* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MSE15
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
MSE15
Time:03 Hours
Max. Marks: 150
Booklet No: ________________
Roll No:_________________
Name of the Candidate: _________________________________________________________________
(in capital letters)
Name of the Centre : __________________________________________________________________
Signature of the Candidate
Instructions
1.
Fill up the information above with a Pen/Ball Point Pen (Black or Blue).
2.
The answer sheet is placed inside the test booklet. Without breaking the seal of the Test Booklet, take the
Answer Sheet out. Don’t break open the seal until you are asked to do so.
3.
There are 150 questions. Each correct answer gets a score of one mark. There is no negative marking.
4.
Each question is followed by four answers. You should select one answer from A, B, C or D considered by
you as the most appropriate or correct answer and color the appropriate circle using a black or blue ball
pen.
5.
Do your rough work only on the blank pages provided at the end of the question booklet.
6.
Mobile phone, calculators, calculator-watch, slide rules, mathematical table, etc. are not allowed in the
examination hall.
7.
Make sure that you do not possess any pages (Blank or Printed) or any unauthorized material. If such
material is found in your possession during the examination, you will be disqualified from entrance
examination.
8.
If you are found copying/helping others you will be disqualified from the entrance examination.
9.
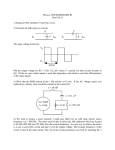
Do not leave examination hall until you have recorded your attendance and submitted the Answer Sheet
to the Invigilator.
10.
You are not allowed to leave the examination hall till the end of the examination.
11.
Ensure that there are 48 pages in this Test Booklet (including front and back page).
12.
At the end of examination, candidate is permitted to take the question booklet.
P.T.O
2
Useful constants
Electron mass (m0)
: 9.10 × 10-31 kg
Electron charge (q)
: 1.60 × 10-19 C
Planck‘s constant (h)
: 6.62 × 10-34 m2kg/s
Boltzmann constant (kB)
: 1.38 × 10-23 J/K
Permittivity of free space (𝜀0 ) : 8.85 × 10-12 F/m
Permeability of free space (𝜇0 ) : 4π × 10-7 H/m
3
4
001. A unit vector orthogonal to both ⃗
⃗
⃗⃗
√
̂ ̂
̂
B.
√
̂ ̂
̂
C.
002.
̂ and ⃗⃗
̂ ̂
̂
A.
D.
̂
√
̂ ̂
̂
√
( )
is identical to ---------------------------
for -1 < x < 1
A.
B.
C.
D.
003. If the given matrix
(
is orthogonal, then
)
can have which of the following value
A. √
B. 0
C. 1
D.
√
5
004. If one of the eigen values of matrix [
] is 2, then what is the normalized eigen
vector corresponding to this eigen value?
1 1
A. 0, ,
2 2
1 1
,
B. 0,
2 2
1 1
C. 0, ,
2 2
D. 0, 1, 0
005. Match the application to the appropriate numerical method.
P1: Numerical integration
M1: Newton-Raphson Method
P2: Solution to a transcendental equation
M2: Runge-Kutta Method
P3: Solution to a system of linear M3: Simpson‘s 1/3-rule
equations
P4: Solution to a differential equation
M4: Gauss Elimination Method
A. P1—M3, P2—M2, P3—M4, P4—M1
B. P1—M4, P2—M1, P3—M3, P4—M2
C. P1—M2, P2—M1, P3—M3, P4—M4
D. P1—M3, P2—M1, P3—M4, P4—M2
006. In the limit x 0 the function f ( x)
A.
B.
C.
D.
sin( Gx)
takes the value
sin( x)
zero
one
G
Infinity
007. The average value of the function ( )
A.
B.
C.
D.
in the interval 1 to 3 is
40
15
80
20
6
008. The solutions of the differential equation given below are
x2
d2 y
dx
2
A.
B.
C.
D.
x
dy
( x2 n2 ) y 0
dx
Legendre Polynomials
Bessel Functions
Hermite Polynomials
Laguerre Polynomials
009. The Newton Raphson Method is used to solve the equation f ( x) x 3 5 x 2 5 x 8 0 .
Taking the initial guess as x 5 , the solution at the end of the first iteration is
A. 5.566
B. 6.764
C. 4.434
D. 3.236
010. A phasor (complex number) is given by a 1120 . The value of a 2 is
A. 1 - j0.866
B. 0.5 - j0.866
C. - 0.5 - j0.866
D. - 0.5 j0.866
1
1
1 3i 1 3i
011. Evaluate
A. - 3
5
B.
3
4
C.
3
5
D. - 3
4
7
012. The value of
z
A.
B.
6i
8
1
3i
16
C.
8
D.
z3 6
dz is
2z i
6i
1
3i
16
013. Laplace transform of ( )
A.
B.
C.
D.
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
is
014. A unit normal to the surface 2 x 2 4 yz 5z 2 10 at the point P (3, -1, 2) is
A.
3i 2 j 6k
7
B.
3i 2 j 6k
7
C.
3i 2 j 6k
49
D.
3i 2 j 6k
49
015. The inverse Laplace Transform of F (s)
6
s 6s 9
2
3t
A. 6te
B. 6e 3t
C. 8e 3t
D. 9te 3t
8
is
016. The Fourier Transform of a function f (t ) e a t is given by
2
A.
B.
C.
a 2
2a
2
a2 2
2 j
a2 2
1
D.
a j
017. A uniform plane wave in air is incident on an infinitely thick glass slab, refractive index
1.5. The percentage of power reflected from the glass air interface is
A. 0
B. 20
C. 10
D. 4
018. Consider light passing through a polarizer analyzer pair, in which the analyzer pass axis is
at an angle of 45 degrees to that of the polarizer. An optical component introduced
between the polarizer and analyzer can make the output intensity zero. The component
can be a
A. quarter-wave plate
B. plane glass sheet
C. full-wave Plate
D. half-wave plate
019. According to Debye theory, the specific heat of a solid is proportional to
A. T 3
B. T 0
C. T 2
D. T 5
9
020. The fundamental frequency (ω) of string of length L, tension T and mass per unit length µ
is given by
A.
T
L
B.
C.
T
T
L
D. L
T
021. ‗Zero point energy‘ is a result of
A. Relativity effects
B. Pauli‘s exclusion principle
C. Uncertainty principle
D. Energy conservation
022. The torque on a particle at position r with momentum p is given by
dp
A. p
dt
dr
B. r
dt
dp
C. r
dt
d d p
D.
r
dt
dt
10
023. The de-Broglie wavelength of particles with mass m and average momentum ⃗ at a
temperature T in three dimension is given by
A.
h
2mk BT
B.
h
3mk BT
C.
h
2m
D.
h
2k BT
024. In C language, what is the output of the following code
main()
{
int i=-3,j=2,k=0,m;
m=++i||++j&&++k;
printf("\n%d%d%d%d",i,j,k,m);
}
A. -2 2 1 0
B. -2 2 0 1
C. -2 3 1 1
D. -2 3 0 0
025. Using hierarchy of operations in C language, what would be the value of integer i in the
following expression?
i=2*3/4+4/4+8-2+5/8
A. 7
B. 1
C. 0
D. 8
11
026. In C language, what is the output of the following code?
main()
{
int arr[]={12,13,14,15,16};
printf("\n%d%d%d", sizeof(arr),sizeof(*arr),sizeof(arr[0]));
}
A. 10 2 2
B. 5 2 2
C. 4 1 1
D. 5 1 1
027. In C language, what is the output of the following code?
int main()
{
int ***r, **q, *p, i=8;
p = &i;
q = &p;
r = &q;
printf("\n%d%d%d", *p, **q, ***r);
}
A. 7 7 7
B. 6 6 6
C. p q r
D. 8 8 8
12
028. In the C program mentioned below, how many times does "abcd" get printed?
int main()
{
int x;
for(x=-1; x<=10; x++)
{
if(x < 5)
continue;
else
break;
printf("abcd");
}
return 0;
}
A. 11 times
B. 10 times
C. 0 times
D. infinite times
029. Which of the following is an example of line defect in crystals?
A. vacancies
B. staking faults
C. interstitials
D. dislocations
030. The second energy state of a particle of mass ‗m‘ in a one-dimensional box of length ‗L‘ is
A.
h2
8mL2
B.
h
2mL2
C.
h2
2mL2
D.
h
2 mL
13
031. In a crystalline solid, the energy band structure (E-k relation) for an electron of mass m is
h 2 k (5k 8)
given by E
The effective mass of an electron in the crystal is
8 2 m0
A. 8m0
B. 2m0
C.
2m0
5
D.
m0
5
032. Consider a doped semiconductor having electron and hole mobilities µn and µp
respectively. Its intrinsic carrier density is ni. The electron concentration n for which the
conductivity is minimum at a given temperature is
A.
( )
B.
( )
C.
(√ )
D.
(√ )
033. An n-type silicon bar is 0.1 cm long and 100 μm2 in cross-sectional area has a majority
carrier cocentration of 5×1020 /m3 and the carrier mobility is 0.13 m2/V-s at 300 K. If the
charge of an electron is 1.6×10-19 C, then the resistance of the bar is
A. 104 Ω
B. 10-1 Ω
C. 106 Ω
D. 10-4 Ω
14
034. Mobilities of electrons and holes in a sample of intrinsic germanium at room temperature
are 0.36 m2/V-s and 0.17 m2/V-s respectively. If the electron and hole densities are each
equal to 2.5x1019 m-3, the resistivity of germanium is
A. 0.70 Ω.m
B. 1.47 Ω.m
C. 2.12 Ω.m
D. 0.47 Ω.m
035.
A diode that has a negative resistance characteristic is the
A. Tunnel diode
B. Zener diode
C. Varactor diode
D. LED
036. If mobility of an electron in Si at 300 K is 1200 cm2/V.s, then the diffusion coefficient of
the electron is
A. 31.01 m2/s
B. 15.50 m2/s
C. 31.01 cm2/s
D. 15.50 cm2/s
037. Solar energy travels through space by the process of
A. convection
B. radiation
C. conduction
D. transportation
038. An n-type bar of silicon having cross sectional area 1.0 mm2 has an effective carrier
density 1016 /cm3. What is the drift velocity of electrons if 50 mA current is flowing
through the bar?
A. 3.125 × 103 cm/s
B. 3.125 × 105 cm/s
C. 3.125 × 109 cm/s
D. 3.125 × 107 cm/s
15
039. The effective mass of an electron in GaAs is m* 0.0852 m0 . What is the thermal velocity
of electrons in GaAs at room temperature?
A. 7.26 × 105 m/s
B. 4.00 × 105 m/s
C. 5.65 × 105 m/s
D. 8.70 × 105 m/s
040. Schottky defect is
A. a line defect in ionic crystal
B. a point defect in metals
C. a point defect in ionic crystals
D. a line defect in metal
041. Built-in potential of silicon p-n junction with doping densities Na and Nd at 300 K
A.
(
B.
( )
C.
(
D.
(
)
)
)
042. Pinch-off voltage in JFET is
A. the gate to source voltage that gives unity drain current
B. a drain voltage that gives zero drain current
C. the gate to source voltage that gives zero drain current
D. the drain voltage that gives infinite drain current
16
043. In a ruby laser, laser action is due to
A. oxygen atoms
B. Al2O3 crystal
C. aluminum atoms
D. chromium atoms
044. A voltage of 2.5 V is applied along the length 100 nm long with cross-sectional area
0.01 µm2. If the material is doped with Nd = 1018 /cm3, what is the current density?
( mobility of electron is
)
A. 9.25
104 mA/cm2
B. 9.25
106 mA/cm2
C. 9.25
106 A/cm2
D. 9.25
104 A/cm2
045. Consider an abrupt pn junction. Let Vbi be the built-in potential of this junction and VR be
the applied reverse bias. If the junction capacitance Cj is 1 pF for Vbi+VR = 1V, then for
Vbi+VR = 4V, Cj will be
A. 0.5 pF
B. 4.0 pF
C. 2.0 pF
D. 0.25 pF
046. Consider a p-n junction, the doping concentrations on the p side and n side are
NA = 9 × 1016 /cm3 and ND = 1 × 1016 /cm3 respectively. The p-n junction is reverse biased
and the total depletion width is 3 μm. The depletion width on the p side is
A. 0.3 μm
B. 2.7 μm
C. 0.75 μm
D. 2.25 μm
17
047. Early effect in a bipolar transistor refers to a reduction of the effective base width caused
by
A. electron hole recombination at the base
B. the reverse biasing of the base collector junction
C. the forward biasing of emitter base junction
D. the early removal of stored base charge during saturation to cut-off switching
048. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor under equilibrium is
A. inversely proportional to the doping concentration
B. directly proportional to the doping concentration
C. inversely proportional to the intrinsic concentration
D. directly proportional to the intrinsic concentration
049. An electron beam consisting of electrons with velocity ⃗
0 ̂ passes through a space
2
with magnetic field of ⃗⃗
̂ weber/m and electric field ⃗⃗
̂
V/m. If the force due to the two fields is equal and opposite the value of 0 is
A. 3.4 104 m/s
B. 6.8 104 m/s
C. 1.7 107 m/s
D. 4.25 105 m/s
050. An ammeter of resistance 1.5 can measure currents up to 5 A. In order to measure a
maximum current of 30 A, the value of a the shunt resistance to be added is
A. 0.25
B. 0.15
C. 0.3
D. 0.1
18
051. The full scale deflection of a millivoltmeter which has a resistance of 40 is 800 mV. To
convert this millivoltmeter into a milliammeter, a shunt resistance of 10 is connected.
The new full scale deflection is for a current of
A. 0.01 A
B. 100 mA
C. 10 mA
D. 1 A
052. The resistance of a nickel coil at 20 C is 25 and it rises to 37.5 when the coil is
immersed in a liquid. If the temperature coefficient of nickel at 20 C is = 0.00625 /K,
what is the temperature of the liquid?
A. 80 C
B. 100 C
C. 120 C
D. 40 C
053. In a circuit consisting of R, L, and C in series, the Q-factor is
A.
R
LC
1 C
B.
R L
L
C. R
C
1 L
D.
R C
054. The voltage (V0) across the 2 Ω resistor shown in figure is
A. 2.5 V
1Ω
1Ω
B. 5 V
C. 10 V
10 V
D. 7.5 V
+
I
2Ω
A
S
+
V0
B
19
055. In the circuit shown in the figure, what should be the value of RL for maximum power
transfer?
A. 50 Ω
B. 65 Ω
C. 73 Ω
D. 13 Ω
056. A series RLC circuit has a resonance frequency of 12000 Hz. If R = 5 Ω and if X L at
resonance is 300 Ω then the bandwidth is
A. 2 kHz
B. 400 Hz
C. 4 kHz
D. 200 Hz
057. If each branch of a Delta circuit has impedance 5Z , then each branch of the equivalent Y
circuit has impedance
A. 5Z
B. 5 5Z
C.
D.
Z
5
Z
5
20
058. A series RC circuit is connected to a DC voltage source at time t=0. Which of the
following represents the current i(t) ?
059. The Q-factor of a parallel resonance circuit consisting of an inductance of value 1 mH,
capacitance of value
and a resistance of 100 Ω is
A. 100
B.
C. 10
D. 1
060. The voltage across an inductor is given by ( )
inductor, assume inductance of inductor to be
A.
(
B.
(
C.
(
D.
(
)
)
)
)
21
V at
Find the current across
061. A d.c. constant voltage source feeds a resistance of
in series with
capacitor.
Find the time taken for the capacitor when charge retained will be decayed to 50% of the
initial value.
A.
(
)
B.
(
)
C.
( )
D.
(
)
062. The ‗Z‘ parameters of the network shown is
A. *
B. *
+
C. *
+
D. *
063
+
+
Voltage across the 5 A source in the given circuit is?
A. 12.5 V
B. 20 V
C. 25 V
D. 17.5 V
064. A lamp rated 10 W, 50 V is proposed to be used in a 110 V system, the wattage and
resistance of the resistor to be connected in series with the lamp is
A. 12 W, 300 Ω
B. 10 W, 250 Ω
C. 15 W, 300 Ω
D. 10 W, 300 Ω
22
065.
The current I, in the figure shown below is
A. 3 A
B. 6 A
C. 1 A
D. 2 A
066.
KCL is a consequence of the law of conservation of
A. energy
B. flux
C. charge
D. all of the above
067. The resistance between opposite faces of a 1 m cube is 1 Ω. If the length is increased to
2 m with the volume remaining the same, then the resistance between the opposite faces
along its length is
A. 4 Ω
B. 1 Ω
C. 2 Ω
D. ½ Ω
068. A source voltage of 10 V is applied to a series resonant circuit LCR, where R = 5 and
L = 2 mH. If the resonant frequency is 5 kHz, the voltage across L or C at resonance is
A. 154 V
B. 197.3 V
C. 105.9 V
D. 125.6 V
23
069. A transistor with a forward current gain hf of 150, is connected to a load. The load consists
of a tank circuit with L= 400 µH and 10 , and C = 200 pF. If the input resistance is
3 k, the voltage gain will be
A. 5,500
B. 2,750
C. 6,500
D. 10,000
070. For op-amp having a slew rate of SR = 2 V/µs, the maximum closed loop voltage gain
that can be used when the input signal varies by 0.5 V in 10 µs is
A. 4
B. 20
C. 40
D. 2
071. An amplifier has an operating bandwidth given by ‗BW‘. If ‗n‘ stages of such amplifier
are cascaded, the bandwidth will become
A.
BW
1
2n 1
B. n.BW
C. BW . 2 n 1
D.
BW
2n 1
072. The second harmonic distortion in an amplifier is reduced from 5% to 1% due to negative
feedback. The amplifier gain is 1000, the feedback ratio will be
A. 0.008
B. 0.02
C. 0.01
D. 0.004
24
073. A Zener regulator has an input voltage that varies from 15 to 20 V and a load current that
varies from 5 to 20 mA. If the Zener voltage is 6.8 V, the maximum value of series
resistor is
A. 410
B. 660
C. 320
D. 570
074. An amplifier comprises of four stages in CE configuration and the overall gain is 9 104.
If the first two stages have a voltage gain of 20 per stage and other two stages are
identical, the gain per stage of other two stages is
A. 22
B. 30
C. 18
D. 15
075. In the given figure what is the base current if
?
A.
B.
C.
D.
076. A forward voltage of 9 V is applied to a diode in series with a 1 kΩ load resistor. The
voltage across load resistor is zero. It indicates that
A. diode is open circuited
B. diode is short circuited
C. resistor is open circuited
D. diode is either short circuited or open circuited
25
077. If an op-amp has open loop voltage gain
and internal output impedance
(without feedback)
, then the closed loop voltage gain and output impedance
respectively are
A.
B.
C.
D.
078. The closed-loop voltage gain of the amplifier when
and
is
A. 20
B. 0
C. 21
D. 150
079. In a Op-Amp, a very high value of CMRR(common-mode rejection ratio) means that the
A. open-loop differential voltage gain is low and the common-mode gain is high.
B. open-loop differential voltage gain is high and the common-mode gain is high.
C. open-loop differential voltage gain is high and the common-mode gain is low.
D. open-loop differential voltage gain is low and the common-mode gain is low.
26
080. For the voltage divide circuit used to bias a silicon transistor shown in figure, the values of
emitter voltage and collector emitter voltage are (Given IC = IE )
A. 4.1 V, 9.0 V
B. 4.1 V, 13.0 V
C. 12.5 V, 9.0 V
D. 12.5 V, 13.0 V
081. In a Wein-bridge oscillator, positive feedback circuit is
A. an LC circuit
B. a voltage divider
C. a lead-lag circuit
D. an RL circuit
082. For a JFET, with parameters I DSS 3.0mA , VGS off 6V (max) and g m0 max 5000μS at
VGS = -4V the forward transconductance and ID are
A. 667 µS, 233 µA
B. 5000 µS, 233 µA
C. 500 µS, 233 µA
D. 1667 µS, 333 µA
083. If (734)8 = (x)16 , the value of x is
A. D C 1
B. C 1 D
C. 1 D C
D. 1 C D
27
084. In the circuit shown diodes D1, D2 and D3 are ideal and the inputs E1, E2 and E3 are 0 V for
logic 0 and 10V for logic 1. What logic gate does the circuit represent?
A. 3 input OR gate
B. 3 input AND gate
C. 3 input NOR gate
D. 3 input XOR gate
085. Which of the following is the fastest logic family?
A. TTL
B. ECL
C. CMOS
D. LSI
086. How many Select lines will a 32: 1 multiplexer have?
A. 8
B. 9
C. 4
D. 5
087. The logic circuit given below converts a binary code y1y2 y3 into:
A. BCD
B. gray code
C. excess-3
D. hamming
28
088. Simplify the Boolean expression F = C(B + C)(A + B + C).
A. C
B. A
C. B
D. ABC
089. A 4-bit synchronous counter uses flip-flops with propagation delay times of 15 ns each.
The maximum possible time required for change of state will be
A. 30 ns
B. 45 ns
C. 60 ns
D. 15 ns
090. The binary equivalent of decimal 5.375 is
A. 101.10111011
B. 101011
C. 101.011
D. 010111
091. Convert the following SOP expression to an equivalent POS expression.
̅ ̅
A. (
B. (
)(
̅
̅
)( ̅
̅
̅
)( ̅
̅
̅)
)( ̅
̅
)
C. (
)(
̅
)(
̅
̅)
D. ( ̅
)( ̅
̅
)(
̅
)
29
̅̅
092. How many gates would be required to implement the following Boolean expression
before simplification?
(
)
(
)
A.
B.
C.
D.
093. Half Adder can be implemented by using ‗k‘ NAND gates. The value of ‗k‘ is
A.
B.
C.
D.
094. The output of a logic gate is 1 when all its inputs are at logic 0. The gate is either
A. OR or EX-NOR
B. NAND or EX-OR
C. AND or EX-OR
D. NOR or EX-NOR
095. The output Y of the circuit below is ‗1‘ when
A. two of more of the inputs P, Q, R are ―1‖.
B. two of more of the inputs P, Q, R are ―0‖.
C. any odd number of the inputs P, Q, R is ―0‖.
D. any odd number of the inputs P, Q, R is ―1‖.
30
096. What is the largest value of output voltage from an eight- bit DAC that produces 1.0 V for
a digital input of 00110010?
A.
B.
C.
D.
097. Simplify the Boolean function
̅
A.
B.
C.
D.
098. Interfacing devices for DMA controller , programmable interval timer are respectively
A. 8253, 8259
B. 8257, 8253
C. 8257, 8251
D. 8251, 8259
099. The speed of a microprocessor depends on
A.
B.
C.
D.
clock
data bus width
size of register
address bus width
100. The status that cannot be operated by direct instruction is
A.
B.
C.
D.
AC
CY
Z
P
31
101. In an 8086 microprocessor, which one of the following instructions is executed before an
arithmetic operation?
A. AAM
B. DAS
C. DAA
D. AAD
102. In a microprocessor, the service routine for a certain interrupt starts from a fixed location
of memory which cannot be externally set, but the interrupt can be delayed or rejected.
Such an interrupt is
A. non maskable and vectored
B. maskable and non-vectored
C. non maskable and non-vectored
D. maskable and vectored
103. In a 16-bit microprocessor, words are stored in two consecutive memory locations. The
entire word can be read in one operation provided the first
A. word is even
B. memory address is even
C. word is odd
D. memory location is odd
104. The ESC instruction of 8086 may have two formats. In one of the formats no memory
operand is used. Under this format, the number of external op-codes (for the co-processor)
which can be specified are
A. 256
B. 512
C. 128
D. 1024
32
105. The first microprocessor to include Virtual memory in the Intel microprocessor family
was
A. 80286
B. 80386
C. 80486
D. Pentium
106. Which of the following instructions of an 8086 microprocessor uses the content of a CX
register as a counter?
1. LOCK
2. LOOP
3. ROTATE
A. Only 1 and 3
B. Only 1 and 2
C. 1,2 and 3
D. Only 2 and 3
107. In 8085 , if the clock frequency is 5 MHz, the time required to execute an instruction of 18
T-states is
A. 3.0 µs
B. 3.6 µs
C. 4.0 µs
D. 6.0 µs
33
108. In the following 8086 program given below
MOV AX, 7000 H
MOV DS, AX
MOV SI, 0200H
MOV DI, 0500H
MOV CX, 0078H
BACK: MOV AL, [SI]
MOV [DI], AL
INC SI
INC DI
DEC CX
JNZ BACK
HLT
How many times (decimal) is the DEC CX executed:
A. 78
B. 119
C. 77
D. 120
109. For the 8085 assembly language program given below
3000 MVI A, 45 H
3002 MOV B, A
3003 STC
3004 CMC
3005 RAR
3006 XRA B
3007 HLT
The content after the execution of the program is:
A. 67 H
B. E7 H
C. 45 H
D. 00 H
110. Which one of the following modes is required for 8253 to generate a square wave?
A. MODE 3
B. MODE 1
C. MODE 2
D. MODE 4
34
111. The 8086 and 8253 run at 6 MHz and 2 MHz respectively. How many numbers of T-states
are required to generate a square wave of period 0.5 ms?
A. 1000 states
B. 3000 states
C. 6000 states
D. 2000 states
112. Consider the following instruction executed in 8086 microprocessor:
LOAD X
ADD Y
STORE S1
LOAD Y
MULT X
ADD S1
STORE Z
The value stored in Z is
A. Z = X+Y+YX
B. Z = X+Y + XY+ S1
C. Z = XY+S1
D. Z = X+Y+S1
113. In a certain medium the Electric field of a propagating plane wave is given by
E 10 cos(108 t 3 y ) xˆ V/m. The medium is
A. free space
B. a lossless dielectric
C. a lossy dielectric
D. a good conductor
114. The Polarization in a dielectric material can be written as
A. P ( r 1)E
B. P 0 ( r 1)E
C. P 0 r E
D. P 0 ( r 1)
35
115. The ratio of conduction current density to displacement current density is
A.
j
B.
j
C.
j
D.
j
116. The electric field of a plane wave propagating in free space is given by
E E 0 (-0.5 xˆ Ayˆ )e j[t k0 ( 0.866x 0.5 y )] V/m. The value of A is
A. 0.866
B. -0.866
C. zero
D. 0.5
117. A cylindrical conductor of radius 0.5 m carries a current with uniform current density
J 4e 2r zˆ A/m2. The magnetic field inside the conductor is given by
1
r
1
r
1
[1 e 2 r 2re 2 r ]φ̂
4r
1
[1 e 2r ]φ̂
4r
A. H [1 e 2 r 2re 2 r ]φ̂
B. H [1 e 2r ]φ̂
C. H
D. H
118. For an air filled rectangular waveguide of dimensions 2.5 cm x 1.2 cm, the cut-off
wavelength of the dominant mode is
A. 2.4 cm
B. 5.0 cm
C. 2.5 cm
D. 3.7 cm
36
119. The attenuation in a typical optical fiber is 0.6 dB/km at 1310 nm wavelength. If 100 W
power is launched into the fiber at 1310 nm, the power (in W ) in the fiber after 10 km
will be
A. 1
B. 16.6
C. 25
D. 50
120. A wire conductor is carrying a current of 40 A. The magnetic flux density at a distance
4 cm is
A. 4 10-7 Wb/m2
B. 2 10-4 Wb/m2
C. 0.04 10-4 Wb/m2
D. 2.0 10-4 Wb/m2
121. A solenoid of 1200 turns is wound uniformly in a single layer on a glass tube of 2 m long
and 0.2 m diameter. When a current of 2 A flows through it, the strength of magnetic field
at the centre of solenoid is
A. 600 A/m
B. 6000 A/m
C. 1200 A/m
D. 2400 A/m
122. In an air filled parallel plate waveguide, the two parallel conducting plates are separated
by 2 cm. The phase velocity of the propagating mode of 6 GHz is
A. 3.3 108 m/s
B. 3.0 108 m/s
C. 1.2 108 m/s
D. 2.4 108 m/s
37
123. A charge Q is uniformly distributed over the surface of a metallic sphere of a radius R. If
is the permittivity of the medium surrounding the sphere, the E field just above the surface
of the sphere is
Q
4R 2
Q 2
B.
4R 2
Q
C.
4 R 2
A.
4R 2
Q
124. A potential difference of 10 V is maintained across the ends of a copper wire of length
2 m in the z- direction. If the mean time between collisions is 1.82 10-14 seconds, the
drift velocity of the free electrons is
D.
⃗ m/s
A.
B.
⃗ m/s
C.
⃗ m/s
D.
⃗ m/s
125. What is the instantaneous value of Poynting vector if for a plane electromagnetic wave Ez
and Hy are given as
Ez a cos x cos ct and H y a sin x sin ct
1 2
a sin 2x sin 2ct iˆ
4
1
B. a 2 sin 2x sin 2ct iˆ
4
1 2
C.
a sin 2x sin 2ct ˆj
4
A.
D.
1 2
a sin 2x sin 2ct ˆj
4
126. The electric flux density in a region is given by D x 3 xˆ x 2 yzˆ nC/m2. The charge enclosed
inside a cube of side 2 m placed centered at the origin with its sides along the axes is
A. 8 nC
B. 4 nC
C. 6 nC
D. 2 nC
38
127. A dipole antenna is to be used at the UHF of 150 MHz. The antenna length should be
A. 2 m
B. 1 m
C. 3 m
D. 1.5 m
128. The Displacement current arises due to
A. positive charges only
B. negative charges
C. time varying electric field
D. both positive and negative charges
129. A conducting sphere of radius R has charge +Q on its surface. If the charge on the sphere
is doubled and its radius is halved, the energy associated with the electric field will
A. increase four times
B. increase eight times
C. remain the same
D. decrease four times
130. The field of vector B is always
A. solenoidal
B. irrotational
C. non solenoidal
D. both irrotational and non solenoidal
131. A source delivers symbol A1, A2, A3, A4 with probability 1/8, 1/4, 1/16, 1/8 respectively.
The entropy of the system is
A. 1.5 bit per second
B. 1.5 symbol per second
C. 1.5 bit per symbol
D. 1.5 symbol per bit
39
132. If a binary PSK modulation is used for transmission, the required minimum bandwidth is
9.6 kHz. To reduce the transmission bandwidth to 2400Hz the modulation scheme
adopted should be
A. 16 – ary QASK Modulation
B. 8 – ary PSK Modulation
C. 16 – ary PSK Modulation
D. 8 – ary QASK Modulation
133. A 20 kW Carrier is sinusoidally modulated by two carriers corresponding to a modulation
index of 30% and 40% respectively. The total radiated power is:
A. 25 kW
B. 28.5 kW
C. 30 kW
D. 22.5 kW
134. 40 Signals each band limited to 5 kHz are to be transmitted over a single channel by
frequency division multiplexing. If AM-SSB modulation guard band of 2kHz is used then
the bandwidth of the multiplexed signal will be:
A. 240 kHz
B. 200 kHz
C. 280 kHz
D. 278 kHz
135. In a super heterodyne receiver, the IF is 455 kHz. If it is tuned to 1000 kHz, the image
frequency will be
A. 2455kHz
B. 1910kHz
C. 1455kHz
D. 910kHz
40
136. Match List-I (modulation) with List-II (ratio of transmitted to carrier power) and select the
correct answer using the code given below
List I
W.
X.
Y.
Z.
A
B.
C.
D.
W
3
1
3
1
List II
100% AM
80% AM
50% AM
FM
X
4
4
2
2
Y
1
3
1
3
1.
2.
3.
4.
1.5
1.32
1.125
1.00
Z
2
2
4
4
137. Match List-I (communication service) with List-II (bandwidth) and select the correct
answer using code given below
List I
W.
X.
Y.
Z.
A.
B
C.
D.
List II
AM Broadcast
Telephone
Wideband FM
Television
W
3
1
1
3
X
4
2
4
2
Y
1
3
3
1
1.
2.
3.
4.
10 kHz
4 kHz
200 kHz
7 MHz
Z
2
4
2
4
138. A certain AM transmitter radiates 9 kW with the carrier unmodulated, and 10.125 kW
when the carrier is sinusoidally modulated. The modulation index
A. 0.4
B. 0.5
C.
D. 1
41
139. The situation when both transmitter and receiver have to work in tandem is referred to as
A. parallel
B. serial
C. asynchronous
D. synchronous
140. The percentage power saving when the carrier and one of the sideband are suppressed in
an AM wave modulated to a depth of 100% is
A. 83
B. 82
C.
D. 80
141. If it is required to transmit at 5 Mbps, and a bandwidth of 1 MHz is used, then the
minimum SNR required is
A. 30
B.
C. 29
D. 31
142. An input signal to a receiver is 50 µV and internal noise at the input is 5 µV. An amplifier
with a noise figure of 2, amplifies the signal to 2 V at the output. The noise at the output is
A. 10 µV
B. 1.5 V
C. 0.5 V
D. 0.4 V
143. A FM broadcast system is working at 100 MHz and a Q of 500. The bandwidth of this
system is
A. ± 200 kHz
B. ± 100 kHz
C. ± 10 MHz
D. ± 20 MHz
42
144. An AM transmitter is modulated by three sources of audio signals with m1 = 0.5, m2 = 0.7
and m3 = 0.4. The unmodulated carrier power is 50 kW. The modulated power output is
A. 68.5 kW
B. 72.5 kW
C. 104.5 kW
D. 98.5 kW
145. The superhet principle is a form of
A. frequency multiplication
B. frequency translation
C. voltage translation
D. voltage multiplication
146. An RF amplifier has an output power level of 100 mW. Its value in dBm is
A. -20 dBm
B. +40 dBm
C. -40 dBm
D. +20 dBm
147. Three voice signals having frequency range of 300-3400 Hz, are frequency division
multiplexed using 20 kHz, 24 kHz and 28 kHz analog carrier signals. The minimum
channel bandwidth of resultant FDM signal assuming 1 kHz as guard band between the
channels to avoid interference is
A. 9.3 kHz
B. 11.3 kHz
C. 2 kHz
D. 12.3 kHz
148. Satellite communication operates in which band?
A. UHF
B. VHF
C. HF
D. SHF
43
149. What is the uplink and down link frequency of GSM?
A. up link 935-960 MHz and Down link 890-915 MHz
B. up link 900-950 MHz and Down link 850-890 MHz
C. up link 600-660 MHz and Down Link 550-590 MHz
D. up link 650-710 MHz and Down Link 540-590 MHz
150. A
carrier is modulated by a
audio sine wave. If the carrier voltage is 4 V
and the maximum deviation is 10 kHz, then the equation of FM modulated wave
A.
(
)
B.
(
)
C.
(
)
D.
(
)
44
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
45
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
46
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
47
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
48