* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Friction study sheet 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
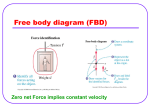
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW For Regents Physics Exam FORCES and MOMENTUMA VERY HELPFUL SKILL is to be able to visualize the forces acting on the OBJECT OF CONCERN and draw them in a FREE BODY DIAGRAM (FBD). ALL Forces are measured in units of newtons(N). A newton is equal to : N = kg*m/s² The seven named forces on the RRT are: INDIVIDUAL FORCES (can be identified as a force acting on an OBJECT, and can be in FBD.) Normal Force(FN)- Force perpendicular to the surface of contact. Friction(Ff)- Force parallel to the surface of contact. Friction can be static or kinetic. (more below) RESULTANT FORCES (The result of adding all forces acting on an OBJECT, and won’t be on FBD.) Net Force(Fnet)- The sum of all forces acting on the OBJECT OF CONCERN. It is this value that causes the OBJECT OF CONCERN to accelerate. 5.1j- 5.1k- 5.1l5.1o- 5.1q- Equilibrium is defined as OBJECT with NO net force(Fnet= 0). The following is well worth knowing. (Fnet = 0) EQUILIBRIUM NO ACCELERATION CONSTANT VELOCITY CONSTANT VELOCITY NO ACCELERATION EQUILIBRIUM (Fnet = 0) Newton’s 2nd Law mathematically connects motion of an OBJECT to the forces acting on it. Fnet = ma You should feel comfortable with making FBD’s. Also, when determining F net from FBD, NEVER add vertical (up-down) forces with horizontal (left-right) forces. Forces acting in same direction are adding, forces acting in opposite directions are subtracted. MASS AND WEIGHT ARE DIFFERENT!-KNOW THE DIFFS! See full page hand out given to you. Static friction is “sticky friction” when surfaces don’t slip. The amount of static friction adjusts to match the need of the OBJECT to stay still up to a maximum force. Then, the OBJECT will start to slide. (Picture lifting one end of a board with book on it). Kinetic friction is “sliding friction” when surfaces slide past each other (skidding, skiing, etc…) The amount of kinetic friction remains constant as long as the OBJECT is sliding. Newton’s 3rd Law-for every action, there is an EQUAL AND OPPOSITE (EAO)reaction. Exam often presents “Compare large thing’s force applied to small with small thing’s force applied to large. (EAO) The force of friction Ff = FN For an inclined plane, Fg,x = mg sin () FN = mg cos () For an object on an inclined plane at constant velocity with no applied force other than gravity, Ff = Fg,x For an object in equilibrium (velocity is zero or constant), the sum of the forces = FNET = zero. For an object in equilibrium (velocity is zero or constant), the acceleration = zero.