* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Giessler/Crookes Tube and Cathode Ray
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Chien-Shiung Wu wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
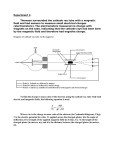
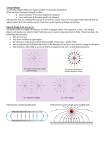
This is very good, se my comments and delete/move/reword things. Please do not make copies until we agree on the details. Eugenia Giessler/Crookes Tube and Cathode Ray Activity This is not an observation activity, this is the whole cycle, right? Delete the underlined, you need to start from observations, this statement should be later, after observations are done, nobody knew about the rays until the first experiments, right? Directions: How will they know what cathode rays are? You need to start with the observations of the glass tubes that led to the idea of the rays. You need to delete the first sentence and only leve the last one, in bold now. Record all observations for each experiment and reason through a possible explanation for the phenomena observed in the tubes. Do you mean come up with explanations? Drawing conclusion is not a scientific term.about the nature of the cathode rays. Delete the underlined. Experiment #1 This observational experiment was made in a bent Giessler tube. The lower case “g” is where the most intense phosphorescence occurs. The intense area of phosphorescence is located directly across the cathode of the Giessler tubes. In the picture below, What are they going to see here? May be you need to describe some of the observations that were made without using the words cathode rays at all. (insert pic) Experiment #2 This observational experiment is made in a Giessler tube with a Maltese cross in the middle of the tube. The picture below shows what is made after the cathode rays hit the cross and the back of the Giessler tube. What are the possible explanations for what was observed? If possible conduct the simulation online here http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/electromag/java/crookestube/ Or examine the pictures below. What kind of an experiment is it? Observational or testing? Specify. Testing Experiment #3 Utilizing the information from Experiments #1 and #2 make a prediction about the nature of the phenomena observed in experiment #1 and #2. Examine the phenomena’s interaction with a magnet. Observe what happens to the phenomena when a bar magnet is placed near it. This was probably already a testing experiment because they were thinking of what the rays could be, so you need to have students come up with the explanations and they decide how they can test them, ok? Bar Magnet S N S Examine the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. What does this information tell us about the magnetic field entering the cathode’s path? S N Testing Experiment #4 Predict what will happen as a magnetic field approach an electromagnetic wave. Examine the interactions of electromagnetic waves and magnetic fields. Observe what happens when a magnet is placed near the path of a laser pointer. Does this experiment disprove or prove anything about the prediction in experiment #3? Revise or restate your prediction if necessary from Experiment #3. Testing Experiment #5 Predict what will happen to the phenomena when it enters an electric field. For this particular device, when the DC voltage is set to - 50 V the bottom plates are positively charged and the upper plates are negatively charged. Examine the cathode rays interactions with an electric field. Adjust the potential difference between the parallel plates on the cathode rays. Observe what happens as the potential changes as the rays pass through the plates. How do these observations compare with your predictions? Conclusion How can you explain what cathode rays are? Are these cathode rays light? Justify why/why not?