* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STM Scanning tunneling microscope History
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
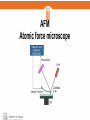
Molecular spectroscopy and reaction dynamics Group III Sigtryggur Bjarki Sigtryggsson Styrmir Svavarsson Úlfar Þór Björnsson Árdal STM Scanning tunneling microscope History • The STM was invented 1981 by Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer. • They received the Nobel prize in physics in 1986 for the STM • The STM was first used in showing its atomic scale resolution in a image of silicon 7x7 restructed (111) surface. Theory • STM works on the principles of tunneling • Electrons can not transfer between the tip of the STM and the sample because there is an energy barrier. • When a voltage is imposed between the two, the shape of the energy barrier changes and electrons can move from the sample to the tip wich results in a small current if the distance is sufficiently small The probability distribution is given by: Ψ 2 𝑧 = 𝑒 −2𝜅𝑧 The current is proportional to: 2 𝐼∝Ψ Where z is the distance and к is given by: 1 2𝑚(𝑈 − 𝐸) 2 𝜅= ℎ Where U is the potential energy, h is the planck‘s constant and E is the energy of the electron . • The tip used is usually made out of tungsten or a palladium-iridium alloy where at the very end of the tip there is only one atom. • The positioning of the tip is changed using array of piezoelectrics. • Piezoelectric materials change shape when a electric field is applied on them. The STM can be operated in two different ways: Constant current mode or constant voltage mode. • In constant current mode the voltage is kept unchanged and the vertical position of the tip is changed to maintain a constant current while scanning over the sample. • In constant voltage mode the vertical position of the tip is kept constant while the current is changed by changing the voltage bias (difference) • The constant voltage mode is faster. • The constant current mode shows contrast directrly related to electron charge density profiles. AFM Atomic force microscope • Contrary to the STM wich can only scan elictricly conducting surfaces the AFM can scan all surfaces. • The AFM measures short distance forces using a cantilever wich is monitored with laser beam pointed at the tip of the cantilever as the schematic picture shows. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4VW767Qh 6sQ