* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Unit Packet energy_unit_packet
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
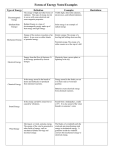
ENERGY Name ______________________ Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the ability to exert a force over a distance. Work is done when force moves an object in the direction of that force. Energy is one of two basic concepts of physics. Physics is the study of matter and energy. The word “physics” comes from a Greek word meaning nature. Physics explains sound to musicians, color to artists, and speed to race car drivers. When Herman lifts this barbell, he is applying an upward force. The distance the barbell moved is measured from its resting place on the floor to the position over Herman’s head. In order for Herman to apply the lifting force, he must use energy. Kinds of Energy We will study two kinds of energy: potential and kinetic Potential Energy Energy isn't always moving. Potential energy is stored energy at rest. Potential energy means that the system could do work but isn't doing so at the moment. There are many different examples of potential energy. For instance, a stretched rubber band or a compressed spring are ready to snap back, exerting a force over distance as they do so. A ton of water at the top of a waterfall has the potential to do a certain amount of work as it tumbles to the bottom. But, when the water has crashed onto the rocks at the bottom of the fall, its work potential has been used up. Potential energy is energy waiting to be unlocked. Herman’s barbell now has potential energy. If he were to drop it, the barbell would exert a force of its own. Look out Herman! Kinetic Energy When energy makes things move it is called kinetic energy. A rotating wheel, a speeding car, a falling leaf - all do work, therefore they possess kinetic energy. Heat is a special kind of kinetic energy - the kind associated with atoms in motion. Sound is caused by the atoms and molecules bumping into each other as waves. We hear sounds because our eardrums vibrate in response to moving air molecules. Mechanical force is the form of energy we use to do work - to push, pull, or lift objects from one place to another. Oh, oh! Herman dropped his barbell. The barbell now has kinetic energy because it is moving. Herman is moving, too. Energy can take several forms. This mnemonic may help you remember the six forms of energy. SCREAM- sound chemical (Includes Food energy) radiant (heat and light. We will treat these as separate energy forms in this unit.) electrical atomic (only covered briefly in this unit) mechanical (motion) These forms are all interchangeable. They can be transformed (changed) into different forms. Chemical energy can be changed into heat by burning a fuel. Heat can be transformed into mechanical energy in an engine. Mechanical energy can be transformed into electrical energy by a generator. An electric light bulb produces light. An electric range produces heat. A radio emits sound energy, and a fan converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, heat energy, and sound energy. During these transformations, the total amount of energy after the change is the same as the amount before the change. Energy cannot be destroyed or created. This is the Law of Conservation of Energy or the First Law of Thermodynamics . A light bulb transforms electrical energy into light and heat energy. Energy from burning gasoline transforms from the chemical energy in the fuel into intense heat energy. The engine then transforms the heat energy into mechanical energy that makes the car move. The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that transformation always leads from more useful energy to less useful forms. For example, when you burn coal or gas, some of the high-grade energy is lost as heat to the atmosphere where it cannot be recovered to do work. Energy Efficiency refers to the amount of energy lost during transformation. A more efficient conversion process means that less energy is lost as heat than would be lost through a less efficient process. Transferring Energy Energy can be moved from one object to another object. For example, a stove burner transfers heat to a frying pan, which then transfers heat to the oil, which then transfers heat to the food. Also, a moving baseball transfers mechanical energy to the catcher’s mitt. Energy Transfer is like a bus transfer. Here Sally Smart is transferring from one bus to another. Sally is like energy being transferred: she is moving from one place to another but is still the same Sally. Forms of Energy Draw one form of energy in each space. Some of your illustrations may use more than one form of energy. Label each form of energy. Light (Radiant) Heat (Radiant) Sound Motion/Mechanical Chemical (Food) Electrical Chemical to Heat and Light (Radiant) A) Match Watch as the teacher lights a match. What did you observe? How was energy transformed, or converted—what forms of energy were involved and how did they change? B) Hand Warmer. Hold the hand warmer. Describe its temperature. After the pack is activated, feel it again. Describe its temperature. What does the inside feel like now? What energy transformations just occurred? Light Energy to Food Energy Leaves of plants like trees and grass transform light energy from the sun into food energy (a special type of chemical energy). Electricity to Radiant Electricity is the flow of electrons from a source and through a circuit. Electrons are tiny negatively-charged particles orbit the nucleus of an atom. These electrons can move from one atom to another. Observe the temperature and color of an incandescent light bulb while it is turned off. Describe your observations. After the bulb is turned on, what do you observe about it? What energy transformations took place? Motion (Mechanical) to Electricity Rub an inflated latex balloon in your hair. What do you notice about your hair? You caused a charge of static electricity to build up in your hair. This was caused by the motions you made as you rubbed the balloon. Static electricity is electricity that is not moving. This is different than the electricity in your wall outlet. Electricity that powers your lights and your television is called current electricity. It moves through a circuit like a current of water moving through a pipe. Static electricity is more like a puddle. We generate this current electricity by passing a massive coil of wire through a magnetic field. You have probably experienced magnetic fields whenever you played with magnets. To move this huge coil of wire requires mechanical energy. This can come from steam produced by coal fires, gas fires, nuclear power, or it can come from hydroelectric power (water falling and turning turbines on its way down), wind power and other sources. A turbine is the machine that encounters the mechanical force and gets turned or rotated by that force. It often has large paddle-like structures on it that water strikes. The turbine is connected to that huge coil of wire. Friction (mechanical) to Heat Rub your hands together. What do you notice? Rub your hands on a carpet. What happens to your hand? Put soapy water in your hands and rub them together again. Did they feel the same as they did without the soap? Explain the difference if any. Friction transforms motion (mechanical) energy into heat. The soap was a lubricant that reduced the friction. How can you use this information to solve the friction problem in a car engine that has lots of moving parts rubbing together? Conduction is the transfer of heat energy through a substance. Heat energy is the motion of atoms and molecules. Moving atoms and molecules bump into their neighbors, causing them to move too. The metal fork conducts or carries the heat from the flame to the hand. Always be very careful around heat sources. The heat energy from the flame travels along this metal rod. A pan on a stove conducts heat from the burner to the liquid in the pan. On an electric stove, electrical energy is converted in to heat and _____________. Heat energy also moves toward the cook’s hand. What prevents the hand from being burned? An insulator is a material that does not conduct heat very well. Wood, some plastics, and certain cloth materials are good insulators. They do not conduct heat as quickly or as efficiently as does metal. They can still get very hot over time, though, so be careful. This insulator slows the conduction of heat energy from the metal rod. Sound Energy If you pluck a tightly stretched rubber band, you may notice a sound. If you look closely at the rubber band as it makes a sound, what do you see? Dip your finger into the surface of some water in a tray. What happens to the water surface as a result of your finger touching it? Sound is actually just vibrations transferred through the air as waves to our ears. What form of energy was transformed into the sound energy as the band was plucked? List four objects or devices that transform some form of energy into sound energy. If you need help, think about musical instruments. Draw a picture for one of them that shows what is happening. Then, explain it with words. 1. 2. 3. 4. Some Renewable Energy Sources A renewable energy source is any means to generate power that can be used again and again without having to produce more fuel. Solar power from the sun is renewable, because the sun is always producing more. The suns radiant energy strikes special plates called solar cells. These plates emit electrons, which eventually flow through a circuit. Solar energy also can be used to heat water for energy purposes. Geothermal power comes from the tremendous heat that the Earth continuously generates. We can place water pipes into this heat, and the heat will turn the water into steam that can turn turbines. Hot water can also be pumped from the ground to heat homes. 3) steam or hot water can turn turbines or can heat buildings. 1) Water is pumped into the pipe. 2) Magma heats the surrounding water and transfers this heat energy to the water in the pipe. Wind is the movement of air that is caused by unequal heating and cooling of the Earth’s surface. Wind can turn turbines as well. Wind has pushed sail boats and ships around for centuries before engines were invented, Tidal power harnesses the energy form the incoming and outgoing tides. As the tide rises, water flows inward towards the land. As the tide falls, water flows towards the sea. This power can turn turbines to generate electricity. Tide coming in turns the wheel turbine Nuclear or atomic power captures the enormous heat given off by atoms as they split apart into smaller atoms. We use Uranium 235 and plutonium for this form of power. They are large atoms that break apart easily. The heat turns water to steam that turns turbines. Gas, coal, and oil come from dead organisms that lived millions of years ago. As these organisms were buried by sediments, they became exposed to great heat and pressure. These forces changed the creatures’ bodies into what we call fossil fuels. This takes a great deal of time—millions of years. Knowing this, are gas, oil, and coal considered renewable sources? Why or why not? Complete the web diagram with the forms of energy you have studied. Do you notice how interconnected energy forms are? Complete the energy chain below. Sunlight helps a tree produce and store food. Light energy to Food energy (a type of chemical energy) Wood from the tree is burned in the firebox of a steam engine. The steam engine propels a train locomotive. The engine generates electricity. Food/Chemical _____________energy ____________energy _______energy to to to ____________energy ___________energy energy to _________energy _____________energy transforms mechanical energy transformation. WORD BANK tidal engine radiant nonrenewable kinetic insulator efficiency generator turbine electron renewable conductor nuclear solar work geothermal potential energy Name _________________________ Date______________ Energy Test Fill in the blanks with words from the word bank. Note: not all of the words will be used. (1 pt each) 1. Stored energy at rest is called ______________________________ (what kind of) energy. 2. _______________ refers to the amount of energy lost during conversion. 3. The_____________________________ states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but that it can be converted from one form to another. 4. A generator converts _________________ energy into electrical energy. 5. ___________ energy includes both heat and light forms. 6. A car rolling down a hill is an example of __________________ (what kind of) energy. 7. ___________ is the ability to exert a force over a distance. 8. Geothermal energy is an example of a ________________________ energy source. 9. When you strum a guitar string, you change mechanical energy into ____________energy. 10. Wax melting on the end of a metal rod when a flame is applied to the opposite end is an example of ________________. Word Bank Kinetic Radiant Chemical Atomic Sound Efficiency Potential Work Mechanical Nonrenewable Renewable Conduction Law of Conservation of Energy 2nd Law of Thermodynamics 11. You turn on an electric motor. Use pictures and/or words to describe three energy conversions that are taking place. Remember to consider all the forms of energy that the electricity may be converted into. (3 pts) 12. Construct an energy chain below by drawing examples of energy conversions involving three different forms (heat, mechanical, chemical, etc.). (3 pts) Converting Energy Crossword Word bank Transparency Tidal Engine Radiant Nonrenewable Kinetic Insulator Efficiency Generator Turbine Electron Renewable Conductor Nuclear Solar Work Geothermal Potential Energy