* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME - Course Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
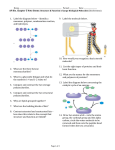
NAME ______________________________ CARBOHYDRATES (K. Riedell) Indicate if each of the following is an example of dehydration synthesis (condensation) or hydrolysis. REACTION #1: _______________________________ REACTION #2: ________________________________ Draw a picture and explain how α- glucose is different from ß-glucose. Why are humans unable to digest cellulose? ____________________________________________________________________ Name the bond that forms when 2 sugar molecules are covalently bonded ________________________________________ Match the description with the correct term A. Disaccharide B. Lactose C. Maltose D. Monosaccharides E. Polysaccharides F. Sucrose _____ Simple sugar _____ General term used to describe a molecule that consists of 100s or 1000’s of simple sugars covalently bonded _____ General term used to describe a molecule that consists of 2 simple sugars covalently bonded _____ Molecule that consists of 2 glucose molecules covalently bonded _____ Molecule that consists of a glucose and a fructose covalently bonded _____ Molecule that consists of a glucose and a galactose covalently bonded * * * * * * * * * * * * * * IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING AS: Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides ______ Sucrose _____ Maltose _____ Galactose ______ Glucose _____ Chitin _____ Lactose ______ Ribose _____ Deoxyribose _____ Starch ______ Cellulose _____ Amylose _____ Amylopectin ______ Fructose _____ Glyceraldehyde ______ Glycogen Listed below are characteristics of FOUR biologically important polysaccharides. Use the key below to indicate the polysaccharide described. You may use them more than once. There may be more than one correct answer. A. CELLULOSE B. CHITIN _______ Polymer of α- glucose _______ Polymer of ß - glucose _______ Polymer of an amino sugar _______ Shows α- 1-4 glycosidic linkages ________ Shows ß-1-4 glycosidic linkages _______ Only linear and unbranched _______ Only branched C. GLYCOGEN D. STARCH * _______ Can be branched or unbranched _______ Storage polysaccharide in animals _______ Storage polysaccharide in plants _______ Structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls _______ Structural polysaccharide in the exoskeletons of arthropods and cell walls of fungi NAME ____________________________ CHAPTER 5 AP BIO - LIPIDS (K. Riedell/Holtzclaw & Holtzclaw study guide) 1. Lipids include fats, waxes, oils, phospholipids, and steroids. What characteristic do all lipids share? 2. What are the 2 kinds of building blocks used to synthesize FATS? 3. Label them on the figure below. 4. Look at the molecule above. How many water molecules will be removed to form it? 5. This process of removing a water molecule to make a bond is called CONDENSATION OR ___________________________________ 6. Draw a fatty acid chain that is 8 carbons long and is unsaturated. Circle the element in your chain that makes it unsaturated, and explain what this means. 7. Why are many unsaturated fats liquid at room temperature? 8. What is a trans fat? Why should you limit them in your diet? 9. List four important functions of fats. 10. IDENTIFY the molecule shown in the diagram below. Label the sketch to show the phosphate group, the glycerol, and the fatty acid chains. Also indicate the region that is hydrophobic, hydrophilic, polar and non-polar. 11. Why is the “tail” hydrophobic? 12. Draw a picture showing the structure of a plasma membrane bilayer containing phospholipids. Label the hydrophilc heads, hydrophobic tails, and location of water. 13. Study your sketch. Why are the tails all located in the interior? 14 Some people refer to this structure as three hexagons and a doghouse. What kind of lipid is it? 15. Give some examples of steroids? NAME ___________________________ AP Biol-PROTEINS (K. Riedell/Holtzclaw & Holtzclaw/Kim Foglia/Lynn Miriello study guides) 1. The monomers of proteins are amino acids. Sketch an amino acid here. Label the alpha or central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, and R group. 2. Explain what the R group means. 3. Sketch two amino acids side-by-side, on one of them label the alpha or central carbon, amino, carboxyl, then show how the two can be joined together. 4. What reaction joins amino acid subunits? 5. What determines the primary structure of a protein? 6. How is a polypeptide different from a protein? 7. Complete the table below comparing the four levels of protein structure. STRUCTURE LEVEL PRIMARY 1° SECONDARY 2° ALPHA HELIX BETA PLEATED SHEET TERTIARY 3° QUATERNARY 4° DESCRIPTION 8. Label each of the levels of protein structure in the figure below. 9. LABEL THE KINDS OF BONDS INVOLVED IN THE 3D STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS 10. What are chaperonins and what is their role in protein structure? 11. What happens to proteins during DENATURATION? Which bonds are disrupted? 12. Name some of the factors that can result in denaturing proteins. NAME ______________________________ AP Biol- NUCLEIC ACIDS (K. Riedell/Holtzclaw & Holtzclaw/Kim Foglia/Lynn Miriello study guides) 1. Name the building blocks of nucleic acids _______________________________ Label the sugar, nitrogenous base, and phosphate group in the diagram shown below 2. COMPARE & CONTRAST NUCLEIC ACIDS: DNA Is it Single/double stranded? Which Nitrogen bases does it contain? Which Nitrogen base is missing? Which Sugar does it contain? Function(s)? 3. Remember we looked at the numbering system for the carbons of a sugar. Label the end of the strand on the left side of the figure below that has the number 5 sugar 5' and the other end of the chain 3'. RNA 4. What two molecules make up the “sides of the ladder” in a DNA molecule? 5. What molecules make up the “rungs”? 6. Which type of bonds hold the nucleotides in the middle together? 7. For the two nucleotides of DNA below, provide the complementary base. Adenine (A) — ________________ Cytosine (C) — ____________________ 8. Explain why the strands are said to be antiparallel? 9. Write the complementary strand for the DNA sequence shown below. Indicate the 5' and 3' ends of the new strand 5'-T A G G C C T-3' .