* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutation, Evolution, and Natural Selection
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
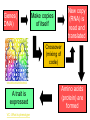
Weekly Schedule- Oct. 11-15 DAY 1 Lesson 21. Identity- DNA Adaptation, Natural Selection, Evolution DAY 2 Lesson 22. Identity- DNA Performance Task- Lab DAY 3 Lesson 23. Identity- DNA Lab (2) Organization of Results Get a laptop (for note taking) Genes( DNA) New copy (RNA) is read and translated Make copies of itself Crossover (mixing of code) www.squidoo.com/geneticsresearch A trait is expressed VC: What is phenotype Amino acids (protein) are formed DNA Cracking the Code VC: Cracking the code copied and read RNA translated http://entomology.wisc.edu/~goodman/wgr...rch.html PROTEIN While the copying of DNA is a very accurate process, what happens when a letter is altered? VC: DNA Mutation GENETIC VARIATION leads to Adaptation Mutation, Evolution, and Natural Selection DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell Http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZK6YP1Smbxk Mutation A mutation is a change in gene sequence. There are many different types of mutations and causes for them. Some mutations are harmful, while others can be beneficial. Harmful Beneficial How does mutations work? DNA is very accurate when making copies of itself, however, sometimes it makes a mistake. Here’s a DNA sequence AGCCCTTATAGGCTC What are the corresponding base pairs? TCGGGAATATCCGAG Now when it’s being copied it replaces the T with a U. Rewrite the your answer with U’s instead of T’s. UCGGGAAUAUCCGAG What amino acids will this be coded for? Serine, Glycine, Isoleucine, Serine, Glutamic Acid The Mutation Here’s our original DNA sequence AGCCCTTATAGGCTC ATCCCTTATAGGCTC we replaced the G with a T Now what are the corresponding base pairs? TAGGGAATATCCGAG Now when it’s being copied it replaces the T with a U. Rewrite the your answer with U’s instead of T’s. UAGGGAAUAUCCGAG What amino acids will this be coded for? Stop, Glycine, Isoleucine, Serine, Glutamic Acid You can see how replacing 1 base will change everything! Who was Charles Darwin? •British scientist that in 1859 published The Origin of Species •Stated that all life come from a common ancestor, called evolution •This happens by a process called natural selection. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nMgLF8n4DnA Voyage of H.M.S. Beagle, 1831 - 1836 90 feet of ship, 74 people living together for 5 years... Darwin Galapagos Evolution Evolution is the change in the inherited traits (passed on from parents to offspring) of a population over many generations. These traits could be physical, chemical or behavioral. This change is caused by mutations in the genes. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yVqJ_mQazik Adaptation Adaptation is the evolutionary process where a population becomes better suited to its habitat. This process takes place over many generations. The term adaptation may also refer to a feature which is especially important for an organism's survival. For example, the adaptation of horses' teeth to the grinding of grass, or their ability to run fast and escape predators. Such adaptations are produced in a variable population by the better suited forms reproducing more successfully, which is natural selection. How does Evolution Work? Natural Selection- survival of the fittest. Natural selection is simply the logical result of four features of living systems: variation - individuals in a population vary from one another (different genes caused by mutations) inheritance - parents pass on their traits to their offspring genetically selection - some variants reproduce more than others time - successful variations accumulate over many generations There are 2 variations of the beetles, green and red. The birds prefer eating the green beetles. Over generations the red beetles increase in population because they are not eaten by the birds. More survive to produce more offspring. Generations later…. Over time the red beetles have been selected over the green beetles Why does this not work? Change through use and disuse Natural Selection’s Explanation Ancestors had different neck lengths Through natural selection, longer necks survived and passed on their genes. Eventually all giraffes had long necks. ONE Ancestor Many Varieties • What are the different types? •What could cause all the variety? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sCEeefdaRcw