* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormones and Blood Sugar
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
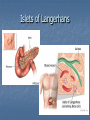
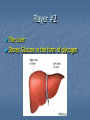
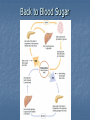
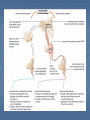
Hormones and Blood Sugar Key Players In regards to maintaining blood sugar levels… The Pancreas The Liver Player #1 The pancreas Contains two types of cells… Digestive Enzymes Focus on hormone producing cells Islets of Langerhans Located where ?? Islets of Langerhans Islets of Langerhans Contain Alpha and Beta Cells Alpha Cells: Secrete Glucagon Beta Cells: Secrete Insulin Player #2 The Liver Stores Glucose in the form of glycogen Before We Look At Mechanisms… Must understand: Body has created Positive and Negative feedback systems Positive Feedback Designed to accelerate or enhance a response that has already started Pushes systems outside of their normal range Example During Childbirth: Pressure receptors encourage the release of Oxytocin in the Pituitary Gland Oxytocin causes contractions Pressure increases on the pressure sensors After the child is born, the pressure receptors are no longer stimulated and Oxytocin production ceases Pressure Sensors cause the release of oxytocin Oxytocin causes contractions to intensify More intense contractions cause more pressure Negative Feedback Designed to maintain the body systems within appropriate parameters Mechanisms are activated to restore conditions to their normal state Keeps delicate systems working ideally and preserves body function Example Calcium Levels If calcium levels in the blood are too low the parathyroid releases parathyroid hormone Parathyroid hormone causes the bones to release calcium Parathyroid hormone also causes intestines to absorb more calcium Blood calcium levels then return to normal Example cont’d Calcium Levels cont’d If your calcium levels in your blood are too high The thyroid produces calcitonin Calcitonin increases the uptake of calcium to the bones Calcium levels return to normal Therefore In the body we see more Negative Feedback Systems… As part of homeostasis And as you can see it is very Structured, precise and complex. Back to Blood Sugar Glucose Regulation You Decide Positive or Negative Feedback ?? Discuss and Explain Your Reasoning Diabetes Caused by insufficient production or use of insulin. If untreated causes: blindness, kidney failure and nerve damage. Insulin Without adequate levels Blood sugar levels rises quickly following meals Kidneys are unable to reabsorb all the blood glucose being filtered What does insulin do… Required for cells of the body to become permeable to glucose Therefore if insulin isn’t present glucose cannot enter cells and they become “starved” Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes Type 1: Juvenile on-set Occurs when the pancreas cannot produce insulin because of the degeneration of beta cells in the islets of Langerhans Type 2:Adult on-set Decreased insulin production or ineffective use Can be controlled by diet, exercise or oral drugs (sulfonamides) Adrenal Glands – Regulating BSL Already Know – Located on top of the kidneys Release the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine How do these affect Blood Sugar Levels ? Nervous system senses a stressful situation Short-term: Adrenal medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood This causes a rise in blood sugar levels Glucagon converted to glucose Why do you think this is important ?? Long-term: Adrenal cortex releases glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids help the body meet the demands of stress. Cortisol – increases amino acids in blood Questions P. 383 # 2,3,4,5 Q. 2 – How Does Insulin regulate blood sugar levels ? Insulin decreases blood sugar levels. When blood sugars are high, insulin is released. Insulin increases glucose utilization by making cells more permeable to glucose, and blood sugar levels are returned to a normal range. Q.3 - How does glucagon regulate blood sugar levels? Glucagon increases blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are low, glucagon is released and liver glycogen is converted into glucose. Blood sugar levels rise as glucose leaves the liver. Q.4 - Using a flow chart, show a homeostatic adjustment for a person who has consumed a significant amount of carbohydrates in the past hour. Q.5 - What advantage is provided by increasing blood sugar above normal levels in times of stress? This provides more glucose for cells. Glucose can be converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cellular fuel. This ensures that greater energy will be available to the tissues of the body.