* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TEAM Solutions Milestone Database
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
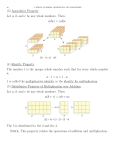
Multiplication and Division Progressions Progression Example CA Solve simple problems by counting all the objects from one. Rote skip count in 2’s 5’s,10’s (then 3’s, 4’s) 3 x 2 = 1,2, 3,4, 5,6 5,10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 AC Use skip counting to solve multiplication problems (involving 2’s,5’s10s) 6 x 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 Understand meaning of “x” using arrays. See that 3 x 6 and 6 x 3 may have the same answer but ‘look’ different. 3 x 6 = ****** ****** ****** Understand the link between addition and multiplication and use repeated addition to solve problems. 5x3=3+3+3+3+3 =6+6+3 Understand division as a ‘sharing” context. 8 4 = ** ** ** ** 8 lollies shared between 4 children, how many lollies does each child have? 8 4 = **** **** 8 lollies put into sets of 4, how many sets? EA Stage 5 Understand division as a ‘grouping“ context. AA Stage 6 AM Stage 7 Solve division problems by skip counting or repeated addition 12 3 = 3,6,9,12 therefore the answer is 4. Understand x 2 by doubling, Understand x5 by halving x 10 KNOWLEDGE: Recall x 2 x 5 and x 10 mult and div facts 2 x 8 = double 8, or 8 + 8 5 x 8 = half of 10 x 8 Derive unknown basic multiplication facts from known facts using: commutative property to make problems easier (change the order) 6x3=3x6 distributive property x 6, x7, x8 from x5 known facts (splitting) x4 and x9 facts from x5 or x10 known facts (tidy numbers) 8 x 6 = (8 x 5) + (8 x 1) 9 x 7 = (10 x 7) – (1 x 7) associative property x4, x8 by doubling and doubling again Apply these strategies to larger numbers. e.g. 6 x 19 = (6 x 20 ) - 6 8 x 6 = 2 x 2 x (2 x 6) Multiply by tens and hundreds 28 x 10=280, 36 x 100=3600 Solve division problems by reversing into a multiplication problem (inverse operations) 36 4 is the same as 4 x ? = 36 KNOWLEDGE: Recall all basic multiplication facts to 10x10 & some division facts (all division facts to be learnt at Stage 7). 6 x 7, 4x3, 9x8 Choose efficiently from a range of mult/div strategies to a full range of contexts and whole numbers. Division Example Multiplication Example 76 4 is the same as (80 4) – (4 4) = 20 – 1 = 19 Tidy Numbers 29 x 6 = (30 x 6) – (1 x 6) 76 4 is the same as (40 4) + (36 4) = 10 + 8 108 12 is the same as (108 2) 6 Place Value 24 x 6 = (20 x 6) + (4 x 6) Splitting Factors 23 x 12 = 23 x 3 x 2 x2 Adjusting both numbers proportionally by finding a common factor. 108 12 is the same as 54 6 = 9 Proportional Adjustment (associative Property) 18 x 3 = 9 x 6 (doubling and halving) 33 x 27 = 99 x 9 (thirding and trebling) Standard Written Forms AP 108 12 is the same as 12 x ? = 108 Reversibility (inverse) Not Applicable 39 4 = Express remainders as whole numbers, fractions, or decimals Not Applicable Divisible by.. 3 and 9 if sum of digits are divisible by 9. Use divisibility rules for 2,3,5 9 (then 4,6,8), Not Applicable 9 = 3 Use exponents (powers and roots of numbers) 32 = 3 x 3 = 9 9r3 or 9 ¾ or 9.75 Apply properties of multiplication and division across a full range of contexts with fractions and decimals and manipulating relationships algebraically. Marie Hirst, Numeracy Facilitator, Facilitator name, Month, year [version ie. Draft v3] 2