* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Questions on Chapter 14 –the digestive system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
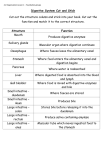
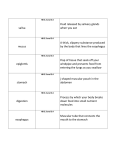
Questions on Chapter 14 –the digestive system I-mention in short *functions of the digestive system *accessory digestive organs * organs of dig. System in sequence *borders of the oral cavity *main functions of tongue *tonsils in oral cavity *the main layers of the wall of alimentary canal *parts of the stomach *sphincters of stomach *curvatures of the stomach *names of omentum *functions of greater omentum *cells of gastric glands and secreation of each *divisions of small intestine *treatment of heart burn *structures that increase surface area of absorptive surface of small intestine *divisions of large intestine *parts of colon *names of salivery glands *important contents of saliva *names of teeth and number of each group *the three regions of tooth *main contents of bile *movements that occur in digestive system *3monosaccharides and 3 disaccharides *the results of chemical breakdown of the 3 main dietary groups *chewing of bread for few minutes leads to sweet taste *enzymes in pancreatic juice *functions of the liver *effects of fever on the body and on pathogens *defecation reflex *phases of deglution II-Define the followings *metabolism *constipation *anabolism *TMR *diarrhea *catabolism *BMR *pyrogens III-fill spaces *GIT begins with ---------------and ends with-------------------*in a cadever,the length of alimentary canal is about-----------------*the cavity cotained by the teeth is called---------------*the m. m. fold which secures the tongue to the floor of the mouth is called--------------.when it is extremely short,it is refferd to as------------------*the ---------- and---------------are common passageways for food and air *the outermost layer of the wall of intestine is called---------------*when stomach is empty,its mucosa is thrown into large folds called---------*digested food leaves stomach as a heavy cream called-----------*chyme enters small intestine through ------------------sphincter *smll intestine begins with-----------------and ends with--------*small intestine is suspended from posterior abdominal wall by----------------- *small intestine joins large intestine at-----------*lymphatic capillaries in villi is called----------------*------------------are local collections of lymphatic tissue in submucosa of small int. *-----------------is the first part of large intestine,it is saclike *-----------------hangs from the cecum ,it is wormlike *-------------------is inflammation of vermiform appendix *---------------and-----------------and ------------------are parts of large intestine that lie in the pelvis *large intestine has two turns called-------------and------------------*------------------anal sphincter is voluntary while the----------------muscle is involutery *goblet cells produce-----------*the wall of large intestine is puckered into small pocketlike sacs called-----------,it is due to contraction of the three bands of longitudinal muscles called----------------*mucus in saliva and mastication helps to bind food together into a mass called-----*inflammation of parotid gland is called-----------------*there are two sets of teeth,the first is called--------------------or--------------------or---------------,its number is-----teeth,it is completed at-------------------years while the second is called----------------teeth,its number is-----------teeth,it begins to appear at----------years *the third molar is called--------------,it erupts between------------and--------*the most common tooth to be impacted is-----------------*the hardest substance in the body is------------------,it covers the----------the -----------of the tooth *the exposed part of the tooth is called-------------while that imbedded in the jawbone is called *the outer surface of the tooth is covered by-------------------which attaches the tooth to the----------------membrane or ligament *-------------------a bonelike material underlies the enamel and forms the bulk of the tooth.It surrounds a centeral cavity called---------------- which contains----------------and------------*--------------------is a soft ,pink ,triangular gland,it extends accros the abdomen from----------------to------------*------------------is a mixed gland *endocrine function of pancreas is production of------------------- and-----------------*---------is the largest gland in the body *------------------is located under the diaphragm,more to the right side of the body *the liver is suspended from the diaphragm and abdominal wall by a ligament called----------*bile leaves the liver through the------------------and enters the-----------------through bile duct *bile salts ----------------fats by breaking large fat globules into smaller ones *-----------------is small,thinwalled green sac in a shallow fossa in the inferior surface of the liver *active voluntary food intake is called-------------*----------------movement moves food back and forth so mixes food with digestive enzymes while---------------squeezes the food along the tract *breakdown of large food particles to their building blocks by enzymes is called------*the building blocks of carbohydrates are--------------while those of proteins are---------------but those of fats are--------------*----------------is the major absorptive site *elimination of indigestible substances via the anus is called----------------------*chemical digestion of starch begins in the mouth by----------------------enzyme *the two major phases of deglution are------------------and---------------*during deglution,tonge blocks the----------------while soft palate closes off the----------------and------------------covers the opening of larynx *food in the stomach and low pH stimulate stomach cells to release------------hormone which increases production of--------------juice *---------protects stomach wall from the effects of HCLand protein digesting enzymes *----------is a gastric protein digesting enzyme,while------------------is another one present in infants which acts primarily on --------------*----------------is protrusion of the superior part of the stomach above diaphragm *when duodenum is filled,----------------------reflex inhibits gastric motility and tightens pyloric sphincter *emetic center is present in--------------------,it is stimulated by local irritants in the --------------or by disturbances of the equilibrium apparatus in the -----------------*brush border enzymes can break----------------into simple sugars by enzymes called-------*---------------- is necessary for absorption of fat soluble vitamins,of which-----------*to make prothrombin, liver needs vit---------*most substances are absorbed by -----------transport except lipids which are absorbed by------------ ----------process *the two major propulsive movements in large intestine are---------------and--------------*---------------is long powerful contraction,3-4 times a day occur in large int. *when rectum is stretched-----------------reflex is initiated *defication reflex causes the wall of-------------to contract and the anal sphincter to--------*the energy value of food is measured by----------------*------------------are the major buildings of cell structures *------------------ is usually broken down to make ATP *--------------------is used to build cell membrane and myelin sheeth *---------------------are carfully conserved by body cells for the future *----------------------is known as blood sugar *O2 using by the cell is called---------------*in hyperglycemia,glucose is stored as-----------------------, a process called------------and if still too high ,it is stored as-----------------------------*in hypoglycemia,glycogen is broken down to--------------,a process called------------*if body uses fat for energy production,intermediate products as-------------and----------------are found in the blood,the condition is called--------------------or----------------.the breath odour become----------* if are not formed by body cells, aminoacids are called------------------they must be taken in diet *if a. acids are used for energy,the amine groups are removed as---------------which combine with --------------in the -------------to form--------------which is removed by the kidneys *--------------------is formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources *the most abundant protein in the blood is-----------------------,it is formed by the---------------And it is responsible for holding fluid in bloodstream by its --------------pressure * %of cholesterol is taken in food while the rest is formed by the -------------*fats cannot circulate freely in blood,they are transported bound to--------------------*lipoproteins are either-------------------or---------------*LDLs are called --------proteins while-----------------are called -----------proteins *high level of LDLs in blood may initiate---------------------*-----------------is the most important factor in determining BMR *the body,s thermostat is in------------------*heat promoting mechanisms include---------------and----------------*heat loss mechanisms include----------------and------------------*------------------and-------------------are hormones secreted by small intestine mucosa .they lead to release of---------------------and---------------*if vasoconstriction in cold weather is prolonged,it may lead to----------------------- *-------------------is a congenital disease in which huge amount of mucus is produced *--------------------is the most common congenital anomaly in digestive system *longitudinal layer in large intestine is reduced to three bands called-------------------*pancreatic juice is rich in-----------------which neutralizes the acid chime *diarrhea is-------------stool while constipation is---------------------*the most common congenital defect in GIT is------------------------- IV-true or false *blood clotting problems occur if either bile or pancreatic juice is absent *alimentary canal is shorter in a living person than in a cadaver *esophagus is only a passageway to food *food moves in esophagus by peristalsis *alimentary canal is surrounded by double layer of serous membrane *stomach lies on the left side of the abdomen *most digestive activity of the stomach occur in the pyloric region *small intestine is the largest section of alimentary canal *large intestine frames the small intestine on three sides *nearly all food absorption occurs in small intestine *no villi are present in large intestine *in large intestine,there are tremendous number of goblet cells *enamel is the hardest substance in the body *dentin forms the bulk of the tooth *pancreas is retroperitoneal organ *pancreatic enzymes can breakdown all categories of food *pancreas is a mixed gland *pancreatic juice is alkaline *liver almost completely covers the stomach *the digestive function of the liver is production of bile *only bile salts and phospholipids(in bile) aid in digestion *cells can actively take aminoacids from blood even if their concentration is more inside the cell *bile does not contain enzymes *while food digestion is not occurring,bile is stored in gall bladder *bile is concentrated in gall bladder by removal of water *when fatty food enters the duodenum,the gall bladder contracts to push bile *hepatitis is most often due to viral infection *liver cirrhosis follows prolonged alcohol drinking *human beings have no cellulase enzyme *active and to a less extent passive transport is needed for absorption *pharynx and esophagus have no digestive function *decrease in mucus secretion in stomach is the main cause of ulcers *esophagus has little mucus protection *heart burn may occur if gastric juice backs up into the esophague *the diaphragm normally reinforces the cardioesophageal sphincter *hiatal hernia is a common cause of heart burn *low pH is necessary for activating pepsinogen to pepsin *absorption starts in the stomach *it takes 4 hours for the stomach to empty completely *high fat diet delays stomach empting *protein and carbohydrate digestion starts before food reaches the dudenum *intestinal juice is relatively enzyme poor *bile is necessary for absorption of fat soluble vitamins *if either bile or pancreatic juice is absent,no fat digestion or absorption occur *proteins and carbohydrates are absorbed by blood capillaries and lacteals *fats are absorbed by lacteals only *the colon produces no digestive enzymes *resident bacteri in large int. can metabolize some nutrients *gasses are produced in large int. due to bacterial effects on remaining nutrients *no absorption occurs in large int. *in large int.,vit. K and B are absorbed * in large int.,most of remaining water is reabsorbed *rectum is generally empty from stool *constipation may lead to water and electrolyte imbalance *fats are the major fuel used normally for making ATP *liver routinely uses fat for making ATP *fats are the most concentrated source of energy *ketosis is a common consequence to no carbohydrate diet *ketosis is a common consequence to uncontrolled diabetes mellitus * ketosis is a common consequence to starvation *cholesterol is never used as a cellular fuel *proteins are not built unless all aminoacids are available *without liver ,we die in 24 hours *cholesterol is the structural basis for vit D *cholesterol is the structural basis for steroid hormones *fatty acids,fats and cholesterol are insoluble in water *energy cannot be created or destroyed *energy intake equals energy output *if external temp. is more than body temp.,heat cannot be lost by radiation *if the air is humid,evaporation is very slow *fever is controlled hyperthermia V-Match table A with table B tableA tableB ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( )amylase )lipase )pepsin )renin )cellulas )gasrin )secretin )CCK )rennin Table A ( 4 )sucrose ( 1 )maltose ( 2 )fructose ( 3 )glucose ( 6 )galactase ( 5 )lactose 1- protein digestion 2- carbohydrate digestion 3- fat digestion 4- kidney enzyme 5- intestinal enzyme 6- not present in humanbeings 7-disaccharidase 8-hormone secreted by stomach 9- hormone secreted by dudenal mucosa 10-hormone contracts gall bladder 11-acts on milk Table B 1-two glucose units 2-fruit sugar 3-blood sugar 4-glucose and fructose 5-glucose and galactose 6-disaccharidase 7-digested by trypsin