* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THINGSYOUNEEDTOKNOWFORCE
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
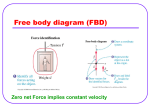
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW For Regents Physics Exam FORCES and MOMENTUMA VERY HELPFUL SKILL is to be able to visualize the forces acting on the OBJECT OF CONCERN and draw them in a FREE BODY DIAGRAM (FBD). ALL Forces are measured in units of newtons(N). A newton is equal to : N = kg*m/s² The seven named forces on the RRT are: INDIVIDUAL FORCES (can be identified as a force acting on an OBJECT, and can be in FBD.) Weight/Force due to gravity(Fg)- Force between ANY two masses (The Earth is often one of them.) Electrostatic Force(Fe)- Force between ANY two charged objects. Normal Force(FN)- Force perpendicular to the surface of contact. Friction(Ff)- Force parallel to the surface of contact. Friction can be static or kinetic. (more below) Spring Force(Fs)- Restoration force of elastic objects (spring, rubber band, etc…) RESULTANT FORCES (The result of adding all forces acting on an OBJECT, and won’t be on FBD.) Net Force(Fnet)- The sum of all forces acting on the OBJECT OF CONCERN. It is this value that causes the OBJECT OF CONCERN to accelerate. Centripetal Force(Fc)- A special case of a net force when the motion of the OBJECT OF CONCERN is circular. 5.1i- 5.1j- 5.1k- Newton’s First Law is the Law of Inertia. It states that the natural tendency of any OBJECT is to keep its motion unless acting upon by a force. For testing purposes, you can always replace the word “inertia” with “mass”, then read the question. Equilibrium is defined as OBJECT with NO net force(Fnet= 0). The following is well worth knowing. (Fnet = 0) EQUILIBRIUM NO ACCELERATION CONSTANT VELOCITY CONSTANT VELOCITY NO ACCELERATION EQUILIBRIUM (Fnet = 0) Newton’s 2nd Law mathematically connects motion of an OBJECT to the forces acting on it. Fnet = ma You should feel comfortable with making FBD’s. Also, when determining Fnet from FBD, NEVER add vertical (up-down) forces with horizontal (left-right) forces. Forces acting in same direction are adding, forces acting in opposite directions are subtracted. 5.1lMASS AND WEIGHT ARE DIFFERENT!-KNOW THE DIFFS! See full page hand out given to you. 5.1m- Spring Force is a good linear/direct relationship, often tested in graph form. Watch out for axis labels though. If F is on y-axis, then the slope is equal to spring constant, k (N/m) Don’t look for spring constant on “List of Constants” from RRT. Each spring has its own k. 5.1n- Centripetal Force acts towards the center of circular path. Centripetal acceleration acts towards the center of circle. Velocity is tangent to the circle. 5.1o- Static friction is “sticky friction” when surfaces don’t slip. The amount of static friction adjusts to match the need of the OBJECT to stay still up to a maximum force. Then, the OBJECT will start to slide. (Picture lifting one end of a board with book on it). Kinetic friction is “sliding friction” when surfaces slide past each other (skidding, skiing, etc…) The amount of kinetic friction remains constant as long as the OBJECT is sliding. 5.1p- IMPULSE is the quantity of force applied to an OBJECT times time (N*s). It is usually involved with collision problems. The amount of impulse imparted to an OBJECT equals its change in momentum. 5.1q- Newton’s 3rd Law-for every action, there is an EQUAL AND OPPOSITE (EAO)reaction. Exam often presents “Compare large thing’s force applied to small with small thing’s force applied to large. (EAO) 5.1r- Momentum is the basic physical quantity of mass times velocity (kg*m/s). It is a vector. The Conservation of Momentum is momentous. If “p” is lost in one object, it is gained in another. Momentum’s variable is “little p”, Power is “big P” (a common mistake) 5.1s and 5.1t- will be discussed on Electricity and Magnetism sheet. 5.1u- The gravitational force between two objects is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL TO THE SQUARE OF THE DISTANCE BETWEEN THEM. Ex: If the distance between two objects is quadrupled (4x), what is the new force? The INVERSEe of 4 is ¼. ¼ SQUARED is 1/16. So the new force would be 1/16 th the original force.