* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summary Table – Series and Parallel Circuits
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Shockley–Queisser limit wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
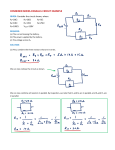
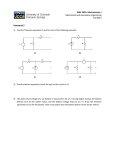
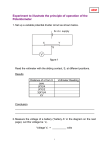
Summary Table – Series and Parallel Circuits Series Parallel Circuit Diagram Draw a diagram of two light bulbs (in series and in parallel) with a 3 cell battery. Number of paths for electrons to follow Is electrical energy (voltage) from the source shared between loads? Is the amount of current (amperage) from the source shared between loads? If one load is turned off, will the other loads stay on? If more loads are added, what happens to the voltage drop across each load? If more loads are added, what happens to the total resistance in the circuit? If more loads are added, what happens to the total current coming out of the source? If more loads are added, what happens to the brightness of the bulbs? One path 2 or more paths Yes, voltage is shared between loads No, current is the same throughout circuit No, all loads turn off. Voltage drop decreases (more sharing). Total resistance increases. No, voltage at each load equals voltage at battery Yes, current splits between paths. Yes, other loads stay on. Voltage drop stays the same. Total resistance decreases. Current decreases Current will as more loads are increase as more added. loads are added. Lights become dimmer (less voltage and current) Lights stay bright. Draw the following circuit diagrams on another piece of paper: 1. A battery (two cells), one open switch, and one light bulb. 2. One cell, two motors, and one light bulb, all wired in parallel. A switch is connected in series with the light bulb so that it can be turned on and off without affecting the rest of the circuit. 3. A battery (three cells), one closed switch, a motor, a light bulb, and a resistor wired in series. A voltmeter is connected to the battery to measure its voltage. 4. One cell is connected to two lights in series. A third light is connected in parallel with the other two. One closed switch controls all three lights. 5. A three cell battery connected to two resistors in series. A motor is connected in parallel with the resistors. Include a voltmeter to measure the voltage of the source and an ammeter to measure the current leaving the source. 6. A 2 cell battery is connected to two resistors in parallel. A third resistor is in series with both other resistors. 7. A circuit contains two light bulbs, a motor, and one switch, and is powered by a 3 cell battery. The motor must stay on at all times. The two light bulbs can be turned on and off together by the same switch. Include a voltmeter to measure the voltage of the source, and an ammeter to measure the current going through the motor.