* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8893794
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
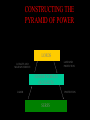
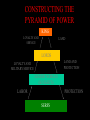
Essential Questions • Describe the effects of the Crusades. • What impact did Feudalism have on Europe? • What were the political, economic, and social effects of the Black Death? The Middle Ages: 500 – 1500 The Medieval Period Rise of the Middle Ages Decline of the Roman Empire Western Europe • • • • • Justinian and the Byzantine Empire Strong Central Government Strong, well-trained military with advanced technology. Justinian the Emperor of the Byzantines codified the laws. Constantinople was the new capital of the Byzantine Empire Gradually weakened by constant battles with Persia Split in the Catholic Church • • • In the West, the Pope was the head of the Church In the East, the Emperor of Constantinople was the most powerful church leader. Byzantines differed from the Western Christian Church on issues of religious practices. – West • • – East • • • services in Latin doesn’t believe in Icons services in local languages Believe in Icons Christianity split into the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. • • Ottoman Empire After Justinian died, the Empire was threatened by outside powers including the Seljuk Turks (the Ottomans) By the 1300’s the Ottomans had, captured Constantinople and ended the Byzantine Empire. • The Ottoman’s Muslim beliefs were later challenged by the Crusades. What were the Dark Ages? After the decline of the Roman Empire: Barbarian tribes ruled Europe – Art and Learning declined The Clergy Religious officials had different ranks within the church structure Vikings Attack invaders who would attack by sea, raid and plunder, then be quickly out to sea again. • Vikings – Germanic people called Norsemen • From Scandinavia • Worshipped warlike gods Feudalism Think of a chess set Relationship Between Lords and Vassals Lord – The person in charge of the land Vassal- provided military service to the Lord in return for land. The relationship between lords and vassals made up a big part of the political and social structure of the feudal system Vassals had certain duties to perform for the lord All nobles were ultimately vassals of the king. CONSTRUCTING THE PYRAMID OF POWER CONSTRUCTING THE PYRAMID OF POWER LESSER NOBLES (KNIGHTS) LABOR PROTECTION SERFS CONSTRUCTING THE PYRAMID OF POWER LORDS LAND AND PROTECTION LOYALTY AND MILITARY SERVICE LESSER NOBLES (KNIGHTS) LABOR PROTECTION SERFS CONSTRUCTING THE PYRAMID OF POWER KING LAND LOYALTY AND SERVICE LORDS LAND AND PROTECTION LOYALTY AND MILITARY SERVICE LESSER NOBLES (KNIGHTS) LABOR PROTECTION SERFS Workers on the Manor ( Fiefdom) • There were peasant workers on the manor • Serfs – workers bound to the land by contract with the nobles. (They had no freedom - they where the noble’s property.) Feudalism Manors The lords estate – The lord provided the serfs with housing, farmland and protection Serfs tended the lands, cared for the animals, maintained the estate Peasants rarely traveled more than 25 miles from the manor Was home to 15 – 30 families Self-Sufficient community Peasants heavily taxed, including a tithe – a church tax of 1/10 their income Feudalism Manors Fief land in exchange for service Same thing was happening in Japan • A war between two clans lead to a clear leader, Yoritomo, became the first Shogun. – supreme general of the Emperors Army. • Surrounded himself with Samurai (one who serves). • Each warrior lived by a code called “Bushido” • After different losses, the Shogun lost money. • Individual samurai chose to support their local lords for land in return for service…Feudalism. Feudal Japan Religious leader with no real power Noble in the warrior class and the leader of the Military Emperor Shogun Samurai Ronin Peasant Merchant Members of the warrior class and loyal to the Shoguns paid soldiers whose loyalty was with the leader they defended at the time. Farmers and fishermen made up 90% of the population sold goods and produce made by others. They produced nothing of value A violent society Noble’s constantly fought each other Defend estates Seize new territories Increased wealth Kept Europe fragmented Glorification of warriors, became superstars The Age of Chivalry The mounted Knights were the most important part of an Army Professional solders – main obligation was to serve in battle Rewarded with land Devoted lives to war The Age of Chivalry Chivalry – a complex set of ideals, demanded that a knight fight bravely in defense of three masters 1. His feudal Lord 2. His Heavenly Lord 3. His Queen Meant to protect the weak and the poor Be loyal, brave, and courteous Is Chivalry around today? The Age of Chivalry Sons of nobles began training at an early age for knighthood Page – at 7 they were sent to another lord to be trained Squire – at 14 they act as a servant to a knight Knight- at 21 they become a knight and gain experience in local wars and tournaments The Age of Chivalry Tournaments – mock battles that combined recreation and combat training Fierce and bloody competitions Castles and Keeps Stone castles were encircled by massive walls and guard towers Home to lord and lady, their family, knights solders, and servants A fortress of defense Castles and Keeps Crusades • military expeditions by the Christians to recover the Holy Land from the Muslims Consequences: – the Holy Land remained in Muslim control – religious intolerance – trade increased – decrease in Popes power – increase in Kings power Magna Carta • document signed by King John of England in 1215 • 1st document to limit the power of a king in Medieval Europe • guaranteed certain rights to citizens major developments of the Late Middle Ages The Hundred Years War • Fought between the French and English for the French throne • Massively destructive • • Gun powder and heavy artillery • Joan of Arc, a French peasant, helped change the course of the war France is victorious over England Famines • Population doubled • Climate became colder and rainier • Harvests shrank Plague • Biotic- disease spread by fleas and rats (living organisms) • also called the Black Plague or Bubonic Plague • killed 1/3 of Europe’s population • helped bring about the end of feudalism: – workers were in higher demand – more people moved to cities The Culprits The Symptoms Bulbous Septicemic Form: almost 100% mortality rate. From the Toggenburg Bible, 1411 Lancing a Buboe Medieval Art & the Plague Bring out your dead! Attempts to Stop the Plague A Doctor’s Robe “Leeching” The Mortality Rate 35% - 70% 25,000,000 dead !!!