difference between a poison and a toxin. See Ch.13 below. 7. Know the 3 main types of vessels and how they are different. [Arteries, veins & capillaries] Use the Powerpoint handout. a. Type of blood that flows in each (oxygenated or deoxygenated). b. Does it have valves? Only the veins have valve flaps so it can work against gravity c. Which type works directly with the cells of the body? Capillaries 8. Know the order from small to large is: cells tissue- organs Organ Systems Ch. 13 Living with your LIVER Regulation: keeping things balanced and responding to changing needs. Toxin: a substance that can cause damage to your body. Poison: a substance that causes severe damage or death with only a little amount. Liver: Helps digest fats. Controls what substances get stored or filtered out Breaks down harmful substances. Such as alcohol, headache medicines and Hepatitis. Second largest organ after our skin. Bigger than the brain. Weighs about three pounds Makes nutrients easier to be taken up by the body. Can grow back if half is damaged. Too much of toxins can permanently damage the liverAlcohol, too many headache medicines Transplants regenerate from one half the liver Too many toxins cause Cirrhosis, which is scar tissue of the liver. Regulates cholesterol, sugar, and fat. CH 15 Digestion Chemical Breakdown: The process if breaking down food using chemicals such as saliva, hydrochloric acid, and bile. Mechanical breakdown: The process of breaking down food using physical forces like chewing with teeth or churning of the stomach muscles. Absorption: The taking in of substances across membranes such as nutrients in blood. Nutrients: Substances needed for energy, growth, and repair. The Heart: Lecture 2 Amazing Heart Facts 1. Your heart is about the same size as your fist. 2. An average adult body contains about five quarts of blood. 3. All the blood vessels in the body joined end to end would stretch 62,000 miles or two and a half times around the earth. 4. The heart circulates the body's blood supply about 1,000 times each day. 5. The heart pumps the equivalent of 5,000 to 6,000 quarts of blood each day. The circulatory system keeps these approx. five liters of blood circulating constantly through the body. Its most important organ is the heart. The double pump of the heart forces the blood through the blood vessels. The body's circulatory system really has 3 distinct parts: Coronary Circulation: Like any other organ, the heart itself needs blood to supply it with nourishment and carry away wastes. The movement of blood through the capillaries of the heart for these purposes is called coronary circulation. The Heart The heart is a hollow muscle is charge of pumping the blood. It is about the size of your fist. It is located slightly to the left of the center of your chest. The Heart in detail: The heart is basically shaped like a 4 paned window. There is a right side, and a left side. There is a top half and a bottom half. Each side has specific responsibilities and works with specific types of blood. Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle The Heart The right upper (right atrium) receives blood from the body. The right lower (right ventricle) pumps blood to the lungs. The left upper (left atrium) receives blood from the lungs. The left lower (left ventricle) pumps blood to the rest of the body. The two halves of the heart are separated by a membrane called the septum. This wall prevents the flow of blood between the two atria or the two ventricles. The heart is set up like a football team. You have receivers, quarterbacks (who push the blood) and running backs. The atriums RECEIVE the blood. The ventricles PUMP the blood out to specific parts of the body and the veins and arteries are the running backs who carry the blood to where it needs to go. Veins carry DEOXYGENATED blood. They carry blood TO the heart. The primary blood vessels that carry the blood are called the upper and lower VENA CAVAS One carries blood from the head region to the heart, the other carries blood from the body to the heart. This blood is designated as a blue color to show that it is LACKING oxygen “deoxygenated”. Once the blood gets to the heart it is RECEIVED by the right atrium. The right atrium then allows the blood to go through a one-way valve to the right ventricle. Once in the right ventricle it is this “quarterback’s job “ to push (or pump) the blood out to the lungs. The blood is pushed out to the lungs by the right ventricle It is carried to the LUNGS by the PULMONARY ARTERY. This is a rule breaker Number 1. What vessels carry what type of blood? Veins carry DEOXYGENATED blood to the heart and ARTERIES carry OXYGENATED blood away from the heart to the body. But what type of blood do we have here??? Deoxygenated blood is being carried in an artery... on it’s way to the lungs. Once it gets to the lungs, what’s going to happen??? The blood is going to get oxygenated. It’s going to become rich with oxygen. This is the blood that has to go out to the body. This is the blood that the body needs. This is the “red” blood of life. The blood gets oxygen, becomes oxygenated and then heads back to the heart. It is carried to the heart by what kind of vessel?? What kind of vessels carry blood to the heart?? VEINS do. This is rule breaker Number 2. The PULMONARY VEIN carries OXYGENATED blood back to the heart. This oxygenated blood is received in the LEFT ATRIUM. (remember the atriums as receivers.) It then goes through another one way valve to the LEFT VENTRICLE. If you look at a heart it is this side which has the greatest amount of musclebecause of the quarter backing it must do! The LEFT VENTRICLE PUSHES the blood into the AORTA (which is the largest artery in the body). The AORTA then carries this OXYGEN rich blood out to the various parts of the body through the artery system. 14. Vena cava 15. Right atrium 16. Rt. Ventricle 17.Pulmonary Artery 18.Pulmonary Vein 19. Left Atrium 20. Left Ventricle 21. Aorta (biggest Artery) 22. lung Color sections: DE-oxygenated(blue) Oxygenated(red) The heart pumps blood in two phases. a. systolic phase: the ventricles contract, pumping blood into the arteries. b. diastolic phase: or second phase, the ventricles relax and blood flows into them from the atria. These two phases of the heartbeat are measured when the blood pressure is taken.. Circulation & Blood (Bill Nye DVD) Blood Components: 1. Plasma contains blood cells, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and other substances that need to get around the body. 2. White blood cells a. Attack foreign invaders b. Live about 2 weeks 3. Red blood cells – a. Carry oxygen b. Hemoglobin uses iron to carry oxygen c. About 25 billion cells d. Live about 4 months e. Blood cells made in the bone marrow 4. Platelets-seal a wound. Blood Vessels could wrap around the earth 2.5 times 1. Arteries a. Take blood away from heart b. Are bigger & wider the closer to the heart (Freeway down to streets) 2. Veins a. Take blood back to heart b. Are bigger & wider closer to the heart (Freeway down to streets) 3. Capillaries (driveway) Deliver nutrients and O2 to cells (houses). a. Connect arteries to veins. b. Only 1 blood cell through at a time. Circulatory System (Blood transport system) 1. Heart is a Muscle a. Size of your fist about 300 grams 2 sides b. 4 chambers c. Needs valves (prevents blood from flowing back) d. Lub is the Big push e. Dub is the reload of the chambers f. Blood pressure = Lub/Dub 2. Facts: a. Body has 5 Liters of blood b. 5 milliliters of this is white blood cells c. Usually donate half a liter of blood d. Travels around your body 100,000 times a day e. Heart i. Pumps about 70 X/min (35-40 seconds) ii. Exercises 140 beats /minute (1 trip around in 10 seconds) iii. 7000 L/ day iv. Beats about 2-3 billion times in a lifetime.