* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Run Standard Diagnostic Tests
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
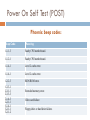
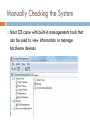
RUN STANDARD DIAGNOSTIC TESTS What is a Diagnostic Test? A diagnostic test is the procedure of examining the state of a computer system hardware or software to locate faults. Built-in Diagnostic tools Each computer system has built-in tools to determine the operating state of the machine. The most common computer problems will be found during these 3 phases: 1. 2. 3. booting the computer loading the operating system manually checking the system. Booting The Computer Booting involves: 1. 2. 3. Turning the machine on Making sure the power LED is on Seeing that the screen reflects the expected activity Involved In this process is the POST or Power On Self Test diagnostic tool. Any fault related to a major component will be detected by POST. Power On Self Test (POST) POST tests every major component that is critical to the computers operation. Power On Self Test (POST) Any faults found during POST will result in either: 1. 2. An error message on the screen A series of beeps called beep codes which are unique to the BIOS manufacture. To view detailed information that POST has gathered you must go into the BIOS. For a Mac system, when you boot the PC will either show a happy face and load, or show a sad face and refuse to load. Power On Self Test (POST) American Megatrends Inc. (AMI) beep codes: Beep Code Meaning 1 beep There is a problem in the system memory or the motherboard. 2 beeps Memory parity error. The parity circuit is not working properly. 5 beeps The system CPU has failed. 6 beeps Keyboard controller failure. 8 beeps Video memory error. The BIOS cannot write to the frame buffer memory on the video card. 9 beeps ROM checksum error. The BIOS ROM chip on the motherboard is likely faulty. 10 beeps CMOS checksum error. Something on the motherboard is causing an error when trying to interact with the CMOS. Continuous beeping A problem with the memory or video. Power On Self Test (POST) Phoenix beep codes: Beep Code Meaning 1-1-1-3 Faulty CPU/motherboard. 1-1-2-1 Faulty CPU/motherboard. 1-1-4-1 Level 2 cache error. 1-1-4-1 Level 2 cache error. 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM error. 1-3-3-1 2-3-1-1 2-3-3-3 2-1-4-3 2-2-1-1 3-1-4-1 3-2-1-1 3-2-1-2 Extended memory error. Video card failure. Floppy drive or hard drive failure. Loading the Operating System Most common faults at this stage are due to failures or mis-configuration in minor hardware as well as system services failing to load. All this activity Is logged and can be viewed at any time. Booting the Operating System If the faults in the OS boot process are so sever that the OS won’t boot most systems offer a restricted or “Safe Mode” as well as recovery tools. Manually Checking the System Most OS come with built-in managements tools that can be used to view information or manage hardware devices. Manually Checking the System Some common diagnostic tools offered by Microsoft Windows OS are: Device Manager Event Viewer Check Disk (chkdsk) Windows Services Memory Diagnostic Performance Monitor Task Manager Disk Defrag Common Problem Scenario System appears dead Listen to the power supply and determine if the internal fan starts up. If the fan does not start up then the cause of the problem could be: 1. The system is not plugged into a power outlet, or the outlet has no power. 2. The power supply unit is faulty. 3. There is an internal short circuit and the fan does not start as a protective measure. 4. The computer is dead! Common Problem Scenario No Video No video appears on the screen when the system is performing its POST. Things to consider: 1. Video card is faulty — swap it out with a known good card. 2. There is a fault in the motherboard. 3. The video card is not inserted correctly. 4. The monitor is turned off or has no power. Common Problem Scenario No boot device or unable to boot. The system could not find a bootable device; the most likely cause is the hard disk drive. Things to consider: 1. Missing boot files — they may have been deleted by the user. 2. A virus has caused damage to the boot files or has corrupted the file system or Master Boot Record (MBR). 3. A common mistake is a floppy disk being left in the drive. 4. Cables not connected to hard disk drive properly. Common Problem Scenario System hangs / locks up One of the most difficult problems with personal computers occurs when it appears as though a system is not responding to any user input. Possibilities are: 1. Faulty memory (RAM) — you could turn memory testing on in CMOS settings which may confirm the problem, or perform a rigorous test using third-party diagnostic software. 2. Conflict with devices — you should check the systems properties information available on you operating system platform, for any messages or indications of conflict. 3. Device driver is faulty — try to isolate the problem occurrence to when a particular device is in use, such as a scanner or printer. A driver update may be a solution. Common Problem Scenario The Operating System has become unstable. The most reliable solution is to reinstall the operating system. Alternatively you may be able to restore to a backup of the system, where performance levels were known to be good. Fault Finding Procedures Communicate Experienced technicians can ask a few pointed questions to isolate the cause of a problem. A history can be established e.g. What worked before, What has changed, What works now. Fault Finding Procedures KISS Principle Keep It Simple Stupid, Look for the simple things first. If a system doesn’t start check if the power is on. If nothing displays on a monitor try another one. If you suspect a video card fault swap it with a known good one. If the mouse-pointer movement seems erratic, then turn the mouse over and clean the rollers, if it still is not working properly then replace it with a new mouse. Fault Finding Procedures POST Card / Diagnostic Card Where a system does not boot, or appears to be dead, there are some specialist interface cards that can be used to diagnose the problem. A set of LEDs display a code that can be referenced from the manual. Preventative Maintenance The best way to avoid many of the issues discussed is to undertake preventative maintenance. Preventative Maintenance When we undertake maintenance we aim to: preserve our IT systems in optimal condition fix problems that occur upgrade the existing systems to minimise future risks to the business. Preventative Maintenance The idea of preventative maintenance to prevent a future problem from occurring. Most of us do this every year or so when we get our cars serviced, their usually isn’t anything wrong with the car in its current state but if the oil, filters, spark plugs aren’t replaced now then they might cause a problem in the future. Reactive Maintenance Reactive Maintenance Reactive maintenance is the process when a problem is fixed after it has occurred. If you get a flat tyre and get it replaced its reactive maintenance. If your monitor explodes then you replace it. Preventative Maintenance Electrical damage can be prevented using surge protected power boards and uninterruptable power supply (UPS) Environmental damage can be prevented by using good ventilation and air-conditioning. Data lose can be prevented by backing up user data and configuration files as well as implementing anti-virus software. Software issues can be prevented by keeping software updated with patches and service packs.
























![Stanley ANSWERS Lesson_15_Task_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003579435_1-9c4d1c0f6e255ef449386e78ad60ddaa-150x150.png)









