* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Facial Skeleton
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
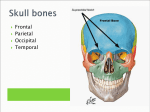
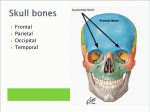
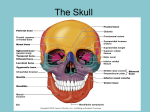
Facial Skeleton • Maxillae (2) – Form the upper jaw – Portions comprise the anterior (???) roof of the mouth (“hard palate”), the floors of the orbits (???), and the sides and floor of the nasal cavity. – Contain sockets of the upper teeth – “Maxillary sinuses” • Inside the maxillae, lateral (???) to nasal cavity • The largest of the sinuses Facial Bones, continued…. • Maxillae, continued…. – “Palatine processes” fuse midline (???) to form anterior section of hard palate – Teeth are found in cavities in the “alveolar arch” (aka “dental arch”) formed by the “alveolar processes” projecting downward from the inferior (???) border of the maxillae. Facial Bones, continued…. • Palatine bones – Behind the maxillae – Horizontal portions form posterior (???) section of hard palate and floor of nasal cavity – Perpendicular portions help form lateral (???) walls of nasal cavity Facial Bones, continued….. • Zygomatic bones (“???”) – Also help form lateral walls and floors of the orbits – Each bone has a “temporal process” that connects to the zygomatic process (forming the zygomatic arch). • Lacrimal bones – Thin, scale-like structure in medial wall (??) of each orbit between ethmoid bone and maxilla Facial Bones, continued….. • Nasal bones – Long, thin, and nearly rectangular – Lie side by side and fused at midline to form bridge of nose • Vomer bone – Thin and flat – Along midline in nasal cavity – Joins perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone posteriorly (???) to form nasal septum Facial Bones, continued….. • Inferior nasal conchae – Fragile, scroll-shaped bones attached to lateral walls (???) of nasal cavity – Support mucous membranes in nasal cavity • Mandible (“???”) – Upward projection at ends: • Posterior “mandibular condyle” articulates with mandibular fossae on _______ bone • Anterior “coronoid process” provides attachments for muscles for chewing – “Alveolar arch” – curved, superior (???) border that contains sockets for lower