* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy of the pituitary gland
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
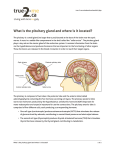
Anatomy of the pituitary gland The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the functions of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalumus (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland) by nerve fibers. The pituitary gland itself consists of three sections: 1 the anterior lobe the intermediate lobe the posterior lobe Functions of the pituitary gland: Each lobe of the pituitary gland produces certain hormones. anterior lobe: 1- growth hormone 2- prolactin - to stimulate milk production after giving birth 3- ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) - to stimulate the adrenal glands 4- TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) to stimulate the thyroid gland 5- FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) to stimulate the ovaries and testes 6- LH (luteinizing hormone) - to stimulate the ovaries or testes 2 intermediate lobe: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone - to control skin pigmentation posterior lobe: 1- ADH (antidiuretic hormone) - to increase absorption of water into the blood by the kidneys 2- oxytocin - to contract the uterus during childbirth and stimulate milk production 3